A faulty ABS sensor can cause significant problems, compromising your vehicle’s safety. But how do you know if your ABS sensor is broken? Fortunately, several ways exist to test the sensor and diagnose any issues. In this article, we’ll cover everything you need to know about ABS sensors. Including how they work, where they’re located, and how to test them using various tools. With our step-by-step instructions and expert tips, you can test your ABS wheel speed sensors like a pro!
What is an ABS Sensor
An anti-lock braking system (ABS) is a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles, designed to prevent wheels from locking up during sudden or hard braking. The ABS system relies on sensors to monitor the speed of each wheel, allowing the system to adjust the brake pressure as needed to maintain control of the vehicle.
Wikipedia explains ABS sensor working principle:
ABS operates by preventing the wheels from locking up during braking, thereby maintaining tractive contact with the road surface and allowing the driver to maintain more control over the vehicle.
From wikipedia
The ABS sensor is a key system component responsible for measuring the wheel speed and transmitting that data to the vehicle’s computer. The sensor is typically mounted on or near the wheel hub or brake rotor and consists of a magnetic or optical sensor, a toothed rotor, and a wiring harness.
When the wheel rotates, the toothed rotor passes by the sensor, generating an alternating current (AC) signal corresponding to the wheel speed. The sensor then converts the AC signal to a digital signal and sends it to the ABS control module.
The ABS control module uses the wheel speed data from each sensor to determine when a wheel is about to lock up and adjust the brake pressure accordingly. By pulsing the brakes on and off rapidly, the ABS system can prevent the wheels from locking up, allowing the driver to maintain steering control and avoid skidding.
ABS sensors come in a variety of types, including magnetic sensors, Hall-effect sensors, and optical sensors. The type of sensor used can vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model.
It’s important to note that a faulty ABS sensor can cause significant problems with the ABS system, compromising the vehicle’s safety. A broken sensor can cause the ABS warning light to illuminate on the dashboard and can also affect the traction control and stability control systems.
If you suspect your anti-lock braking system sensor is malfunctioning properly, you must be tested and repaired as soon as possible. Testing the ABS sensor can help diagnose any issues and ensure the system functions properly, keeping you and your passengers safe on the road.
ABS Sensor Located

The location of the ABS sensor can vary depending on the vehicle’s make and model. The ABS sensor is usually mounted on or near the wheel hub or brake rotor.
The ABS sensor is usually located on the front wheel hub assembly on front-wheel-drive vehicles. The sensor is typically located on the rear differential or axle on rear-wheel-drive vehicles.
To locate the ABS sensor, consult your vehicle’s owners or service manual. In many cases, the ABS sensor can be easily accessed by removing the wheel and brake assembly.
Once you have located the sensor, inspect it for any signs of damage or corrosion. Check the wiring harness for any frayed or broken wires, as this can also cause issues with the sensor.
If the sensor or wiring is damaged, it may need to be replaced or repaired. Sometimes, simply cleaning the sensor or wiring harness can help resolve any issues.
How do I know If My ABS Sensor is Broken?
Signs of a Faulty ABS Sensor
A faulty ABS sensor can cause many problems with the ABS system and compromise your vehicle’s safety. Here are some signs that your ABS sensor may be faulty:
- ABS warning light: The most obvious sign of a faulty anti-lock braking system sensor is the illuminated ABS warning light on the dashboard. This light indicates an issue with the ABS system, and it’s important to have it inspected and repaired as soon as possible.
- Traction control and stability control issues: A faulty ABS sensor can also affect the vehicle’s traction control and stability control systems. If you notice issues with these systems, such as difficulty maintaining traction or stability, it may indicate a problem with the ABS sensor.
- Braking issues: In some cases, a faulty ABS sensor can cause the brakes to lock up or engage randomly, even under normal driving conditions. This can make it difficult to control the vehicle and can be dangerous.
- Noisy ABS system: A damaged or broken ABS sensor can cause the ABS system to make unusual noises, such as grinding, clicking, or buzzing sounds.
- Irregular speedometer readings: A broken ABS sensor can also affect the speedometer’s accuracy. If the sensor sends incorrect speed data to the vehicle’s computer, the speedometer may not display the correct speed.
- ABS system not working: If the ABS system is not functioning at all, it may be due to a faulty ABS sensor. Without the sensor’s input, the ABS system cannot function properly.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to have the anti-lock braking system diagnosed and repaired as soon as possible. Ignoring a faulty ABS sensor can compromise the vehicle’s safety and lead to more significant and expensive repairs down the road. Testing ABS sensors can help diagnose issues and ensure the system functions properly, keeping you safe on the road.
Common ABS Sensor Failure Causes
ABS sensors are designed to last the vehicle’s life, but they can still fail for various reasons. Here are some of the most common causes of ABS sensor failure:
- Impact damage: The location of ABS sensors near the wheels and brakes makes them susceptible to impact damage. If the sensor is hit or damaged during maintenance, it may fail.
- Corrosion: Corrosion can also cause ABS sensors to fail, especially in areas with high levels of salt or moisture. Over time, this can cause the sensor to fail or send incorrect signals to the vehicle’s computer.
- Electrical issues: Electrical problems, such as a blown fuse or damaged wiring, can also cause the anti-lock braking system sensor to malfunction or fail. Issues with the vehicle’s battery or alternator can also affect the sensor’s performance.
- Wear and tear: Like any other component, ABS sensors can wear out over time. The sensor’s internal components can become damaged or worn, leading to a loss of signal and other issues.
- Contamination: Dirt, dust, and other debris can accumulate on the ABS sensor, affecting its performance. This can cause the sensor to malfunction or fail completely.
- Improper installation: If the ABS sensor is not installed correctly or is not tightened to the proper torque specifications, it can cause the sensor to malfunction or fail.
- Faulty wheel bearing: A faulty wheel bearing can cause the ABS sensor to malfunction, as the sensor relies on the wheel speed to function properly.
- Manufacturing defects: In rare cases, ABS sensors may fail due to manufacturing defects. This can include issues with the sensor’s design, construction, or materials.
You need to keep your ABS sensors clean and debris-free for a long time and check them regularly. This is to ensure that they function properly over a long period of time. If you have problems with your anti-lock braking system system, be sure to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified mechanic or technician who can help you diagnose any problems with your vehicle and prevent further damage.
Using ABS Sensor Test Tool
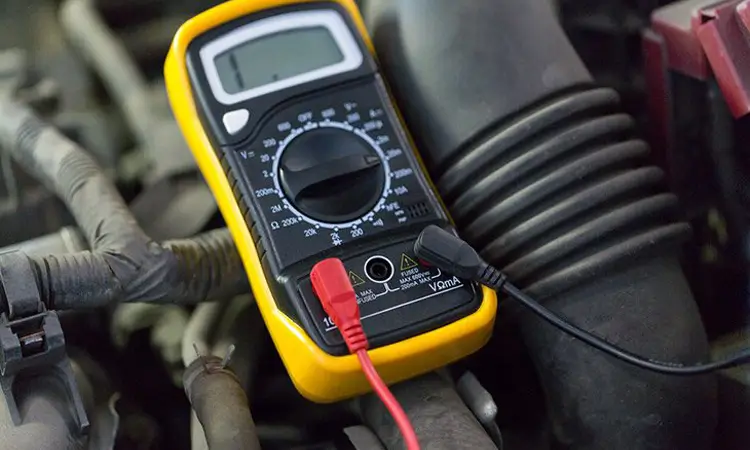

Using an ABS sensor test tool can help diagnose issues with the ABS system. It connects to the vehicle’s computer and can provide real-time data about the sensor’s performance. There are several types of ABS sensor test tools available. Including multimeters and oscilloscopes. These tools can help you diagnose various issues, from faulty sensors to wiring problems. If you’re experiencing ABS system issues, an ABS sensor test tool can help you quickly identify the problem and safely get your vehicle back on the road.
How to Test ABS Sensor with Multimeter
Testing the ABS Sensor with a multimeter is a common method for diagnosing ABS system issues. Here are the steps to test a ABS wheel speed sensor with a multimeter:
- First, locate the ABS Sensor you want to test. This will usually be near the wheel hub, on the inside of the wheel well.
- Use a multimeter to test the resistance of the sensor. Set the multimeter to the resistance setting, and touch the leads to the sensor’s terminals.
- Check the multimeter’s reading. A good ABS wheel speed sensor will have a resistance reading that falls within the specified range and fluctuates as the wheel rotates. If the reading is outside this range, the sensor may be faulty.
- Test the sensor’s wiring. You may have a wiring issue if the sensor’s resistance is within the normal range. Use the multimeter to test the continuity of the sensor’s wiring, checking for any breaks or shorts.
- Inspect the sensor for physical damage. If the sensor’s resistance and wiring are both in good condition, inspect the sensor itself for any physical damage or signs of wear.
Multimeter testing is a quick and easy way to test your anti-lock braking system sensors. However, this method may not be able to detect all types of sensor failures, such as intermittent signal loss. If you’re experiencing ABS system issues, having your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician or mechanic is always a good idea.
Related Guide: How to Test a Knock Sensor
How to Check ABS Sensor with Voltmeter
Using a voltmeter is another way to check your ABS sensor for issues. Here’s how to do it:
- First, locate the ABS sensor you want to test. This will typically be near the wheel hub, on the inside of the wheel well.
- Disconnect the sensor’s wiring harness. This will allow you to test the voltage of the sensor’s signal wire.
- Turn the ignition on and set your voltmeter to the AC voltage setting.
- Touch the voltmeter’s leads to the sensor’s signal wire and ground. The signal wire will usually be the one with the smaller connector.
- Touch the voltmeter’s probes to the two terminals of the ABS sensor. You should see a voltage reading on the voltmeter display.
- Spin the wheel by hand. The voltmeter should show a voltage reading that fluctuates as the wheel spins. A good ABS sensor typically produces a voltage reading between 50 and 200 millivolts.
- Test the sensor’s wiring. You may have a wiring issue if the sensor’s voltage reading is within the normal range. Use the voltmeter to test the continuity of the sensor’s wiring, checking for any breaks or shorts.
- Repeat the test for each ABS sensor on your vehicle.
How to Test ABS Sensor with Oscilloscope
An oscilloscope can be used to test your anti-lock braking system sensors in greater detail than a multimeter or voltmeter. Here’s how to do it:
- First, locate the ABS sensor you want to test. This will usually be near the wheel hub, on the inside of the wheel well.
- Connect the oscilloscope to the sensor. Attach the oscilloscope leads to the sensor’s two terminals, being careful not to damage the leads.
- Set the oscilloscope to AC coupling. This will allow you to see the sensor’s AC voltage signal.
- Turn on the vehicle’s ignition and rotate the wheel to which the sensor is attached. This will cause the sensor to generate a voltage signal.
- Check the oscilloscope’s display. You should see a waveform representing the sensor’s output signal. A healthy ABS sensor will produce a clean, regular waveform with a consistent amplitude.
- Compare the waveform against a known good waveform. You can usually find these waveforms in your vehicle’s service manual or from an online resource.
- Check for any abnormalities in the waveform, such as noise or distortion. The sensor may be faulty if the waveform looks significantly different from the known good waveform.
- Repeat the test for each ABS sensor on your vehicle.
An oscilloscope can provide more detailed information about your ABS sensor’s performance than a multimeter or voltmeter. However, oscilloscopes can be more expensive and complex to use. You may require some training or experience to operate effectively.
Related Guide: Testing O2 Sensor Guide
How to Check ABS Sensor with Ohm Meter
An ohmmeter can also be used to test your ABS sensor. Here’s how to do it:
- Disconnect the sensor from the vehicle’s wiring harness. This will prevent any electrical interference from other vehicle components.
- Set your ohmmeter to measure resistance. This will allow you to check the sensor’s internal resistance.
- Touch the ohmmeter probes to the two terminals of the ABS sensor. You should see a resistance reading on the ohmmeter display.
- Check the resistance reading against your vehicle’s specifications. The resistance reading should be within the range specified by the manufacturer. If it’s not, the sensor may be faulty.
- Repeat the test for each ABS sensor on your vehicle.
Using an ohmmeter is a straightforward way to test your ABS sensors. However, like other testing methods, it may not be able to detect all types of sensor failures.
How to Test ABS Sensor Specific Parts
How to Test ABS Sensor Wiring
If you suspect a problem with your ABS system, it’s also a good idea to check the wiring that connects the sensors to the vehicle’s electronic control module (ECM). Here’s how to test the wiring:
- Locate the wiring harness that connects the ABS sensor to the ECM. This harness may be buried in the vehicle’s wiring loom, so you may need to consult your vehicle’s service manual to find it.
- Disconnect the wiring harness from the anti-lock braking system sensor. This will allow you to test the wiring separately from the sensor.
- Use a multimeter to test the wiring for continuity. Set the multimeter to measure resistance and touch the probes to the wiring terminals. If the wiring is intact, you should see a low resistance reading on the multimeter display.
- Check the wiring for voltage. Set the multimeter to measure voltage and touch the probes to the wiring terminals. You should see a voltage reading that matches your vehicle’s specifications.
- Check the wiring for shorts. Set the multimeter to measure resistance and touch one probe to the wiring terminal and the other probe to a known ground point on the vehicle. If you see a very low resistance reading, the wiring may have a short circuit.
- Check the wiring for open circuits. Set the multimeter to measure resistance and touch one probe to each end of the wiring. If you see a very high resistance reading, the wiring may have an open circuit.
- Check the wiring for signs of damage, such as frayed or corroded wires, loose connections, or damaged insulation. If you find any damage, repair or replace the affected wiring.
Testing the wiring that connects your ABS sensors to the ECM can help identify problems such as broken wires, poor connections, or corroded terminals. Fixing any wiring problems can improve the reliability and accuracy of your ABS system. If you’re not comfortable working with electrical wiring, it’s best to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician or mechanic.
How to Check ABS Sensor on Trailer
Checking the ABS sensor on a trailer is similar to checking the ABS sensor on a vehicle. Here’s how to do it:
- Locate the ABS sensor on your trailer. The sensor is typically located near the brake assembly on each wheel.
- Inspect the sensor for any damage or corrosion. Look for any physical damage to the sensor or its wiring.
- Check the sensor’s wiring for continuity. Use a multimeter to test the wiring for continuity, just as you would on a vehicle.
- Check the wiring for voltage. Set the multimeter to measure voltage and touch the probes to the wiring terminals. You should see a voltage reading that matches your trailer’s specifications.
- Check the sensor for proper operation. If the wiring is intact and you get the correct voltage readings, you can test the sensor. To do this, rotate the wheel hub by hand and use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s voltage output. You should see a pulsating voltage signal as the wheel hub rotates.
- Check the tone ring. Some ABS systems use a tone ring or tone wheel to generate the signal that the ABS sensor detects. Check the tone ring for damage or missing teeth, which can cause ABS system issues.
By checking the ABS sensor on your trailer, you can ensure your trailer’s braking system is functioning properly. It also keeps yourself and others safe while towing.
Testing your ABS sensor is essential to ensuring that your vehicle’s ABS system is functioning correctly. By following the steps outlined in this blog, you can effectively test your anti-lock braking system sensor using various tools and techniques. Remember, regularly testing your ABS sensor can help keep you safe on the road and prevent potential accidents. Test ABS Sensor today to ensure your safety on the road.
Related Guide: How to Test 3 Wire Crank Sensor with Multimeter
More Question About ABS sensor
-
What is the voltage of an ABS sensor?
The voltage of an ABS sensor varies depending on its type and design. Most ABS sensors produce a signal voltage between 0.5 and 1.5 volts. However, this voltage can increase to 3 volts under heavy braking or when the sensor is faulty. It’s important to consult the manufacturer’s specifications for specific voltage ranges.
-
How to test 2 wire ABS sensor?
To test a 2-wire ABS sensor, you can use a multimeter to measure the sensor’s resistance. The resistance should be between 1,000 and 2,000 ohms. Check the sensor’s wiring and connectors for damage or corrosion. Rotate the wheel to check for a stable AC voltage signal of 50-700mV. Compare readings with specifications from the manufacturer. If there are no issues, the sensor may be functioning correctly. You also use an AC voltage test on the sensor’s signal wire while rotating the wheel. A functioning sensor should generate an AC voltage signal. Of course, these steps should refer to the manufacturer’s production instructions.
-
How many ohms should a wheel speed sensor have?
The resistance of a wheel speed sensor should be between 1,000 and 2,000 ohms. This value may vary depending on the manufacturer’s specifications and the type of sensor used. The resistance can be measured with a multimeter between the two sensor wires. If the resistance is outside the recommended range, it may indicate a faulty sensor or a problem with the wiring or connectors. For specific resistance values, you need to consult the manufacturer’s specifications.
-
Can a car work without an ABS sensor?
The car can work without an ABS sensor. However, the vehicle’s anti-lock brake system will not function properly without ABS sensors. This may cause longer stopping distances and reduced control during braking in slippery conditions. So you need to address any ABS sensor issues promptly to ensure the vehicle’s safe operation.
-
Do ABS sensors have a fuse?
ABS sensors do not have a specific fuse. However, they may share a fuse with other electrical components in the vehicle. In some cases, a blown a fuse may cause issues with the ABS system, including ABS sensor malfunction.
-
How do you reset an ABS sensor?
It’s not possible to reset an ABS sensor. However, the ABS system can be reset using a diagnostic tool, which clears any stored fault codes and recalibrates the system. If the sensor is faulty, it should be replaced to restore the proper functioning of the ABS system. Of course, it is still practical to consult the vehicle’s service manual or a qualified mechanic. They can help you properly diagnose and repair any problems with your ABS system.