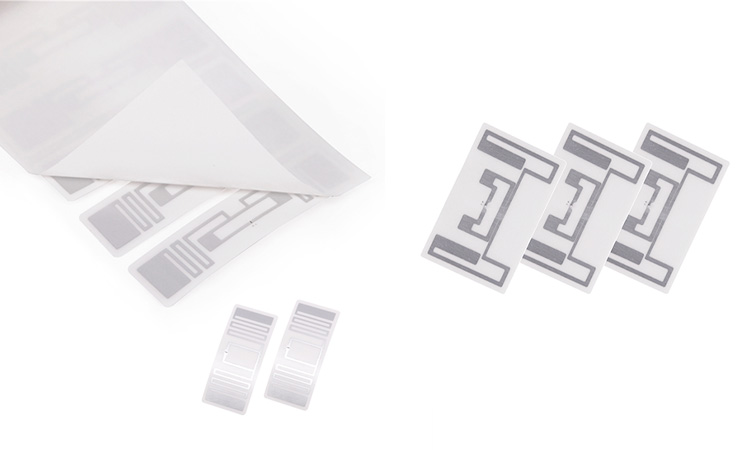
UHF RFID tags are a type of RFID technology that operates in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) range, providing longer read ranges and faster read rates than other RFID technologies. This blog post will explore the benefits and potential applications of RFID UHF tags.
What is a UHF RFID Tag?
A UHF RFID tag is a type of radio-frequency identification (RFID) technology that operates in the UHF range. RFID UHF tags have longer read ranges and faster read rates than other RFID technologies. They are typically used for supply chain management, inventory tracking, and asset management.
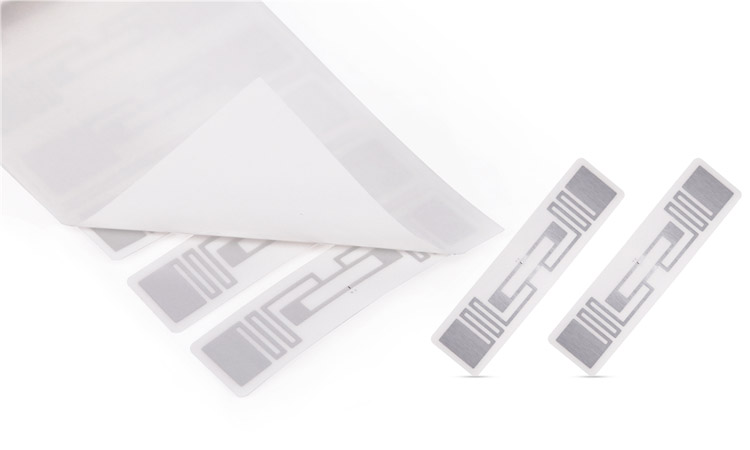

RFID UHF tags consist of a small electronic chip and antenna embedded in a label or tag. The chip contains a unique identification number, which an RFID reader can read. The reader sends a radio frequency signal to the tag, which powers the chip and allows it to transmit its unique identification number back to the reader.
RFID UHF tags offer many benefits, including long read ranges, fast read rates, improved accuracy, and versatility. They are a valuable tool for improving efficiency and accuracy in various industries.
UHF radio-frequency identification tags are a type of RFID tag that operates within the UHF frequency range (typically between 300 MHz and 3 GHz). These tags are used in various applications, including supply chain management, inventory tracking, and asset management.
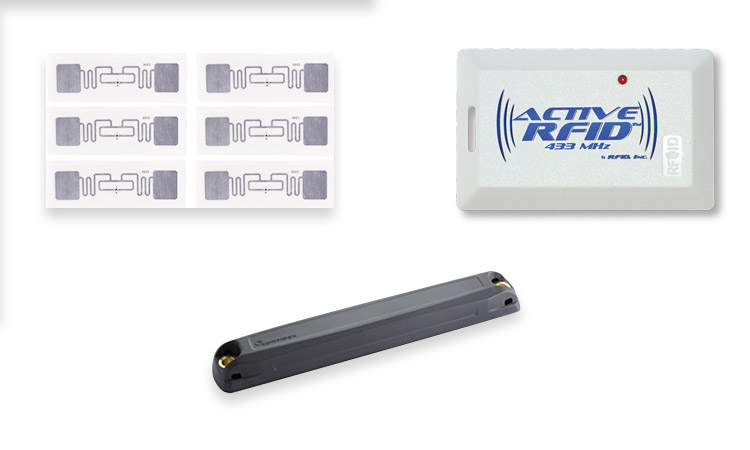

UHF RFID tags are typically small and lightweight and can be easily attached to objects. They contain a microchip and an antenna, which allows them to communicate with an RFID reader. When a UHF RFID tag comes within range of a reader, it responds by transmitting its unique identification code.
There are several different types of RFID UHF tags, including passive tags, active tags, and battery-assisted passive tags. Passive tags are the most common type of RFID UHF tag and do not contain a power source. They are powered by the RFID reader, which sends out a radio frequency (RF) signal that the tag uses to transmit its data.
On the other hand, active tags contain their power source, typically a battery. This allows them to transmit data over longer distances and at a higher power level than passive tags.
Battery-assisted passive (BAP) tags are a hybrid of passive and active tags. They do not contain their power source, but they can use power from the RFID reader to boost their transmission range and power.
UHF RFID tags are a type of RFID tag that operates within the UHF frequency range and are used for various applications. They are typically small, lightweight, and easy to attach to objects, and they use radio waves to communicate with RFID readers.
How does a UHF RFID System Work?
A ultra-high-frequency RFID system uses radio waves to communicate with tags attached to objects. The tags contain electronically-stored information that the RFID system can read.
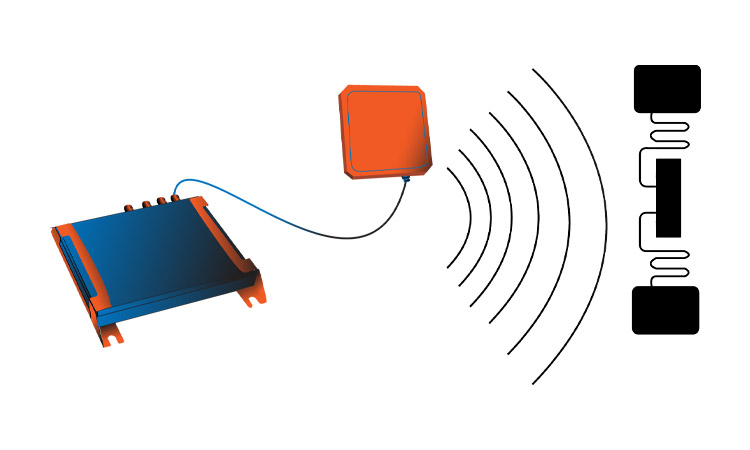
The RFID system consists of two main components: a reader and one or more tags. The reader sends out radio waves at a specific frequency, and the tags respond by transmitting their unique identification code back to the reader. The reader then processes this information and sends it to a computer, where it can be stored or used in other applications.
UHF RFID systems operate within a frequency range of 300 MHz to 3 GHz, and they are typically used for applications where the tags need to be read from a distance of up to several meters. This makes them well-suited for supply chain management, inventory tracking, and asset management applications.
A UHF RFID system uses radio waves to communicate with tags and transfer data wirelessly. This allows for quick and efficient identification and tracking of objects without requiring direct contact.
Is UHF an RFID?
UHF is a type of RFID technology. RFID technology uses radio waves to transmit data from a small electronic chip (called an RFID tag) to a reader.
UHF RFID tags have longer read ranges and faster read rates than other RFID technologies and are typically used for applications requiring longer and faster read ranges. They are commonly used in supply chain management, inventory tracking, and asset management.
In summary, UHF is a type of RFID technology that operates in the UHF frequency range and offers longer read ranges and faster read rates than other RFID technologies.
Which is Stronger, UHF or VHF?
UHF and VHF (very-high-frequency) are two different ranges of radio frequencies. UHF signals are generally considered stronger and more capable of penetrating obstacles than VHF signals.
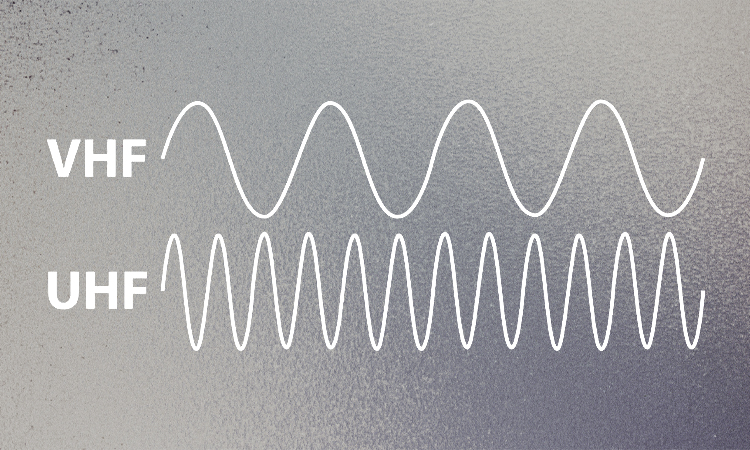
This is because UHF signals have shorter wavelengths, which allows them to pass through objects and obstacles. This makes them well-suited for applications such as satellite communication, where the signal needs to pass through the Earth’s atmosphere.
On the other hand, VHF signals have longer wavelengths and are better at reflecting off surfaces. This makes them well-suited for applications such as television broadcasting, where the signal must travel long distances and be easily picked up by receivers.
In terms of strength, UHF signals are generally considered more powerful than VHF signals. However, the specific strength of a signal will depend on various factors.
Including:
- The frequency,
- Antenna design,
- The distance and environment in which the signal is being transmitted.
Is UHF RFID Safe?
In general, UHF RFID systems are considered safe for use. The radio waves used by UHF RFID systems are similar to those used by other devices, such as cell phones and Wi-Fi routers, and they do not pose any known health risks.

However, as with any technology, it is important to use UHF RFID systems responsibly and follow relevant regulations or guidelines. For example, some countries have regulations regarding the maximum amount of RF energy emitted by UHF RFID systems, and it is important to ensure that these limits are maintained.
Additionally, it is important to take appropriate measures to protect the data transmitted by UHF RFID systems. This might include implementing appropriate security protocols and regularly updating software to prevent unauthorized access to the system.
Overall, while UHF RFID systems are considered safe, it is important to use them responsibly and take appropriate measures to protect the data they transmit.
UHF RFID tags offer many benefits over other RFID technologies, including:

- Longer read ranges: RFID UHF tags have read ranges of up to 12 meters, which is significantly longer than other RFID technologies. This allows for greater flexibility in the placement and use of the tags.
- Faster read rates: RFID UHF tags have read rates of up to 1,000 tags per second, which is significantly faster than other RFID technologies. This allows for the efficient and rapid processing of large numbers of tags.
- Improved accuracy: RFID UHF tags are less sensitive to interference from other RFID tags or metal objects, which can improve the accuracy of the read results.
- Versatility: RFID UHF tags can be used in various applications, including supply chain management, inventory tracking, and asset management.
- Cost savings: RFID UHF tags can reduce labor costs and improve efficiency, leading to cost savings in various applications.
UHF RFID labels offer many benefits and can benefit a wide range of industries.
The following video conducts a reading distance test on UHF RFID tag stickers:
UHF RFID tags have many potential applications, including:
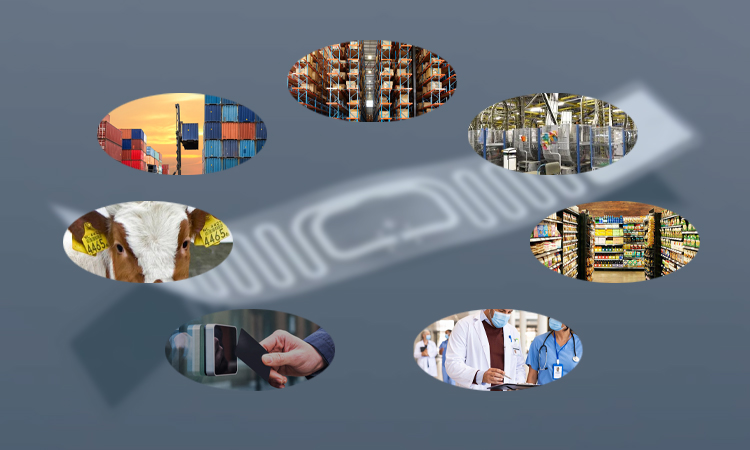

- Supply chain management: UHF RFID labels can track products and materials throughout the supply chain, providing real-time visibility and improving efficiency.
- Inventory tracking: UHF RFID labels can automate inventory management, allowing for accurate and efficient tracking of stock levels.
- Asset management: UHF RFID labels can track and manage the location and status of high-value assets, such as equipment and machinery.
- Retail: UHF RFID labels can improve inventory management and reduce shrinkage.
- Healthcare: UHF RFID labels can track and manage medical equipment and supplies.
- Access control: RFID UHF labels can be used in access control systems to grant or deny access to restricted areas based on the tag’s unique identification number.
- Agriculture: RFID UHF labels can track and manage livestock and other animals.
UHF RFID tags have many potential applications and can provide valuable benefits in various industries.
Related Articles:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Q1: Can Smartphones Read UHF RFID?
A1: Some smartphones are capable of reading UHF RFID tags. This requires the smartphone to have an RFID reader, which can be built-in or added through an external accessory.
UHF RFID tags operate in the ultra-high frequency (UHF) range between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. To read these tags, the smartphone’s RFID reader must be able to operate in this frequency range. Not all smartphones have RFID readers capable of reading RFID UHF labels.
If a smartphone has an RFID reader capable of reading RFID UHF labels, You can use it to read the unique identification number on the tag. You can use this for various applications, such as supply chain management, inventory tracking, and access control.
Whether a smartphone can read RFID UHF labels depends on whether it has an RFID reader capable of operating in the UHF frequency range.
- Q2: Do Cell Phones Use UHF?
A2: Cell phones use UHF (ultra-high-frequency) frequencies as part of their radio communication systems.
Cell phones use various frequencies to communicate with cellular networks and other devices. These frequencies are divided into different bands, including low bands (below 1 GHz), mid bands (1-6 GHz), and high bands (above 6 GHz). UHF frequencies are typically considered high-band and used by cell phones for various purposes, including voice and data transmission.
In addition to UHF frequencies, cell phones use other frequency bands, such as VHF (very high frequency) and HF (high-frequency) bands. The phone’s specific frequency depends on its model and the cellular network to which it is connected.
Overall, cell phones use UHF frequencies as part of their radio communication systems to transmit and receive data and voice signals. These frequencies are an important part of the modern cellular network and are critical for enabling the widespread use of mobile devices.
- Q3: Which UHF is Best?
A3: It is difficult to say which UHF frequency is best, as the optimal frequency will depend on the specific application and the environment in which the UHF system is being used.
In general, UHF frequencies are typically considered to be better for penetrating obstacles and transmitting over longer distances than lower frequencies. However, higher UHF frequencies may be more susceptible to interference from other sources, such as other RFID systems or wireless devices.
It is important to consider the application’s specific requirements and the environment in which you will use the UHF system when choosing a UHF frequency. This will help to ensure that the system can operate effectively and efficiently.
In general, it is best to consult with an experienced RFID provider who can help to determine the optimal UHF frequency for your specific needs. They can provide guidance and advice based on their knowledge and expertise.