Advances in RFID technology have led to a significant reduction in the cost of their dedicated reading devices. It means that proximity cards and vicinity cards can be an option for everyone. You can learn more about how they work and the benefits they offer. Then consider whether to upgrade your existing legacy technology to proximity cards or vicinity cards.
What is a Proximity Card?
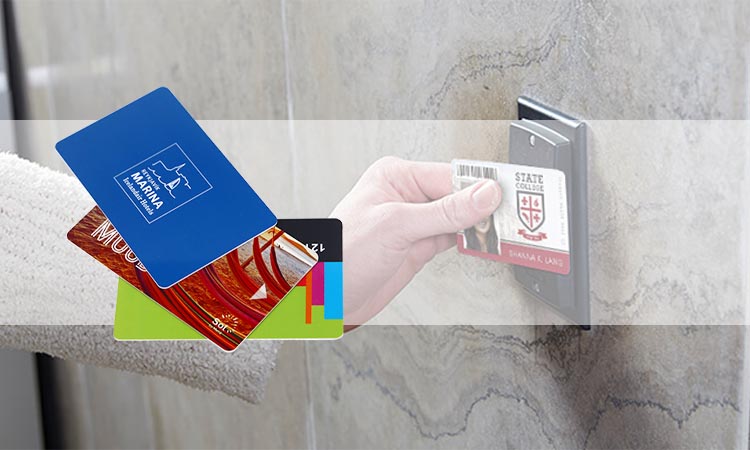

The proximity card is short for a Prox card, also called a contactless smart card. A prox card is a contactless card used in place of a traditional card. It is different from ordinary cards in that it can be read and identified without inserting into a card reader. This feature makes them more convenient and user-friendly than traditional access control methods, such as key cards or keys. Therefore, it allows people to leave their cards in their wallets or purses and not have to worry about losing them.
Wikipedia describes the standard for these contactless smartcards:
Contactless smartcards are covered by the ISO/IEC 14443 and/or the ISO/IEC 15693 OR ISO/IEC 18000 standards.
It is very easy to use in your daily life. You don’t need to swipe the card. Just scan it on a specific device to achieve some purpose.
Earlier it can be defined as 125KHz devices or low-frequency RFID prox cards. It has a very short read range of a few centimeters. It uses ISO 14443 air interface protocol standard.
They look the same as standard PVC cards, but they contain an antenna coil. This allows them to hold encoded data without requiring any swiping. In most cases, the chip provides the proximity card reader with the card’s unique identification number or field facility code. The obtained data information is convenient for the remote computer to verify it. It is read by a prox card reader and secures its transmission.
Proximity cards are common, and you’ve seen them in hotels if you travel a lot. Of course, some companies also use it in their access control systems. Employees can access the company via proximity access cards. It can also be used as a library card, contactless payment system, and transportation fare card.
Proximity Card Types
Proximity cards utilize radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to communicate with card readers through wireless radio signals. Proximity cards come in different frequencies and applications.
Low frequency (LF) proximity cards operate at 125 kHz and range up to 3 feet. LF proximity cards are commonly used for access control, time, and attendance tracking. High frequency (HF) proximity cards function at 13.56 MHz with a range of up to 6 feet. HF proximity cards are implemented for access control, public transit, and cashless payments.
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) proximity cards operate within the 860 to 960 MHz range and range up to 30 feet. UHF proximity cards are utilized for inventory management and asset tracking. Near-field communication (NFC) proximity cards operate at 13.56 MHz with a range of up to 3 feet. NFC proximity cards are used for tap-and-go transactions and phone-based transactions.
Some proximity cards use magnetic fields for wireless connectivity with a reader, typically employed for access control systems. The above options represent the prevalent proximity card technologies, though additional variations and RFID technologies exist.
Proximity cards enable convenient cashless and contactless transactions through wireless signals and the emission of stored card details. The specific frequency, range, and functions vary across proximity card types to accommodate different needs like mobile payments, resource tracking, or secured access. Proximity cards offer a flexible and integrated solution for various wireless transaction and identification requirements.
Proximity Card Price
The price of proximity cards can vary depending on several factors, such as the card type, quantity ordered, and manufacturer. Generally, low-frequency (LF) and high-frequency (HF) proximity cards are more affordable compared to ultra-high frequency (UHF) and near-field communication (NFC) cards.
As a rough estimate, a basic LF or HF proximity card can range from $1 to $5 per card, while UHF or NFC cards can range from $5 to $20 per card. However, prices can be lower if you order in bulk.
It’s worth noting that some manufacturers may offer discounts for larger orders, customized designs, or longer-term contracts. Additionally, the proximity card system’s cost may include additional expenses such as card readers, software, and installation fees.
If you want an accurate price quote for proximity cards, it’s best to contact a reputable supplier or manufacturer and provide them with your specific requirements.
What is a Vicinity Card?
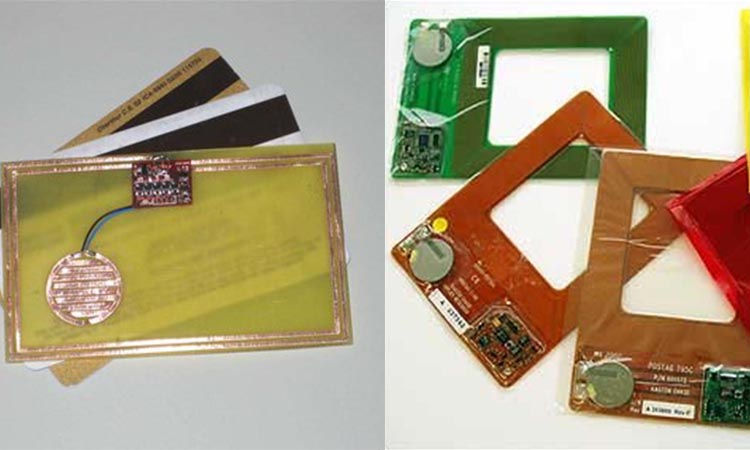
A vicinity card, like a proximity integrated circuit card, is a contactless smart card. It contains a passive high frequency (HF) transponder inside it. It uses a different protocol standard than proximity cards, which generally use the ISO 15693 air interface standard. It can typically be used as user access control or inventory control.
It contains a lithium battery inside. It allows a greater distance between the reader and the card. It also has many advantages in specific situations. The battery inside it enhances the signal sent by itself. It allows the card reader to read the card at a distance of up to 2 meters. It has a limited life span, with the battery inside each card typically lasting 5-7 years.
The vicinity integrated circuit card readers use low or high frequency radio signals to detect the card’s unique ID number. Once the card is detected, the reader sends a signal to the access control system, which checks the card’s ID number against a database of authorized users. If the ID numbers match, the system grants the access to the user.
People mostly use it for other applications, such as toll roads or security gates.
Proximity Card and Vicinity Card: How do They Work?
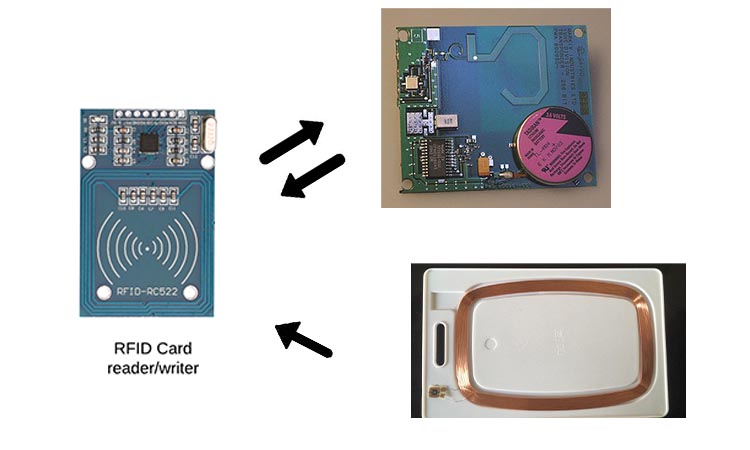
RFID technology is used in both vicinity cards and proximity integrated circuit cards. RFID is a technology that transmits data to a microchip or smart card through a digital code. Usually, people use RFID labels that have been developed with RFID.
It has the same points as the barcode system. It needs to be scanned using a specific device to get the data. However, it is more secure than the barcode system. The barcode system uses barcode numbers that are usually exposed, and the barcode numbers are visible. RFID technology hides these.
By using RFID technology, companies can easily verify the cardholder’s ownership. They look almost identical, but they work in very different ways. Proximity RFID cards use an operating frequency of 125 KHz, while vicinity cards are 13.56 MHz.
They communicate with the card reader through inductive coupling. Proximity access cards contain an antenna, a capacitor, and an integrated circuit (IC) containing only a specific ID number. On the other hand, the vicinity card has an additional flat lithium battery than the proximity card. When the proximity integrated circuit card is within the range of the reader, the card obtains energy through inductive coupling. It then sends an RF signal to the card reader. The reader receives the signal and looks for the ID number in the body database for identification. After confirming the accuracy of the ID number, it performs the specific function programmed by the reader for that ID number. Since it is a passive card, it must be very close to the reader to operate.
The vicinity integrated circuit card contains a battery and a receiver that amplifies the signal emitted by the card reader. The card can detect the reader even at a great distance.
The functions enabled by the two of them are also different. Vicinity cards are usually enabled for reading and writing functions. Proximity cards are only for reading-only functions.
Proximity Card and Vicinity Card: What’ the Difference?

- The working frequency is different. The induction card is a low-frequency 125KHz card, and the vicinity card is a high-frequency 13.56MHz card.
- The reading range is different. The reading range of the induction card is only a few centimeters, while the vicinity card can read the distance within 2 meters.
- If there is a battery in the body, induction cards do not have a battery, while vicinity cards do.
- Different life spans. Sensor cards have a longer service life, while vicinity cards must be replaced after 5-7 years of use.
- Different functions are enabled. Induction cards are read-only, while vicinity cards are read and write enabled.
- Different protocol standards are used. Sensor cards usually use the ISO 1443 air protocol standard, while vicinity cards use ISO 15693.
Related Articles: Proximity Card Readers: Pros and Cons
Smart Card vs Proximity Card
Here’s a table comparing proximity cards and smart cards:
| Feature | Proximity Cards | Smart Cards |
|---|---|---|
| Communication Method | Uses Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) technology to communicate with the reader | Uses an embedded microprocessor and integrated circuit (IC) technology to communicate with the reader |
| Data Storage | Typically only contains a unique identifier or access code | Can store personal information, access rights, financial information, and more |
| Security | Less secure, susceptible to cloning or skimming attacks | More secure, can use encryption, authentication, and other security measures |
| Functionality | Typically used for physical access control, such as building or room access | More versatile, can be used for physical access control, payment, transportation, loyalty programs, and more |
| Cost | Generally lower than smart cards | Generally higher than proximity cards |
| Examples | HID Prox Card, Indala Proximity Card | MIFARE Card, DESFire Card |
Proximity cards and smart cards are both used for access control but differ in their communication method, data storage, security, functionality, and cost. Proximity integrated circuit cards use RFID technology, have limited data storage and safety, and are less expensive. Smart cards use IC technology, have more extensive data storage and security, are more versatile, and are generally more expensive.
Related Articles: Smart Card Authentication Gives You a Higher Level of Security
Proximity Card and Vicinity Card: Common Advantages

Vicinity and proximity cards offer many astounding advantages over traditional ID cards.
No Maintenance Required
There are no moving parts on an inductive reader. It lasts much longer than traditional card readers. The cards also last just as long. It is difficult for criminals to tamper with or damage it because the reader has no openings. In use, we can also integrate the reader into the wall. It increases not only its security but also its aesthetics.
Easy to Use
Generally, the traditional card reader requires the cardholder to take out the card especially. It also requires interaction with the card reader to enter. In the long run, this is a hassle. They have the same security as traditional ID cards. It allows cardholders to enter without making too much contact with the reader. Some vicinity card holders can quickly enter a secure path without stopping at a security checkpoint.
High Security
Their holders can encrypt their cards on a deeper level. It provides a higher level of security in some sensitive and important places. It further ensures that only genuine authorized parties can enter the designated area.
Same Cost
They do not cost much more than traditional ID cards. It is because the company can combine it with considering post-maintenance costs. Traditional ID cards and card readers require long maintenance to last longer. They require no more maintenance. Then the money saved from the maintenance, they both need the cost is almost the same. Using it allows you to increase the level of security without increasing your budget. It also improves the ease of operation for the cardholder.
The Future is Promising
In the future, all ID cards will likely rely on proximity technology. It is the result of predictions by many renowned experts. In the future card, people may expect the functionality to increase and become more secure and flexible. If you switch to this technology now, you can be one step ahead.
Drawbacks of Proximity Card and Vicinity Card
Vicinity and proximity cards are as useful tools as other physical security measures. But they all have some security vulnerabilities to a greater or lesser extent. These security holes can be filled by active and responsible management.
They can store relatively large amounts of data in their bodies. Assuming they fall into the hands of criminals, one can gain access to the holder’s information by stealing the data inside them. Of course, people can avoid this situation. If the cardholder notifies the administrator immediately after the loss, he can void the card. Once the card is invalidated, it also has no other use. It is not reusable.
The reading range of the proximity integrated circuit card is limited. Assuming that the item you need to read is placed within a distance of up to 2 meters, you can choose a vicinity card. The vicinity card has wider coverage than the proximity RFID card.
Proximity Card and Vicinity Card: Which Card is Right for You

The impact of COVID-19’s popularity makes contactless extra important. They also have a tracking feature that provides real-time positioning for stream tuning.
Contactless card readers are ideal for contactless access control in commercial spaces.
It is very modern and suitable for any place in the city. It can also provide security for your office space, rooms, and lobbies.
Assuming you want to start a membership card program, the vicinity card is the best choice. It is because it has read and write capabilities. When registering a member, you can enter the user data. Even if a customer claims, you can easily use the card reader to retrieve their purchase date. Of course, you can also use it if you want to access it remotely. It works from a distance of up to 2 meters. People can use it at access control or toll booths.
Before deciding which card to use, consider the following points.
- What is most important in your building security?
- Why do you need an RFID card system?
- What will you do with it?
- Where do you plan to use it?
Many confuse RFID cards, proximity cards, and vicinity cards. They are technically very similar in that they all use RFID technology. People can use RFID tags in logistics, inventory, healthcare, and other industries. Vicinity and proximity cards can be used more for access control, ticketing, billing, and attendance.
The Science Behind the Scenes
Bit formats are used to encode the data on your card. There are a number of options available, including 26, 32, 34, 35, and 40 bits. The most common format is 26-bit. Other formats are brand specific and not as secure because they are easily compromised by hackers.
Proximity Card Encoding Example
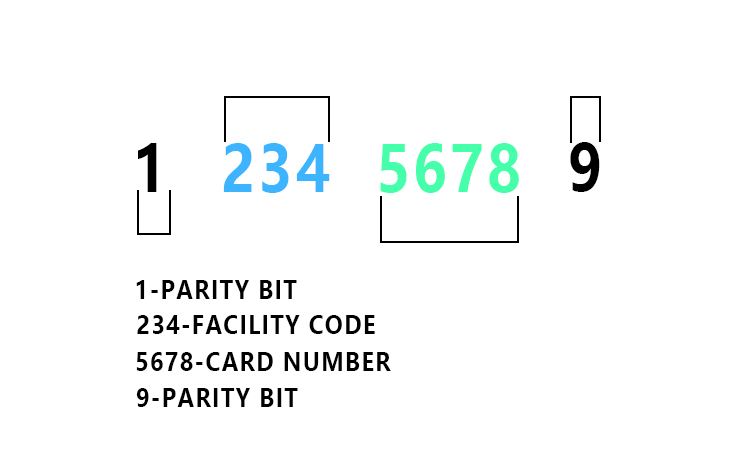
Your card number is made up of four parts: parity bits, a Facility Code, and the card number itself.
- Parity bits help protect your card from being duplicated.
- The Facility Code is a number between 1 and 255 that helps secure your building by allowing each building to have its own unique Facility Code.
- The digits in your numbers are like anyone else’s—they start at 0 and go up to 9999.
About Proximity Card Q&A
-
What is a proximity card, and how does it work?
A proximity card is a type of contactless smart card that uses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology to communicate with a reader. The card contains a small chip that stores data and an antenna that sends and receives signals to and from the reader. When the card is held within a certain distance of the reader, the reader emits a signal that powers the card and reads the data stored on the chip.
-
What are the benefits of using proximity cards for access control?
Proximity cards offer several benefits for access control, including convenience, speed, and security. They eliminate the need for physical keys or passwords, which can be lost, stolen, or shared. They also allow for quick and easy access without requiring users to interact physically with the reader.
-
How secure are proximity cards compared to traditional key-based systems?
Proximity cards are generally considered more secure than traditional key-based systems, as they cannot be easily picked or duplicated. However, they are not foolproof and can be vulnerable to hacking or cloning if proper security measures are not in place.
-
Can proximity cards be easily cloned or duplicated?
Proximity cards can be cloned or duplicated if they are not properly secured. But most modern systems use encryption and other security measures to prevent this.
-
What are the different types of proximity cards available, and how do they differ?
There are several types of proximity cards available, including low-frequency (LF), high-frequency (HF), and ultra-high-frequency (UHF) cards. They differ in their operating frequency, range, and compatibility with different types of readers.
-
How are proximity cards programmed and managed in an access control system?
Proximity cards are typically programmed and managed using a software system. It allows administrators to assign access privileges and monitor usage. This software may be hosted on-site or in the cloud.
-
What are the limitations of using proximity cards for access control?
Proximity cards have limitations, such as their range and susceptibility to interference from other electronic devices. They may also be vulnerable to physical damage, such as bending or scratching.
-
How do proximity cards compare to other types of access control systems, such as biometric systems?
Proximity cards are generally considered to be more secure than traditional key-based systems. But less secure than biometric systems that use unique physical characteristics such as fingerprints or facial recognition for identification.
-
Are proximity cards compatible with mobile devices and smartphones?
Most modern proximity cards can be used with mobile devices and smartphones through a mobile app or by integrating the card with the device’s NFC capabilities.
-
What are some best practices for implementing a proximity card-based access control system?
Best practices for implementing a proximity card-based access control system are more. This includes securing the physical cards, encrypting data transmissions, and regularly monitoring and updating the system for vulnerabilities. It is also important to provide training and education to users to ensure they understand how to use the system and follow security protocols.










