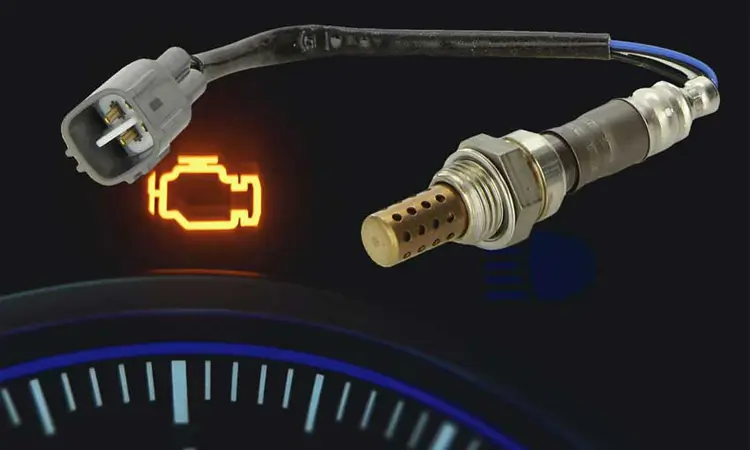
Did you know oxygen sensors are critical to a vehicle’s emissions system? Regularly testing them can help ensure that your car runs smoothly and efficiently. In this guide, we’ll cover everything you need to know about testing O2 sensors, including symptoms of a bad Oxygen sensor, common causes of failure, and the various testing tools available. By the end of this guide, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge and skills to test O2 sensors in your vehicle effectively.
What is O2 Sensor and How Does It Work?
An oxygen or O2 sensor is a critical component of a vehicle’s emissions system. It is responsible for measuring the amount of oxygen in a vehicle’s exhaust and relaying that information to the engine control module (ECM). The ECM then uses that information to adjust the air-fuel ratio, which helps ensure that the vehicle is running efficiently and meeting emissions regulations.
An O2 sensor consists of two main parts: the sensing element and the heater circuit. The sensing element is responsible for measuring the amount of oxygen in the exhaust, while the heater circuit warms up the sensor to ensure accurate readings.
The oxygen sensor is typically located in the exhaust system, either in the exhaust manifold or downstream in the exhaust pipe. It is a small, cylinder-shaped device with a threaded end that screws into a fitting in the exhaust system.
The Oxygen sensor measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust stream. It contains a ceramic element that is coated with a layer of platinum and zirconia. The element acts as a chemical catalyst, reacting with the oxygen in the exhaust stream to create a voltage signal.
There are different types of oxygen sensors, including zirconia and titania. Zirconia sensors are the most common type and are used in most vehicles. They are more accurate and more reliable than titania sensors, which are used in some older cars.
In addition to helping maintain optimal combustion, the Oxygen sensor also helps detect problems in the engine and emissions system. If the Oxygen sensor detects a problem, it will set a diagnostic trouble code (DTC) and turn on the check engine light. This can help alert the driver to potential problems and prompt them to take their vehicle in for repairs.
How can You Tell if Your O2 Sensor is Damaged?
There are several signs that your O2 sensor may be damaged:
Symptoms of Bad Oxygen Sensor

A bad Oxygen sensor can cause various issues with a vehicle’s performance and emissions. Here are some common symptoms of a bad O2 sensor:
- Check engine light: A faulty Oxygen sensor can trigger the check engine light to come on. The ECM will detect an issue with the sensor and store a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
- Poor fuel economy: A bad Oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run rich or lean, resulting in poor fuel economy.
- Rough idling: If the air-fuel ratio is incorrect, the engine may idle roughly or stall.
- Reduced power: A bad Oxygen sensor can cause the engine to run poorly, resulting in reduced power and acceleration.
- Failed emissions test: If the Oxygen sensor is not functioning properly, the vehicle may fail an emissions test.
- The smell of gasoline: If the engine is running rich due to a faulty O2 sensor, you may smell gasoline in the exhaust.
- Increased emissions: A bad oxygen sensor can cause the vehicle to emit more pollutants than it should, harming the environment.
- Ignition timing issues: If the Oxygen sensor is not providing accurate information to the ECM, it can cause ignition timing issues, leading to engine damage over time.
It’s important to note that some of these symptoms can also be caused by other issues with the vehicle. That’s why it’s essential to have the vehicle diagnosed by a professional mechanic to determine the root cause of the issue. If a faulty O2 sensor is the problem, it should be replaced. This makes it possible to prevent further damage to the vehicle and ensure that it runs efficiently and meets emissions regulations.
Common O2 Sensor Failure Causes
Here are some of the most common reasons why an O2 sensor may fail:
- Age: Like any component in a vehicle, Oxygen sensors can wear out over time. Most sensors have a lifespan of around 100,000 miles, but some can last longer or shorter depending on the vehicle and driving conditions.
- Contamination: The O2 sensor is exposed to various contaminants in the exhaust stream, including soot, oil, and coolant. If these contaminants build up on the sensor, they can reduce its effectiveness or cause it to fail completely.
- Physical damage: The Oxygen sensor is located in a vulnerable spot in the exhaust system and can be damaged by road debris or contact with the ground.
- Overheating: If the engine is running too hot, it can cause the Oxygen sensor to overheat and fail.
- Electrical issues: Wiring problems or a faulty ECM can cause the Oxygen sensor to malfunction.
- Fuel additives: Some fuel additives can damage the Oxygen sensor and cause it to fail prematurely.
- Improper installation: If the Oxygen sensor is not installed correctly, it can cause it to fail or provide inaccurate readings.
- Exhaust leaks: If there is a leak in the exhaust system, it can cause the Oxygen sensor to fail or provide inaccurate readings.
It’s important to address any issues with the Oxygen sensor as soon as possible to prevent further damage to the vehicle and ensure it runs efficiently and meets emissions regulations. A professional mechanic can diagnose the problem and determine if the Oxygen sensor needs to be replaced or if another underlying issue must be addressed.
Specific Process for Testing O2 Sensor in Car
If you want to test Oxygen sensor in your car, you need to follow a few simple steps. First, locate the sensor, usually mounted in the exhaust manifold or pipe. Then, disconnect the electrical connector and remove the sensor from the exhaust. Next, clean the sensor using a wire brush or sandpaper to remove debris or buildup. After cleaning, inspect the sensor for any signs of damage or wear.
Connect a voltmeter to the sensor’s signal wire and ground to check the sensor’s voltage output. Start the engine and let it idle for a few minutes. Then, rev the engine a few times and watch the voltmeter reading. It should fluctuate between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
To test the sensor’s resistance, you will need an ohmmeter. Connect the ohmmeter to the sensor’s terminals and check the resistance. The exact resistance value will depend on the sensor’s type and manufacturer. Consult the sensor’s specifications to determine the correct resistance range.
Another method to test O2 sensor in the car is using a scan tool. Connect the scan tool to the OBD-II port, and read the live data to check the sensor’s voltage and resistance values. You can also use the scan tool to check the sensor’s response time, which should be less than 100 milliseconds.
It’s essential to ensure that the sensor is getting sufficient power and ground when testing O2 sensor in the car. Check the sensor’s wiring and connectors for any signs of damage or corrosion. A faulty wiring connection can lead to inaccurate readings and affect the sensor’s performance.
Related Articles: How to Test ABS Sensor
O2 Sensor Testing Tool
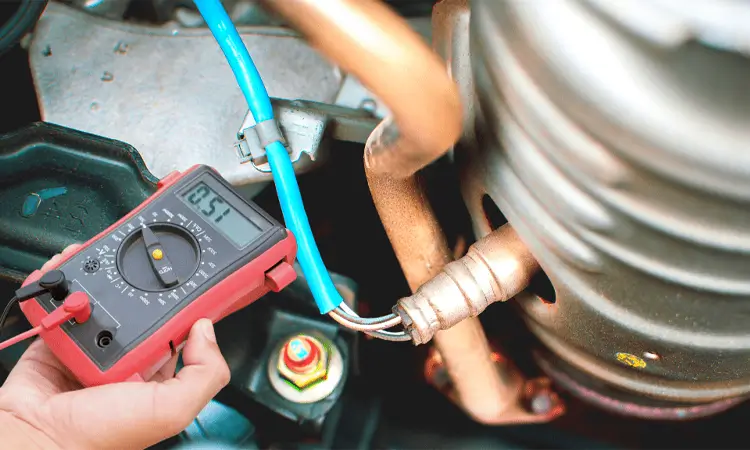

To test an O2 sensor, you will need a few specialized tools. Here are some of the most common O2 sensor testing tools:
- Scan tool: A scan tool is used to read diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and live data from the O2 sensor.
- Multimeter: A multimeter can measure voltage and resistance in the O2 sensor circuit.
- Ohm meter: An ohm meter is used to measure the resistance of the O2 sensor.
- Voltmeter: A voltmeter can be used to measure the voltage output of the O2 sensor.
- O2 sensor simulator: An O2 sensor simulator can be used to simulate the output of an Oxygen sensor to test the vehicle’s fuel management system.
You need to know not all O2 sensor testing tools are created equal. Some tools are designed specifically for certain types of sensors or vehicles. So it’s important to choose the right tool for the job. Additionally, Oxygensensor testing can be complicated and requires a good understanding of how the sensor works and how to interpret the data it produces. If you’re uncomfortable with testing an O2 sensor, it’s best to have the vehicle diagnosed by a professional mechanic.
How to Test O2 Sensor with Scan Tool
Testing O2 sensor with scan tool is one of the most common methods. Here’s how it’s done:
- Connect the scan tool: Connect the scan tool to the OBD-II port under the dashboard. The diagnostic port is usually located under the dashboard on the vehicle’s driver’s side.
- Access the sensor data: Use the scan tool to access the sensor data. Look for data related to the O2 sensor, such as oxygen sensor voltage and oxygen sensor heater voltage.
- Monitor the sensor data: Start the engine and let it run until it reaches normal operating temperature. Monitor the O2 sensor data on the scan tool to see if the readings are within normal range.
- Check for trouble codes: Use the scan tool to check for any trouble codes related to the O2 sensor. If any trouble codes are present, diagnose and repair the issue before testing Oxygen sensor.
- Interpret the data: Interpret the O2 sensor data on the scan tool to determine if the sensor is functioning properly. A healthy sensor should produce a steady voltage reading between 0.1 and 0.9 volts, with quick transitions between high and low voltage.
- Compare the data: Compare the O2 sensor data to the manufacturer’s specifications to determine if the sensor is within the normal range. If the readings are out of range, the sensor may need to be replaced.
PS: The scan tool readings should be used as a diagnostic tool, not as the sole determining factor for O2 sensor replacement. Additional tests may be necessary to confirm a faulty O2 sensor.
How to Test O2 Sensor with Ohm Meter
Testing O2 sensor with ohm meter is a similar process to using a multimeter. Here’s how to do it:
- Disconnect the sensor: Use an O2 sensor socket to remove the sensor from the exhaust system.
- Set the ohmmeter: Set the ohmmeter to measure resistance and connect the leads to the sensor’s terminals.
- Check the resistance: Check the sensor’s resistance against the manufacturer’s specifications. A healthy sensor should have a resistance of approximately 6-20 ohms at room temperature.
- Warm up the sensor: Warm the sensor using a propane torch or other heat source. As the sensor heats up, the resistance should decrease.
- Check the resistance again: Check the sensor’s resistance while it is still warm. If the resistance is still within the manufacturer’s specifications, the sensor is likely functioning properly.
Using an ohmmeter to test an O2 sensor is similar to using a multimeter, as both tools measure resistance. However, using an ohmmeter alone may not be sufficient to diagnose all problems with an O2 sensor. For example, an ohmmeter does not measure the sensor’s output voltage, which is another important factor in determining sensor function.
How to Test O2 Sensor with Voltmeter
A voltmeter can be used to test voltage output of O2 sensor. Here’s how to do it:
- Connect the voltmeter: Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the sensor’s signal wire and the negative lead to a ground source.
- Set the engine to idle: Start the engine and let it idle.
- Check the voltage: With the engine running, check the sensor’s voltage output using the voltmeter. A healthy sensor should generate a fluctuating voltage between 0.1 and 0.9 volts, with the voltage changing rapidly as the engine’s RPM changes.
- Increase engine RPM: Increase the engine’s RPM to 2,500 and hold it steady.
- Check the voltage again: With the engine RPM held steady at 2,500, check the sensor’s voltage output again. A healthy sensor should generate a steady voltage between 0.4 and 0.6 volts.
- Interpret the results: If the sensor’s voltage output does not fluctuate rapidly or the voltage is consistently low or high, the sensor may be faulty and require replacement.
Using a voltmeter to test an O2 sensor can help identify issues with the sensor’s voltage output, which can indicate a faulty sensor.
How to Test O2 Sensors with Real-Time Data
Testing O2 sensors with live data is a diagnostic technique to identify issues with the sensor’s output signals while the vehicle is in motion. Here’s how it works:
- Connect a diagnostic tool: Connect a diagnostic tool to the vehicle’s OBD-II port.
- Monitor the sensor data: Using the diagnostic tool, monitor the O2 sensor data in real-time while driving the vehicle.
- Analyze the data: Analyze the data from the O2 sensors to identify any abnormalities or inconsistencies in the readings. Look for patterns in the data that may indicate a problem with the sensor or its associated wiring.
- Compare to expected values: Compare the live data from the Oxygen sensors to expected values based on the vehicle’s make, model, and year, as well as the sensor’s specifications.
- Interpret the results: Based on the data analysis, determine if there is a problem with the Oxygen sensor or its wiring. Replace the sensor or repair the wiring to resolve the issue.
Testing O2 sensors with live data can provide a more comprehensive diagnostic than static testing with a multimeter or voltmeter alone. By monitoring the sensor output in real time while the vehicle is in motion, this technique can help identify issues that may not be evident during static testing. However, it’s important to use a diagnostic tool compatible with the vehicle and the O2 sensors to interpret the data accurately to avoid misdiagnosis.
How to Test O2 Sensor with Multimeter
Most people choose to use a multimeter to test oxygen sensors. Here’s how to do it:
- Prepare the multimeter: Set the multimeter to measure DC voltage and connect the positive and negative leads to the corresponding terminals on the multimeter.
- Disconnect the O2 sensor: Locate the O2 sensor and disconnect the electrical connector.
- Connect the multimeter: Connect the positive lead of the multimeter to the O2 sensor signal wire, and the negative lead to a good ground on the vehicle.
- Turn on the ignition: Turn the ignition on, but do not start the engine.
- Monitor the multimeter: Monitor the multimeter reading as you rev the engine. The voltage reading should fluctuate rapidly between 0.1V and 0.9V.
- Check the specifications: Compare the multimeter readings to the manufacturer’s specifications. The O2 sensor may be faulty if the readings are outside the specified range.
- Repeat the test: Repeat the test for each of the vehicle’s O2 sensors.
Using a multimeter can be a useful method for testing O2 sensors, but it may not always provide accurate results. Some multimeters may not be sensitive enough to detect small voltage changes, making it difficult to identify a faulty sensor. In addition, this method only tests the sensor’s output voltage, which may not provide a complete picture of the sensor’s overall performance. For a more comprehensive test, it may be necessary to use additional testing tools or methods.
Related Articles: How to Test 3 Wire Crank Sensor with Multimeter
Testing Specific Parts of the O2 Sensor
In addition to testing the O2 sensor itself to troubleshoot, you can also test other parts of it. Some of the more common specific parts include the heater circuit, and the wiring location.
How to Test O2 Sensor Heater Circuit
Testing Oxygen sensor heater circuit is an essential step in diagnosing problems with your vehicle’s engine. Here’s how to do it:
- Step 1 : Identify the heater circuit: Locate your vehicle’s O2 sensor heater circuit. It is typically identified by a four or five-wire sensor.
- Step 2 : Check for power: Use a multimeter to check for power to the O2 sensor heater circuit. Connect the multimeter to the sensor’s electrical connectors and turn on the ignition. You should see 12 volts of power.
- Step 3 : Check for ground: Use the multimeter to check for a ground signal. Connect one probe to the sensor’s ground wire and the other to the battery’s negative terminal. You should see close to zero volts of resistance.
- Step 4 : Monitor the sensor: Start the engine and monitor the sensor’s voltage output. The voltage should fluctuate between 0.1 and 0.9 volts.
- Step 5 : Interpret the results: Analyze the voltage readings to determine if the sensor functions properly. Further testing may be necessary to isolate the issue if the voltage is stable or outside the expected range.
- Step 6 : Test the sensor: Further testing may be necessary to determine the root cause if the voltage reading indicates a problem. This could involve using specialized O2 sensor testing tools or other diagnostic equipment.
Testing O2 sensor heater circuit is critical to diagnosing problems with your vehicle’s engine. The heater circuit provides power to the O2 sensor, allowing it to operate properly. If the heater circuit is not functioning correctly, the O2 sensor may not provide accurate readings, which can lead to engine performance problems. By monitoring the voltage output and checking for power and ground signals, you can quickly identify problems with the Oxygen sensor heater circuit and take corrective action to keep your vehicle running smoothly. However, interpreting voltage readings requires a certain level of expertise and experience, so it’s often best to consult with a professional mechanic if you suspect that your vehicle’s O2 sensors are not functioning properly.
How to Test O2 Sensor Wiring
The wiring for an O2 sensor can be tested to ensure that the sensor receives the proper voltage and ground signals. To test the wiring, start by visually inspecting the wiring harness for any damage or lose connections. Next, use a voltmeter to test the voltage at the sensor’s power and ground wires. The voltage should be within the manufacturer’s specifications. If the voltage is outside the acceptable range, the wiring may be damaged, or there may be a problem with the sensor’s control module.
In addition to voltage testing, you need to check the continuity of the wiring. Continuity testing is done by using an ohmmeter to test the resistance of the wiring between the sensor and the control module. If there is no continuity or the resistance is too high, the harness may have a break or a damaged wire. Some O2 sensors have multiple wires for different purposes, such as a heater circuit, and each wire should be tested separately.
If all wiring tests pass and the sensor is still not functioning properly, it may be necessary to replace the sensor itself. Proper wiring testing can help ensure that the O2 sensor receives the signals it needs to function correctly and can help prevent unnecessary replacement of a functioning sensor.
Testing your O2 sensor is an essential part of maintaining your vehicle’s performance and fuel efficiency. Using the appropriate testing tool and method, you can identify any issues with your sensor and make the necessary repairs. Remember always to follow safety precautions and refer to your car’s manual for specific instructions.
Related Guide: How to Test a Knock Sensor
About O2 Sensor FAQs
- FAQ 1: How Many Ohms Should an Oxygen Sensor Read?
The resistance of a good Oxygen sensor is approximately 6-20 ohms at room temperature.
- FAQ 2: How do You Test an O2 Sensor with 4 Wires?
To test a 4-wire oxygen sensor, first, locate the signal wire. Then use a multimeter to measure the voltage between the signal wire and the ground. The voltage should fluctuate between 0.1V and 0.9V when the engine is running. The sensor may be faulty if the voltage is steady or outside of this range.
- FAQ 3: How do You Bench Test an Oxygen Sensor?
First, to test a 4-wire Oxygen sensor, identify the signal wires using a wiring diagram. Next, use a digital multimeter to measure the sensor’s voltage output. With the engine running and the sensor heated up, the voltage should fluctuate rapidly between 0.1 and 0.9 volts. If the voltage remains steady or does not change, the sensor may be faulty and must be replaced.
- FAQ 4: How Many Volts does an O2 Sensor Need?
An O2 sensor typically needs around 0.5 to 1.0 volts.
- FAQ 5: What’s the Resistance of an O2 Sensor?
The resistance of an O2 sensor varies with temperature. At room temperature, it is typically around 6-20 ohms.
- FAQ 6: What is the Life Expectancy of an O2 Sensor?
The life expectancy of an Oxygen sensor varies. Typically, they last between 30,000 and 100,000 miles. Factors like driving habits, fuel quality, and the environment affect it.
- FAQ 7: Are Rear O2 Sensors Really Necessary?
Rear O2 sensors are necessary for proper engine performance. They help monitor emissions and ensure fuel efficiency. Removing them can lead to decreased performance and potential legal issues.
- FAQ 8: What if the O2 Sensor won’t Come Out?
If the Oxygen sensor won’t come out, apply penetrating oil. Allow it to sit for a few minutes. Use a sensor removal tool and carefully apply force. If the sensor still doesn’t budge, try heating the area with a propane torch. If all else fails, seek professional help.
Video Source: Department of Environmental Protection