Welcome to our comprehensive guide on RFID tag types. This article will delve into the different types of RFID tags, specifically passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC tags. A comprehensive understanding of these tag types will help you successfully implement and effectively utilize RFID technology in different industries. Join us as we explore the intricacies of RFID tag types and their wide-ranging applications.
Understanding RFID Tag Types
There are a variety of RFID tags on the market, and their frequency range generally distinguishes them. RFID tag types can be classified as low-frequency, high-frequency, and ultra-high-frequency. RFID cards typically use one of these three frequencies to communicate via radio waves. Almost every RFID type we can see can be active (powered), passive (un-powered), or semi-passive (battery-assisted).
The following video shows smart card low-frequency, high-frequency and ultra-high-frequency inlays, and high-quality RFID inlay testing:
Relevant articles: Inside RFID Labels: Structure Revealed
Passive RFID tags are an integral part of many tracking and identification systems. These tags rely on the energy emitted by RFID readers to power their operation. They are commonly used in applications where long battery life and cost-efficiency are crucial factors. For instance, inventory management, access control, and supply chain logistics extensively leverage passive RFID tags. By harnessing radio frequency waves, these tags transmit stored data back to the reader, enabling seamless tracking and identification.
Relevant articles: Active vs. Passive RFID Tags: Understanding the Difference
In contrast to passive tags, active RFID tags have their own power source, typically a battery. This power source allows them to actively transmit signals to RFID readers, providing an extended read range and enhanced performance. Active tags excel in applications that require real-time monitoring, such as asset tracking, vehicle identification, and personnel tracking. With their longer read ranges and active communication capabilities, these tags offer robust and reliable performance in dynamic environments.
Relevant articles: What are Active RFID Tags and How it Saves Money
Semi-passive RFID tags combine the best of both worlds: they’re powered by an external source but can also store data for later transmission without recharging by that same source. Semi-passive tags can also maintain their charge for longer than passive ones—typically up to 10 years.
Relevant articles: Efficiency Choice: Semi Passive RFID Tags
Low-frequency RFID tag is a popular type of RFID. It has a band between 30KHz-300KHz and a wavelength of about 2,400 meters.

LF RFID systems generally only allow communication in a small range between 125KHz-134KHz. It is because multiple types of signals exist between 30KHz-300KHz. Its unique communication channel allows it to penetrate metal and water easily. It is extremely friendly to metal and liquid environments.
LF RFID tag has a short read range, even though it has a relatively long wavelength. It has a much shorter read range than HF and UHF, reaching only up to about 50 cm under ideal conditions. It relies on inductive coupling.
LF RFID tags can be relatively expensive. Different types and applications can lead to price differentiation. The price per tag typically ranges from $0.70 to $20. Since they are powered by inductive coupling, they can last indefinitely. However, because different applications cause different levels of wear and tear, the lifetime can vary. All low-frequency RFID tags use the same type of magnetic coupler for communication, but they can still be made in various shapes and sizes.
It takes longer for the reader to receive and decode the signal from the tag. Because its read rate is slow, the data rate transmitted will also be relatively lower.
Different applications choose different LF antenna or reader combinations. They need to spend from a few hundred dollars to a thousand dollars in cost. The obvious difference between it and other RFID tags is that LF tags do not have security standards. Thus, it is recommended that companies do not use it for applications that require encrypted communications.
LF RFID Tags Application Example
Livestock Tracking
Applying RFID to cows is a durable and effective method of tracking. Tracking is achieved by attaching an ear tag or foot ring with an RFID tag to the cow. People can trace all the links between birth and delivery to market in the RFID tag. In case of contamination, it helps one to recall the exact batch of meat in case of a problem. LF tags are the ideal RFID tag type for livestock tracking applications.
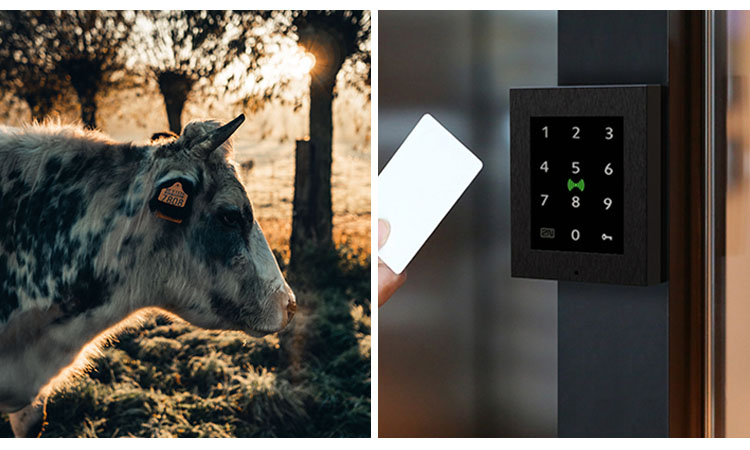

Ear tags with RFID tags have better results than barcodes. They will be more durable and long-lasting. Because livestock may be in the rain, sun, or the presence of other animals for long periods, barcodes are relatively easier to damage. For things that require long-term monitoring, the use of barcodes has yielded suboptimal results.
Access Control
Low-frequency RFID access control card is one of our common types of RFID tags. It can be used as a key to access control office buildings. These low-frequency RFID access control cards require proximity to the reader to function. It will inevitably cause wear and tear on the access card. If barcodes are used, it is estimated that a new batch of access control cards will need to be replaced in a short time. It is also very easy for criminals to copy access cards made of barcodes, which carry too much insecurity. Access cards made with RFID technology will be more durable and secure.
Relevant articles: Key Card Door Lock Sale, Installation & Price
HF (High Frequency) RFID tags operate at the frequency range of 13.56 MHz. While HF tags offer shorter read ranges compared to UHF tags, they exhibit superior data transfer speed and reliability performance. HF tags find common use in applications like contactless payments, access control systems, and electronic ticketing. These tags enable secure and efficient transactions, making them particularly well-suited for environments requiring swift and accurate identification processes.

Both HF and LF use the same operating principle. The tag and the reader/antenna use magnetic coupling for communication. HF waves allow them to pass through most materials except water and dense metals. For example, HF tags are not affected and work properly in environments with thin metals such as aluminum.
HF RFID Tags Application Example
Library Management
High-frequency RFID technology can effectively improve the efficiency of library checkout and returns. We can use barcodes in conjunction with RFID. The checkout counter’s reader scans the library card’s barcode to get your personal information. The reader detects the RFID tag on the book to obtain text information and quantity. People usually scan their library cards at the register and stack the books on the RFID pad to complete the return record. Afterward, the book is dropped into the designated box to confirm the return of the book. The reader uses the information in the RFID tag to sort the books logically and efficiently.
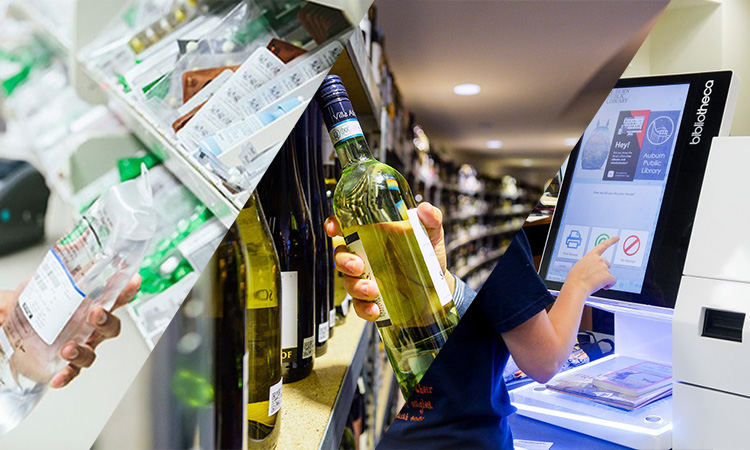

RFID technology offers a more accurate, efficient, and faster way to get books back on the shelves. It is especially reliable for libraries that want to do more with less. A library needs more work if it uses a barcode system. Staff needs to scan each book separately during the checkout and return process. If the barcode is scratched or marked so it cannot be read, the employee will need to handle it manually. Employees need to enter project information into a computer system. It also causes employees to spend more time doing this.
RFID provides a higher level of security than barcodes. When faced with the number of books checked out, one can scan the barcode on the book to confirm that it has been returned. But what if someone puts down one book and takes the other books that have been confirmed to be returned? RFID readers will immediately identify the discrepancy and let you know.
Relevant articles: RFID in Libraries: Implementation Examples
Managing Medical Supplies
High-frequency RFID can be used to monitor the use of surgical items by patients on the operating table. The check and balance system is beneficial in helping doctors and nurses keep track of the number of sponges used during surgery. It will ensure that no sponge is left inside the patient by the medical staff during the procedure. The reader will count the number of sponges used before and after. If 15 sponges are prepared on the operating table, readers will also check for this after the operation. It ensures the same amount of sponges are taken out of the operating room before and after surgery.
Relevant articles: RFID in Healthcare: Pros and Cons
Quality Control
Companies can use high-frequency RFID to monitor the quality of their wines. It is perfect for tracking wine from when it leaves the winery to the distribution center and then to the retailer. Wine needs to be kept in a suitable condition at all times during transportation. Too high or too low a temperature can make it problematic. Companies can program RFID tags. People can use RFID tags to check temperature and other environmental factors affecting wine quality. By reading the tag on the wine, companies can also get a good idea of the environment the wine is in and how long it has been stored. If the data indicates that the wine has been stored in a sub-environment for a long time, it will be treated as damaged goods and removed for destruction. Unlike RFID, barcodes are read-only and cannot actively collect other data. RFID, by contrast, has more functionality.
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) RFID tags operate from 860 MHz to 960 MHz. They are known for their long-range capabilities, making them suitable for applications where reading tags from a distance is crucial. UHF tags are widely used in inventory management, supply chain optimization, and retail operations. Their ability to read multiple tags simultaneously and their adaptability to various surfaces and materials make them a popular choice for many industries.
UHF RFID is not universal. It adheres to the communication protocol standards established by GSI. It is also subject to frequency standards set by individual countries.
The UHF RFID system uses a different communication principle than low and high frequencies. It uses passive backscatter modulation. It is governed by the GS1 EPCglobal UHF Class 1 Generation 2 specification (known as the ISO-18000-6C standard).
The UHF wavelength can be as small as 12 cm at 2.45 GHz. If you look at the average length, it’s about 33cm. We can usually see it in passive RFID systems and active RFID systems.
Relevant articles: UHF RFID Tags Guide: Types, Applications, and Advantages
UHF RFID Application Example
UHF RFID is usually the most common type of RFID tag used in large warehouses and distribution centers. It supports the tracking and identification of multiple items at the same time.

We are more commonly used in shipping and receiving modules. It is especially important for end-to-end manufacturing and industrial asset management. HF RFID differs from the other two RFID types in that it can provide a read range of up to 30 feet under certain conditions. The data transmitted at high-frequency wavelengths will also be relatively faster. It demonstrates that companies can move large quantities of products faster in a short time.
High-frequency RFID technology can reduce the time required to receive pallets or large boxes. RFID readers can be installed at designated platform doors and tuned to the same bandwidth as the tags on the received items. Companies can minimize disruption to their workflow with appropriate adjustments. It provides companies with an efficient and accurate way to move warehouse items through the supply chain.
However, UHF RFID systems are not as mature as those using low and high-frequency RFID frequencies. There is no international standard global bandwidth. The frequency range varies depending on the country/region in which it is used. As far as I know, the US currently uses a higher HF bandwidth than Europe.
NFC (Near Field Communication) tags represent a subset of HF RFID tags that facilitate short-range wireless communication. These tags are commonly found in mobile devices and serve a variety of purposes. These include mobile payments, electronic ticketing, and smart home automation. NFC tags have experienced significant growth and adoption by enabling quick and secure connections between devices.
The NFC exists in the high-frequency band of the RFID spectrum. NFC is a global communication standard, and it is regulated internationally. It uses communication protocols approved by the International Organization for Standardization or ISO. Because of its global nature, it makes it easy to adapt NFC to a variety of applications.
Both HF and NFC tags are relatively inexpensive. Depending on the size and shape customized by the company, each tag can cost anywhere from $0.35 to $10. It exists in many forms, usually stickers, cards, or plastic-wrapped labels. It is usually small enough to be used on many items.
NFC tags can be read by the same HF reader or any smartphone with an HF/NFC reader. Since an NFC-enabled smartphone can read it directly, people can use HF/NFC tags in most applications.
Relevant articles: NFC Mobile Payment: Tap, Pay, and Go!
Choosing the Right RFID Tag
When it comes to selecting the right RFID tag for your application, there are several factors to consider. Each tag type has its own characteristics and capabilities. Understanding these aspects will help you make an informed decision. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Application Requirements
Start by clearly defining your application requirements. Determine the purpose of using RFID technology and the specific goals you want to achieve. Are you looking to track inventory in a warehouse, monitor assets in a healthcare facility, or enable contactless payments in a retail environment? Understanding your application’s unique needs will guide you in selecting the appropriate tag type.
Read Range
Evaluate the required read range for your application. The read range is the distance between the RFID reader and the tag, within which the reader can effectively communicate with the tag. Consider the physical environment and the desired scanning distance. Different RFID tag types offer varying read ranges, so choose a tag that can meet your specific range requirements.
Environmental Conditions
Assess the environmental conditions in which the RFID tags will operate. Factors such as temperature, moisture, chemicals, and physical stress can impact tag performance and durability. If your application involves extreme temperatures, exposure to liquids, or harsh chemicals, opt for RFID tags specifically designed to withstand these conditions.
Tag Form Factor
Consider the physical form factor of the RFID tag. Tags come in various shapes and sizes, including adhesive labels, key fobs, wristbands, and more. The choice of form factor depends on how the tag will be attached to or incorporated into the items or assets you wish to track. Choose a tag form factor that is practical and compatible with your intended use case.
Tag Memory and Data Storage
Evaluate the memory and data capacity requirements of your application. Some applications may require storing additional data or unique identifiers on the RFID tags. Ensure that the chosen tag provides sufficient memory and data capacity to accommodate your specific needs. Additionally, consider whether you require read-only or read-write capabilities for the tags. This will depend on whether you need to update or modify the tag’s data during its lifecycle.
Compatibility
Ensure compatibility between the RFID tag and the RFID reader infrastructure. Different RFID frequencies, such as UHF or HF, require corresponding readers for successful communication. Verify that the RFID tag operates at the same frequency as your RFID reader to ensure compatibility.
Cost-effectiveness
Consider the cost-effectiveness of the RFID tags for your application. While it is essential to choose high-quality tags that meet your requirements, it’s also crucial to evaluate the cost implications. Compare the pricing of different RFID tag options and consider factors such as tag lifespan, maintenance costs, and potential return on investment.
This comprehensive guide delves into passive, active, UHF, HF, and NFC RFID tag types. It explores their applications, considerations for choosing the right tag, and key factors like read range, environmental conditions, and compatibility. Make informed decisions for your RFID system implementation with this valuable resource.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
FAQ 1: What is the difference between passive and active RFID tags?
Passive RFID tags rely on the power transmitted from the RFID reader, while active RFID tags have their own power source.
-
FAQ 2: What is the read range of RFID tags?
The read range can vary depending on the RFID tag type and the reader used. Passive RFID tags typically have shorter read ranges compared to active RFID tags.
-
FAQ 3: Can RFID tags withstand harsh environmental conditions?
Some RFID tags are designed to withstand extreme temperatures, moisture, chemicals, and physical stress. Choose tags specifically suited for the environmental conditions of your application.
-
FAQ 4: Are RFID tags compatible with all RFID readers?
RFID tags operate at different frequencies, such as UHF or HF. Ensure that the RFID tag frequency matches the frequency supported by your RFID reader for successful communication.
-
FAQ 5: How do I test the performance of RFID tags?
You can conduct tests using sample tags to assess their performance, read range, and compatibility with your RFID reader before deploying them on a larger scale.
-
FAQ 6: Can I get guidance and support in choosing RFID tags?
RFID experts and vendors can provide valuable insights, recommendations, and even offer sample tags for testing. Consultation and support can help you make informed decisions.








