Semi passive RFID tags are a type of RFID tag that can enable data collection but not necessarily enable data read-out or transmission. With the maturity of RFID technology, we can often see a variety of RFID labels in our lives. Can you tell which are active, passive, and semi passive RFID labels in these labels? How much do you know about RFID semi-passive tags? Next, let’s take a deeper look at semi-passive RFID tags.

Semi-passive RFID tags, also known as battery-assisted passive (BAP) tags. It combines the benefits of both active and passive RFID technology. They feature a built-in battery that powers certain functionalities, such as boosting signal strength during data transmission. This enhances the efficiency and performance of the RFID system.
It is more popular than passive RFID tags. It has a relatively extended read range, and the body accommodates onboard environmental sensors. For the item to which the tag is attached, the semi-passive tag is more helpful in recording its ecological experience. It provides excellent convenience to laboratory staff.
A test result shows that if the tag is placed at 4 meters from the reader and reads the output rate of 21, it can achieve more than 50% of the reading rate decibel.
Overview of RFID Technology
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology uses radio waves to transmit data between RFID tags and readers wirelessly. RFID tags contain an antenna and a microchip that store and transmit information. Unlike barcodes, RFID tags can be read without a direct line of sight. This enables faster and more automated data capture.
Semi-passive RFID tags possess distinct characteristics that make them a preferred choice for efficiency-focused applications. They offer extended battery life compared to active tags, eliminating the need for frequent battery replacements. Moreover, they are cost-effective alternatives to fully active tags, making them more accessible for organizations with budget constraints. Combining passive functionality with selective battery-assisted features ensures optimized performance and resource utilization.
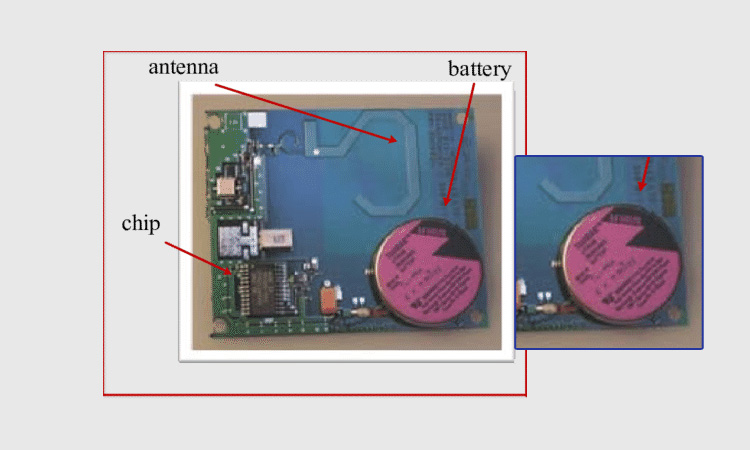
Semi-passive RFID labels contain batteries for two reasons. One is that the battery is needed to power the IC. The forward link typically provides power to the tag and also provides tag communication capabilities. Its range is generally much shorter than the return link. The return link refers to the round trip from the reader to the tag and back to the reader. So it has a more extended range than the forward link. It shows that the limiting factor of the passive tag reading range is power supply rather than distance. The tag is not how far away from the antenna it can decode the signal, but where in the antenna it is powered. Thus the battery inside the tag can continuously power the IC and has a more extended read range than a passive tag.
The second is that the environmental sensor is located on the tag. The ecological sensor requires a constant source of power to guarantee operation. It also requires a higher power level than the IC inside the tag. Passive tags do not have internal batteries, so they cannot provide a reliable power source for environmental sensors. It can only passively receive the energy supplied by the reader, which is also still very limited.
If a battery is added to the passive RFID tag, it can bring reliable power to power the sensor and tag IC. Of course, even with a battery, it is cheaper than active RFID.
The sensor inside a semi-passive tag can continuously collect data. It can also transmit that data with a unique ID when the reader interrogates the tag. The semi-passive tag has a great deal of promise. For example, it can automatically collect the object’s temperature experience as it moves around. It is well suited for applications such as temperature-sensitive drugs or food. The semi passive tag can effectively record when the object exceeds a specific temperature limit while in transit. The recording of the time allows a rough calculation of the expiration date or efficacy of the medicine. Of course, sensors with the ability to collect temperature, pressure, vibration, etc., can be placed on the tag.

In most cases, a RFID semi passive tag is dormant. The power supply inside it provides power only to the part that holds the data and does not do anything with the rest. Due to the relatively low power consumption, it can last for a long time.
Electromagnetic induction is generated when the tag enters the recognition range of the reader. The RFID reader will first activate the label with a low-frequency signal so that the tag enters the working state. Then the microwave signal and tag data transmission. First, low-frequency signal precision positioning activation, then work with the high-frequency signal. That is, multiple low-frequency readers are placed at different locations within the coverage of the HF signal.
These readers are based on activating semi-active RFID lebels. These readers mainly activate semi-active RFID tags. Working in this way allows for product positioning, information collection, and delivery functions. It dramatically satisfies the strict environmental requirements of some products.
Advantages of Semi Passive RFID
- Long-Range Detection
You can read semi-passive RFID tags over longer distances than passive tags as they have an active energy source to broadcast their information back. They can be read up to 30m, depending on the environment and type of tag used. This makes them ideal for tracking assets over long distances in warehouses or manufacturing facilities
- Longer Read Range
The presence of a battery in a RFID semi-passive tag allows for a longer read range compared to a passive RFID tag. This is because the tag can transmit data over longer distances. It makes it possible to read tags from greater distances. This is particularly useful in applications where tags need to be read from a distance. Some of the more common ones are supply chain management and inventory tracking.
- Improved Accuracy
The energy provided by the battery in a RFID semi passive label also makes it possible to read the tag with improved accuracy. Such tags with batteries can emit stronger signals. It makes it easier for the reader to receive the data and reduces the chance of errors.
- Lower Cost
The cost of a semi-passive RFID tag is typically lower than that of an active RFID label because it does not require additional batteries, which you must replace periodically, as well as other components, including sensors. This makes them a cost-effective option for large-scale tracking applications.
- Increased Data Capacity
Due to their internal memory and battery, semi-passive RFID tags can store more data than passive tags. This allows for more accurate tracking of assets and the ability to store more complex information, such as product serial numbers and asset location data.
- Increased Privac
RFID semi-passive labels are often more secure than passive RFID tags as they require users to authenticate themselves and then send an activation signal to read the tag data. This can reduce the chances of someone maliciously reading the tag and gaining access to confidential data.
- Durable and Low Maintenance
RFID Semi-passive tags are sealed in plastic with no external components, which makes them highly durable and resistant to wear and tear. They also require very little maintenance as they do not require frequent battery replacements.
- Flexibility
You can use passive semi RFID tags in various applications since they are smaller and do not require additional energy sources. Due to their small size, you can use them in harsh industrial and retail settings.
- Ease of Use
Semi-passive RFID tags are easy to set up and manage as all that is required is to activate them with an activation signal and then read the data stored in the chip. This makes them a popular choice for asset-tracking applications.
It contains a battery, and a transmitter inside that actively emits a signal to the reader. When the tag comes within range of the reader, the two generate a magnetic field coupling. The tag will actively transmit data to the reader. Because the active RFID tag is small, it is usually embedded in the smartphone’s protective case through rivets, screws, etc.
It is typically used in large-scale applications where labels are read over long distances. The most common applications are construction, petroleum, and other industrial and logistics applications. It can generally transmit data at high frequencies and over long distances. More common is the electronic toll. It is more significant than passive and semi-passive but also has a larger capacity. It houses environmental sensors that collect temperature, humidity, and other data. Thus it can be used as an application to protect high-value and sensitive assets.
It also has obvious limiting attributes. It requires a higher cost, limited battery life, and larger size. It still has a very impressive ROI for tracking and protecting high-value assets.
It is a passive factor that relies on a reader to deliver energy. Because of this, the reader can generally only read the tag at a very close distance. Usually, some smaller-scale applications and RFID inventory systems use passive RFID tags.
It also has its undeniable advantages. Its cost per tag is lower than the other two. It has a longer life and can be embedded in almost any product. It’s primarily used in item-level tracking applications, badge access control, etc.
It is an intermediate product between active and passive. Semi-passive RFID tags are similar to passive RFID tags in size and manufacturing. It is compact and takes less time to produce. But it also contains a power source like active RFID tags.
It brings together many of the advantages of both. These advantages include a lower production price than active tags and longer read distance than passive tags. And support for partial sensors and memory functions. Of course, it also has a fatal disadvantage: limited battery life. It is usually used for: access control entry, item location, area location management, security alarms, etc.
Also Read: RFID Inventory System: What are Its Pros and Cons?
This table summarizes some of the key differences between passive, semi-passive, and active RFID tags:
| Feature | Passive RFID Tags | Semi-Passive RFID Tags | Active RFID Tags |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Source | No internal power source, powered by reader | Internal battery powers some components, but not transmission | Internal battery powers both components and transmission |
| Range | Shorter range, typically less than 30 feet | Longer range than passive, up to 100 feet or more | Longer range than passive or semi-passive, up to hundreds of feet |
| Cost | Lower cost per tag | Higher cost per tag than passive, but lower than active | Higher cost per tag |
| Size | Smaller and lighter weight | Similar size and weight to passive tags | Larger and heavier |
| Applications | Ideal for close-range applications, such as inventory tracking | Suitable for applications where longer range is needed, such as asset tracking | Best for applications where long-range, real-time tracking is required, such as vehicle tracking or logistics |
Note: These are just general characteristics, and the specific features and capabilities of RFID tags can vary widely depending on the manufacturer, frequency, and other factors. In addition, some RFID tags may fall into a “gray area” between these three categories. For example, they may be called “battery-assisted passive” or “semi-active” tags.
Semi-passive RFID labels typically offer longer read ranges and more advanced features than passive RFID tags. It is suitable for applications without high power and continuous communication of an active RFID tag. Some examples of semi-passive RFID tag applications include:
- AeroScout T2 Tag: It is used for asset tracking in healthcare, industrial, and enterprise environments. It has a long battery life and can be used for indoor and outdoor tracking.
- Metalcraft Sentry Flex Tag: This is a rugged, durable semi-passive RFID tag that can be used for asset tracking in harsh environments. It features a read range of up to 20 feet and can be mounted on metal surfaces.
- Xerafy MicroX II RFID Tag: This is a small, high-performance semi-passive RFID tag. It can be used for tracking small assets such as tools, medical equipment, and IT assets. It features a read range of up to 10 feet and is designed for use in harsh environments.
- Invengo XC-RF807 RFID Tag: You can use it for various applications, including asset tracking. It features a read range of up to 26 feet and can be mounted on metal surfaces.
In What Circumstances can They be used?

Active RFID tags can operate at high frequencies between 433MHz – 960MHz. It gives it a much longer range to transmit data. Readers can read the data stored on the tag at a distance of over 100 meters. It is the most suitable choice for tracking real-time location, inventory, and asset management. In addition to this, it can operate on a variety of other frequencies. Especially at lower frequencies, it can even be used on materials such as water and metal.
Passive RFID labels come in quite a few variants. The most common are inlays and hard tags. The inlays are usually attached to the physical asset by an adhesive, which is the cheapest option. Hard passive tags are made of materials such as plastic and metal, which are rugged and durable. It is ideal for products that must stay in harsh environments for long periods.
Semi-passive RFID labels are a hybrid of the previous two types of tags. It is more cost-effective as compared to active and passive. It is the ideal and inexpensive option for environmental and condition monitoring of items.
Operators need to choose the correct label according to their needs and according to the characteristics of the product. Choose between active and semi-passive in particular. If your product is unique, you need to consider the surrounding environment. Depending on the particularity and cost-effectiveness of the product, passive semi RFID tags may be the best fit for you. Assuming you want to track and manage your warehouse inventory, passive RFID tags may be your ideal choice.
Semi-passive RFID tags may not be as widely known as active RFID tags and passive RFID tags. But in terms of practical production applications, it is cheaper and has a broader range of use. It is suitable for use in products with stringent environmental requirements during transportation.
About Semi Passive RFID Tag FAQs
-
What is the Meaning of Semi-passive?
The term “semi-passive” generally refers to a system or device that is partly active and partly passive. In other words, it combines elements of both active and passive systems. This hybrid approach allows semi-passive RFID tags to benefit from some of the advantages of both active and passive systems. Specifically, they are partially powered and transmit data actively, like active RFID tags. Still, they also have some passive components that allow them to operate with a smaller battery and at a lower cost than fully active tags.
-
How Much does a Semi Passive RFID Tag Cost?
There are several factors can affect the semi-passive RFID tags price. These factors include the type of tag, the frequency range it operates in, and the quantity that you order. Typically, prices vary widely, ranging from just a few cents to several dollars per unit. You need to note that the cost of semi-passive RFID tags can also fluctuate based on market conditions and specific requirements. We recommend consulting with a reputable supplier for the most up-to-date pricing information.
-
If you’re curious about the range of semi-passive RFID tags, there are several factors that can affect it. The range of these tags typically depends on their frequency and power output and can vary from 10 to 100 feet. This range can be extended using a larger antenna. In addition, the actual range of a semi-passive RFID tag will also depend on the specific environment and equipment being used.







