Barcoding technology is crucial for accurate product tracking and management in today’s business world. Two popular code systems are pharmacode and barcode, each with distinct differences. This blog will explore the design, encoding, reading, and application differences between Pharmacode and Barcode. By the end, you’ll know which code system is best for your needs.
What is a Barcode?
A barcode is a visual representation of data that a scanner can read. It consists of a series of vertical bars and spaces representing a unique code. We can use barcodes in various industries, including the pharmaceutical industry. It can help us streamline inventory management and improve product accuracy. Different types of bar codes exist in the market, including Universal Product Code (UPC) and European Article Number (EAN). These bar codes are used for specific purposes depending on their design. Advances in barcode technology have made 2D barcodes and 2D codes more desirable. They can store more information and can be read by smartphones. Bar code technology has become an important tool for companies to increase efficiency and reduce product management errors.

Related Articles: Warehouse Barcodes: Why Choose It?
What is a Pharmacode?
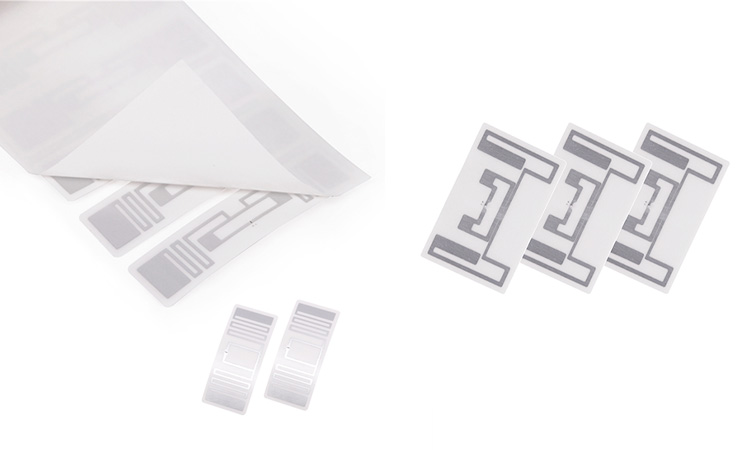
Pharmacode also stands for Pharmaceutical Binary Code. It is a barcode specifically designed for the pharmaceutical industry. It is a one-dimensional barcode that consists of a series of vertical bars and spaces. Each bar represents a “0” or “1” in binary format. Drug codes typically encode product information such as lot numbers, expiration dates, and other related data. They are typically designed to be smaller and more compact than bar codes. This compact size also makes them ideal for small pharmaceutical packages like drug labels. We can read these drug codes from any direction. They offer a high degree of accuracy in tracking medications. Their presence also ensures patient safety and regulatory compliance.
Related Articles: What is Pharmacode?
Pharmacode vs Barcode:What is the Differences between Pharmacode and Barcode
While barcodes have been widely used for decades, pharmacodes are a more recent addition with specific applications in the pharmaceutical industry. Here are the key differences between pharmacode and barcode:
Design Differences
Pharmacode and barcodes differ significantly in design. pharmacode is a one-dimensional barcode that uses a series of vertical bars of varying widths to represent numeric data. Compared to barcodes, Pharmacode is more compact and efficient at encoding and decoding data. It can encode up to 131,070 sets, making it ideal for drug tracking in the pharmaceutical industry.
On the other hand, A barcode is a two-dimensional code that consists of a series of parallel lines of different widths and the space between them. It can store more data, including alphanumeric characters, symbols, and even images. Bar codes can encode up to 7,089 characters, making them more suitable for encoding complex product information. Barcodes can also be customized to include company logos and other branding elements. This makes it a popular choice for use in retail and other industries.
Encoding Differences
Another difference between Barcode and Pharmacodes is how they are encoded. pharmacode uses a binary format to encode digital data. Here each bar represents a “0” or a “1.” The binary format Pharmacode allows for more efficient encoding and decoding of data. This makes it more accurate in tracking medications.
In contrast, barcodes use a different encoding standard, depending on the type of barcode used. For example, the Universal Product Code (UPC) uses a series of 12 digits to encode product information. The European Article Number (EAN) uses a series of 13 digits. Bar codes can also encode alphanumeric characters and symbols. Thus, it has additional uses in encoding complex product information.
Reading Differences
We also found a significant reading difference between a pharmacode and a barcode. pharmacode, as a one-dimensional barcode, is read by a scanner to read the vertical bars of the code. Pharma code scanners are designed to read the code in one pass, allowing faster and more accurate data decoding.
As a two-dimensional code, a bar code is read by the scanner with horizontal lines and the space between them. Bar code scanners require many passes to read the entire code correctly. This can be time-consuming and less efficient than a pharmacopeial scanner. However, bar codes can store more information, including alphanumeric characters and symbols.
Another important reading difference between a pharmacode and a barcode is the orientation of the code. Pharmacode can be read in any orientation, making it more flexible to track medications. However, barcodes require a specific orientation to be read correctly, which can be challenging in some applications.
Applications Differences
Next comes the application differences. People use Pharmacode primarily in the pharmaceutical industry. Its primary use is to track medications and enable efficient inventory management.
On the other hand, Barcodes have a much wider range of applications in various industries. This would include retail, logistics, and healthcare.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pharmacode and Barcode
With the above, you may clearly understand the main differences between barcodes and drug codes. Next, I will summarize their advantages and disadvantages are:

Advantages of Barcodes:
- Barcodes are widely recognized and accepted in various industries.
- They can store more information than pharma codes, making them suitable for tracking large inventories.
- They are versatile and can be used on different types of packaging, such as boxes, cartons, and labels.
- They can be read by most barcode scanners, making them easy to use and accessible.
Disadvantages of Barcodes:
- Barcodes are susceptible to damage or misreading, which can affect their accuracy.
- They require a proper alignment for scanning, which can be time-consuming.
- They are not as accurate as pharmacodes in tracking medication, which can pose risks to patient safety.
Advantages of Pharmacodes:
- Pharmacodes are more accurate and efficient in tracking medication. It ensures patient safety and regulatory compliance.
- They are more robust and less susceptible to damage or misreading. This makes them a reliable option for pharmaceutical packaging.
- They can be read at any orientation, which saves time and reduces errors.
- They are exclusively used in the pharmaceutical industry.
Disadvantages of Pharmacodes:
- Pharmacodes can only be read by specialized scanners, which may require additional equipment and training.
- They cannot store as much information as barcodes, limiting their use for other applications.
- They are limited to small packaging, which may not be suitable for larger inventories.
By understanding the above, you should already know the difference between Pharmacode and Barcode. While both coding systems have unique advantages and disadvantages, the actual application depends on your specific needs. With the continuous development of technology, we believe that barcode technology will go further in the future.
About Difference Between Pharmacode and Barcode FAQs
-
What is the main difference between pharmacode and barcode?
The main difference between pharmacode and barcode is in their design and encoding. Barcodes consist of vertical bars and spaces, while pharmacodes use vertical bars and dots. Barcodes represent the product code directly, while pharmacodes use a system of dots to represent numbers that specialized scanners can decode.
-
How does the design of the pharmacode differ from that of the barcode?
The design of the pharmacode differs from the barcode in that it uses vertical bars and dots instead of vertical bars and spaces. Pharmacodes are also smaller and more compact than barcodes, making them ideal for small packaging such as medication labels.
-
What is the significance of the encoding differences between pharmacode and barcode?
The encoding differences between pharmacode and barcode are significant because they represent the product code in different ways. Barcodes represent the product code directly, while pharmacodes use a binary code system requiring specialized decoding scanners.
-
Why do pharmacodes require specialized scanners for decoding?
Pharmacodes require specialized scanners for decoding because they use a binary code system to represent the product code. These scanners are designed to interpret the pattern of dots and convert them into numbers that can be used to identify the product.