Radio frequency identification (RFID) technology has been transforming industries for decades, providing efficient and accurate tracking and management of various objects, from products to people. A key component of RFID technology is the RFID symbol, which has evolved to become a recognized and standardized icon worldwide. This article explore the common RFID symbol standards that ensure compatibility and interoperability across diverse industries. By adhering to these standards, organizations can leverage the benefits of standardized protocols, promote seamless integration, and facilitate efficient data exchange in their RFID deployments.
What is RFID Symbol?

Since the inception of RFID technology, the RFID symbol has evolved from a simple concept to a widely recognized global standard. The original RFID symbol, which resembles an antenna, indicated that a product or device was RFID-enabled or had RFID-blocking technology. Today, the RFID symbol is available in various formats such as RFID symbol png, RFID symbol vector, and RFID symbol sticker.
One of the common places you can find the RFID symbol is on debit cards. The RFID symbol on debit card serves as a visual reminder that the card is RFID-enabled and can be used for contactless payments. Additionally, the symbol is also used to indicate the presence of RFID technology in other products, such as the RFID reader symbol and WiFi symbol.
Read More: BarCode Symbology Basic Guide
The Origins of the RFID Symbol
The RFID symbol means the radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology used to identify and track objects. The RFID Lab first developed the symbol at Auburn University in the United States.
The RFID symbology was created to provide a visual representation of RFID technology and to help promote the use of RFID in various applications. The symbol was designed to be simple and easy to recognize, with a distinctive shape that would be easily recognizable even to those unfamiliar with RFID technology.
People chose interlocking arrows to represent how RFID technology uses radio waves to communicate with RFID tags.
People chose the circle to represent the global nature of RFID technology and its potential applications.
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) officially adopted the RFID logo in 2014, and it is now recognized as the global standard for representing RFID technology. The Global RFID icon is widely used in various applications, including product labeling, packaging, and marketing materials.
The organization develops and publishes international standards in all technical and nontechnical fields other than electrical and electronic engineering, which are the responsibility of the International Electrotechnical Commission.[7] As of February 2023, the ISO has developed over 24,676 standards, covering everything from manufactured products and technology to food safety, agriculture, and healthcare.
— From Wikipedia’s ISO overview
Discover Common RFID Symbol Standards
Electronic Product Code (EPC)
The Electronic Product Code (EPC) symbol standard is a widely adopted protocol for RFID symbols, particularly in the supply chain and retail industries. It provides a unique identifier for each item, enabling real-time inventory management, visibility, and traceability throughout the supply chain. EPC symbols use a combination of letters and numbers to represent product data, such as manufacturer information, product details, and serial numbers. This standardized format ensures compatibility and interoperability across different RFID systems and enables seamless data exchange between trading partners.
The EPC symbol has also undergone several updates and revisions since its introduction, reflecting changes in technology and industry standards. The most recent version of the EPC symbol is the Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) EPC, which provides enhanced functionality and increased data capacity. → Check out how GTIN works
International Organization for Standardization (ISO) Symbol Standards

The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed a series of standards to govern various aspects of RFID technology. The ISO 18000 series defines air interface protocols for RFID systems operating at different frequency bands, including LF (Low Frequency), HF (High Frequency), and UHF (Ultra-High Frequency). These standards specify communication protocols, data encoding methods, and anti-collision algorithms, ensuring compatibility and interoperability between RFID tags and readers. ISO 15693 is another ISO standard designed explicitly for vicinity cards and tags, promoting compatibility and interchangeability in RFID systems operating at HF.
Global Organization (GS1) Symbol Standards
GS1, a global organization dedicated to standardizing supply chains, has established guidelines for implementing RFID technology. GS1 EPCglobal standards align with ISO standards and provide additional specifications and best practices for RFID symbol usage in retail, healthcare, and transportation industries. These standards ensure that RFID symbols are encoded and represented consistently, enabling seamless integration and data exchange across different trading partners and supply chain stakeholders. GS1 standards also facilitate the synchronization of RFID data with other supply chain management systems, enhancing visibility, accuracy, and operational efficiency.
There is also a PDF document from GS1 “Recommendations for the use of EPC and ISO RFID symbols“.
What is the RFID Symbol on My Credit Card?
The RFID symbol on a credit card looks like a set of four curved lines that form a partial circle. The symbol typically appears on the front or back of the credit card, near the card’s brand logo or the magnetic stripe. This symbol indicates that the credit card has an embedded RFID chip, which allows for contactless payments using NFC technology.
Here is a picture of the RFID symbol on credit card:
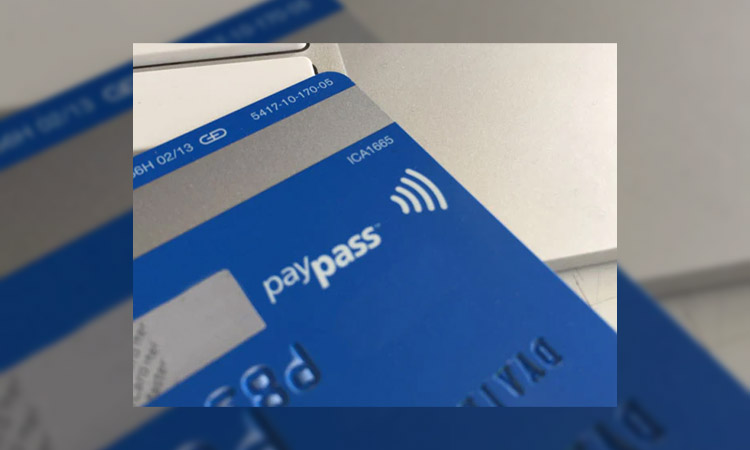

Related Articles: What is RFID Card and RFID Credit Card?
Do All Credit Cards have RFID Symbol?
Not all credit cards have an RFID symbol. While many credit cards today come with RFID chips embedded in them, some older cards and certain types of cards may not have this feature. Additionally, some credit card issuers may choose not to include the RFID feature on their cards.
To determine if a credit card has an RFID chip, you can check it for the RFID symbol or contact the issuer to inquire about its features. It’s important to note that having an RFID chip on a credit card does not necessarily mean it can be used for contactless payments. Some issuers require cardholders to activate this feature before they can use their credit card for contactless transactions. If you want to use your credit card for contactless payments, check with your issuer to see if it has this feature and how to activate it.
Some examples of RFID symbols include:
- The RFID blocking symbol, a circle with a diagonal line through it, indicates that a product or device has RFID-blocking technology. This symbol may be printed on the product or packaging / displayed on a label or tag attached to the product.
- The RFID reader symbol is a stylized representation of an RFID antenna. This symbol is often used to indicate that a device or system can read RFID tags or chips.
- The RFID tag symbol is rectangular with a curved line on the top resembling a miniature antenna. This symbol often indicates that a product or item has an RFID tag attached, allowing it to be tracked or identified by an RFID reader.
Related Reading: Barcode vs RFID What are They Difference
Frequency and Range Considerations: One of the key challenges in achieving RFID symbol interoperability is the variation in operating frequencies and read ranges of RFID systems. Different industries and applications may utilize RFID technology at various frequency bands, such as LF, HF, or UHF. This diversity can lead to compatibility issues when readers operating at a different frequency cannot read RFID symbols designed for one frequency band. Similarly, the read range of RFID systems can vary depending on factors such as antenna design, power output, and environmental conditions. Mismatched frequency bands and read ranges can hinder effective communication and limit interoperability between RFID symbols and readers.
Interoperability Challenges and Ways to Overcome Them
Interoperability is critical for successfully implementing RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology across industries. Achieving seamless communication and data exchange between RFID symbols and systems is essential for realizing the full potential of this technology. However, several challenges need to be addressed to ensure interoperability. This section will explore the key interoperability challenges associated with RFID symbols, including frequency and range considerations, data encoding and representation, and reader compatibility.

Data Encoding and Representation
RFID symbols encode and represent data in different formats, such as ASCII, binary, or hexadecimal. Incompatibilities in data encoding and representation can create barriers to interoperability. For instance, if an RFID reader expects data in a specific format but encounters symbols encoded differently, it may fail to interpret or process the information correctly. Consistent data encoding standards and practices are essential to ensure that RFID symbols can be read and understood by diverse RFID systems.
Reader Compatibility
RFID reader compatibility is another challenge in achieving interoperability. Different RFID readers may support different protocols, air interface standards, or data transmission formats. This can create difficulties when attempting to integrate RFID symbols from various manufacturers or deploy a unified RFID system across multiple locations or business partners. Compatibility issues between RFID symbols and readers can result in unsuccessful reads, data inconsistencies, and limitations in system performance.
To address these interoperability challenges, industry stakeholders and standards organizations are actively working towards developing solutions and best practices:
- Collaboration and Standardization Efforts: Industry organizations, such as EPCglobal and GS1, are driving the adoption of standardized protocols and guidelines for RFID technology. These efforts promote interoperability by establishing common frameworks facilitating communication and data exchange between RFID symbols and systems.
- Interoperability Testing and Certification: Rigorous testing and certification programs are in place to validate the interoperability of RFID symbols and readers. Manufacturers can submit their products for testing to ensure compliance with standardized protocols and protocols. Certification guarantees end-users that their RFID systems will work seamlessly with other compatible devices and technologies.
- Enhanced Middleware Functionality: Middleware software solutions are crucial in bridging the gap between RFID symbols and backend systems. Advanced middleware platforms can handle different data formats, protocols, and reader configurations, providing translation and compatibility layers. These solutions facilitate the integration of diverse RFID systems, promoting interoperability and data synchronization across the supply chain.
- Industry Collaboration and Best Practices: Sharing experiences, challenges, and best practices among industry peers can help identify and address interoperability issues. Collaboration forums, industry associations, and working groups provide platforms for stakeholders to exchange knowledge and drive the development of interoperable RFID solutions.
The Future of the RFID Symbol
As the use of RFID technology continues to grow and evolve, the RFID symbol will continue to play an important role in promoting and representing the capabilities of RFID technology. The symbol will continue to be used as a visual representation of RFID-enabled products and services and will continue to be a global standard for representing RFID technology.

In the future, you may also use the RFID symbol in new and innovative ways. For example, it may indicate the presence of RFID-enabled smart cities or represent the growing use of RFID technology in various industries and applications.
The use of RFID technology is expected to continue to expand in the coming years, and the symbol for RFID will likely play a key role in promoting and representing the capabilities of this technology. The symbol will continue to be a valuable tool for consumers, businesses, and others interested in using RFID technology.
Today, the RFID symbol is widely recognized and used across various industries, from retail and logistics to healthcare and security. It is often found on credit cards, wallets, and other personal items, as well as on product packaging and labels. The symbol may be printed in black or contrasting to make it more visible. In some cases, the symbol may also be accompanied by the letters “RFID” or “NFC” to indicate the type of technology used.
Related Reading: 21 Top RFID Companies in World
Conclusion
Seamless integration and compatibility are paramount for successful RFID symbol system implementations across diverse industries. By adopting recognized standards, conducting thorough interoperability testing, and leveraging middleware solutions, organizations can overcome challenges and harness the full potential of RFID technology. The streamlined integration of RFID symbols significantly boosts supply chain efficiency, optimizes inventory control, and fuels innovation across various sectors, resulting in heightened productivity and customer satisfaction.
If you are interested in RFID, you can also read the following articles:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
Are RFID symbols compatible with existing barcode systems?
RFID symbols and barcode systems are not inherently compatible. However, there are hybrid solutions available that integrate both technologies to leverage their respective benefits and enable a smooth transition.
-
Can RFID symbols be read by any RFID reader?
RFID symbols must comply with the same standards and protocols supported by the RFID reader for successful communication. Different frequency bands and protocols may require specific reader capabilities.
-
What are the advantages of standardized RFID symbol protocols?
Standardized protocols ensure seamless integration, interoperability, and compatibility between different RFID systems. They enable efficient data capture, improve supply chain visibility, and promote widespread adoption of RFID technology.
-
How can industries benefit from standardized RFID symbols?
tandardized RFID symbols enable industries to optimize operations, enhance inventory management, improve customer experiences, increase efficiency, and ensure regulatory compliance.
-
Where can RFID be Used?
Radio frequency identification (RFID) is a radio-based technology which uses electromagnetic fields to transfer data between devices. It’s used in many applications, including health care and hospital settings.
-
How is the RFID Blocking Symbol Represented?
The symbol for RFID blocking is typically represented as a circle with a diagonal line, similar to the “no” or “prohibited” symbol. This symbol often indicates that a product or device has RFID-blocking technology, preventing unauthorized access to your cards’ RFID chips. The symbol may be printed on the product or packaging / displayed on a label or tag attached to the product. Some RFID-blocking products may also have the letters “RFID” or “NFC” alongside the symbol to indicate the type of technology used.