Autonomous AI is no longer a distant dream. Significant progress has been made in developing robots that can think for themselves in recent years. With advances in machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision, autonomous AI has become a reality. From self-driving cars to drones that can navigate complex environments, these intelligent machines transform how we live and work.
What is Autonomous AI?
Autonomous AI is a machine that relies on a built-in program to communicate or serve set content. It makes vehicles and other devices perform extended maneuver sequences autonomously without human guidance. Artificial intelligence (AI) can already help us perform many simple tasks. Autonomous AI can do things in the real world without human involvement. Examples include self-driving cars, chatbots, etc.
The National Artificial Intelligence Act of 2020 explains artificial intelligence (AI):
“The term ‘artificial intelligence’ means a machine-based system that can, for a given set of human-defined objectives, make predictions, recommendations or decisions influencing real or virtual environments.”
NATIONAL ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE ACT OF 2020
Self-driving cars are the most familiar. But there are other places researchers use AI to explore vehicle capabilities. As AI advances by leaps and bounds, self-driving AI may take over even more jobs. These include flying planes, delivering cargo, and possibly operating ambulances. Some researchers have also found that autonomous AI may do the job more efficiently and safely than humans.
Autonomous mode AI is more complex than expected. Researchers must develop and build more step-by-step strategies to get more algorithms for more tasks. This is the way to achieve the goal of extending this functionality. We can gain more capabilities through AI than ever before.
Autonomous AI requires strategic thinking. This thinking approach covers many different successful applications of AI. There are many typical examples. Examples include machine vision or speech recognition algorithms. They all focus on a specific moment in time. Users also allow them to access databases and find all the data they may need. To the best of our knowledge, most machine learning applications use a training set of almost all possible outcomes.
These AI autonomous operations require us to imagine potential outcomes that may occur in the future. We must predict the possible problems and set the corresponding course of action. This way, it helps us to cut the chance of danger. It can also improve the speed of the AI and other factors. We could have these AIs learn to play chess. Playing chess is the best training method for both AI and humans.
Many autonomous devices have become good helpers for humans. Digital maps of roads and tools that pass tests are the best examples. We can use them to find the best route to a specific location. The use of sonar sensors and cameras helps people to detect potential dangers.
The History of Autonomous AI
The history of autonomous AI dates back to the 1950s, when the concept of artificial intelligence was first introduced. However, it wasn’t until the 1980s that autonomous robots began to emerge. The first autonomous robot was developed in 1985 by Rodney Brooks, a professor at MIT. This robot, called Genghis, could navigate its environment and avoid obstacles using a simple set of rules. Since then, autonomous AI has continued to evolve, with researchers developing increasingly complex algorithms and machine learning techniques to train these systems. Today, autonomous AI is used in a variety of industries, from self-driving cars to drones and medical devices.
This video presents U.S. Secretary of State Anthony Blinken’s views on artificial intelligence:
How Autonomous Artificial Intelligence Works?
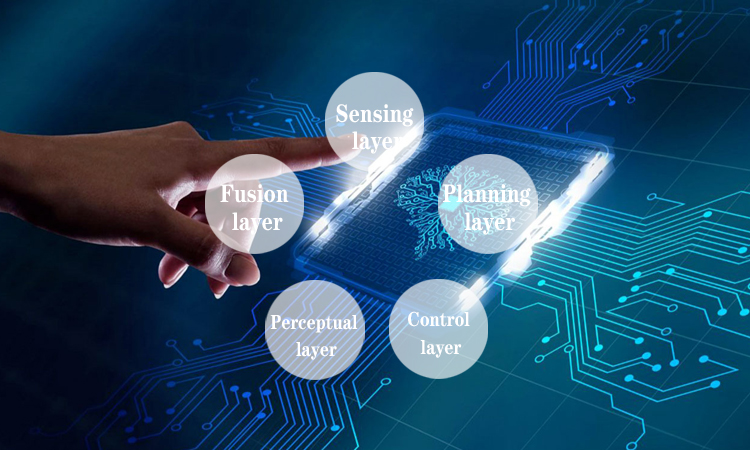
Autonomous artificial intelligence is still a very new field for us. Many researchers are working on refining their algorithms and finding ways to solve problems. We can break down the work of autonomous AI into the following.
- Sensing layer: Sensors are used to build out an ever-changing model of the world. Cameras are often chosen as sensors to study this direction. These cameras are usually still controlled by illumination from lasers or other sources. Researchers can also use these sensors to get location information from GPS or other independent agencies.
- Fusion layer: These details obtained from the various sensors must be organized into a single and complete view. This view must also represent what is happening around the vehicle. While in this, some images may not be visible due to occlusion. Some may not track specific things. They may need to track more consistent information. This is when sensor fusion algorithms are the best way to go. They will classify the details collected from the sensors and build a reliable model. This model can be used in later stages of planning.
- Perceptual layer: The system needs to identify the specific area for which the model has been constructed. Whether a road, a path, or a specific moving object.
- Planning layer: The autonomous AI will study the constructed model to find the best path forward. It also obtains additional information through mapping software, weather forecasts, and traffic sensors.
- Control layer: It also needs to ensure that the motors and steering system are not diverted by any obstacle when it chooses and moves along that path.
The decision information made by the autonomous system AI is transmitted through the top layer of sensors to the control layer. Of course, some feedback loops bring the information back to the top layer through the lower layers. This way, it helps to improve the sensing, planning, and perception layers above.
Autonomous system AI can also bring in data through external sources. Autonomous systems are particularly helpful when two devices communicate with each other. They exchange information in a process called “fleet learning.” And achieve the purpose of information gathering and learning. Sensor fusion algorithms allow devices to use the history of other devices in the same location. It can also help you make more informed decisions. Let’s use the example of detecting moving objects, such as pedestrians. It is challenging to use a few seconds of video to determine the speed or otherwise of a moving object. This is because people may not be moving during that time. But if we use the sensor data to compare with similar images taken earlier in the day. We can easily conclude.
We can also classify these AI autonomous systems. Based on the amount of human interaction required for its operation, it can be classified into the following types.
- Direct interaction computer system: This system can be said to be controlled almost entirely by the operator. We can also call this human-operated process remote operation. This process requires human input to change position, attitude, and state. We commonly see excavators, cranes, and drones operating processes of this kind.
- Operator-assisted robotic applications: Robots require the help of a human operator to perform certain high-end tasks. At the same time, these robots can perform certain activities and make choices. However, these systems require supervised human input before completing the task.
- Fully autonomous systems: This system allows long periods of operation without operator help. It is well suited for use in remote areas where there may be delays, or direct supervision is impossible.
Autonomy vs. AI
The concepts of artificial intelligence and autonomy are completely different in practice. They can be used individually or in concert. You can express the difference between them in the following way.
Artificial Intelligence Autonomy = Artificial Intelligence + Task Completion = Problem Solving
This artificial intelligence with autonomy can be called an autonomous robotic system. You can use them in predictable environments. They help us do tasks in a specific and pre-planned environment. Sensors provide the robot with detailed information about its location. Autonomous robotic systems can perform tasks with the data collected by these sensors. They can be said to bring together all the potential of every artificial intelligence algorithm with which they interact. In addition, we can get the desired autonomous systems and devices by combining traditional software and AI systems. The combination of the two can make them able to learn and adapt on the job.
Yale University has a unique perspective on artificial intelligence. They feel that AI is “systems you can build to solve complex tasks in ways that traditionally need human intelligence.” Traditional AI detects, organizes, and creates some results by ingesting a large number of labeled data. An example is the appearance of a particular car. A video analytics system needs to look at thousands of examples of cars to understand how it looks. And all these results need to be provided and labeled by data analysts and AI engineers.
In general, AI is useful for producing autonomous robotic systems. They are effective tools and techniques for producing that technology. Artificial intelligence automatically performs tasks that are highly analytical and scalable. On the other hand, Autonomous AI performs various actions to produce desired results without the help of humans.
Weak AI vs. Strong AI vs. Autonomous AI
Artificial intelligence can be categorized into three types: weak, strong, and autonomous. Weak artificial intelligence, also known as narrow AI, is designed to perform a specific task or set of tasks. These systems are programmed to follow predefined rules and cannot learn beyond those rules. Common examples of weak artificial intelligence include chatbots, voice assistants, and recommendation algorithms.
In contrast, strong AI is a hypothetical form of AI that can perform any intellectual task that a human can. This type of AI could learn and understand any intellectual concept, just like a human being. While strong AI has existed for decades, we have yet to develop a system that truly meets this definition.
As we discussed earlier, autonomous AI is a type of self-aware AI that can make decisions and act independently without human intervention. It relies on machine learning, deep learning, and other techniques to learn from data and make decisions based on that learning. Autonomous AI is already used in various industries, from self-driving cars to manufacturing.
One of the key differences between weak AI and strong AI is their level of flexibility. Weak AI is programmed to perform specific tasks, and while it may be able to learn from experience, it cannot adapt to new situations without being reprogrammed. Strong AI, on the other hand, could learn and understand any new task or concept, just like a human.
Autonomous AI is a form of strong AI, as it can learn and adapt to new situations without being specifically programmed for them. However, it is important to note that autonomous AI is still limited by its programming and the data it has been trained on.
While weak AI and strong AI have their own unique applications and challenges, autonomous AI is the most relevant and practical form of AI for the foreseeable future. It can potentially revolutionize industries and change how we live and work, but it also raises important ethical concerns that must be addressed.
Applications of Autonomous AI
Autonomous AI has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries, and its applications are already being explored and implemented in various ways. One of the most prominent applications of autonomous AI is in the field of transportation. Self-driving cars are already being developed and tested to reduce accidents and improve traffic flow.
Autonomous AI is being used in the manufacturing industry to improve efficiency and productivity. Robotic systems can perform repetitive tasks with a high degree of accuracy and work around the clock without getting tired. This can help reduce costs and increase output.
The healthcare industry is also exploring the use of autonomous AI, particularly in medical imaging. AI systems can analyze medical images with a high degree of accuracy, helping to detect diseases and injuries earlier and more accurately.
In finance, autonomous AI is used to analyze financial data and make investment decisions. This can help investors make better decisions based on data-driven insights.
In the military, autonomous AI systems can be used for reconnaissance and surveillance and for planning and executing complex operations. Autonomous AI can control rovers and other equipment on remote planets in space exploration.
Autonomous AI has potential applications in education, entertainment, and even art. For example, AI-generated music and art are already being created and could become more sophisticated with the development of autonomous AI.
Autonomous AI has Limitations

Autonomous AI is still a relatively young technology and depends upon the accuracy of the data it is fed. The machine’s decision-making and behavior can be compromised if the data is corrupted or inaccurate. Additionally, machines may not be able to “think outside the box” as much as humans, and there may be certain scenarios where a human perspective is needed. Finally, some believe that autonomous AI technology has the potential to lead to job replacement. This is because you can use machines to replace certain human jobs.
These AIs capable of being independent of human guidance are unsuitable for all applications. This is because some applications need help to quantify the best results. In this case, AI is suitable to act as our automatic advisor. Because we also need to consider those intangible factors when we perform this task. We also need to be accountable for the decisions we make. So it would be easy for accidents to happen in this if it were all performed autonomously by AI. After all, it always makes decisions based on facts without considering the consequences we must bear.
The Ethics of Autonomous AI and Its Impact on Society
As autonomous AI becomes more prevalent, ethical concerns about its impact on society are being raised. One of the major concerns is job displacement, as many industries are beginning to replace human workers with autonomous robots. Additionally, there are concerns about the potential for these systems to malfunction or make decisions that go against human values or ethics. For example, what decision will it make if an autonomous vehicle faces a situation where it must choose between hitting a pedestrian or swerving off the road and potentially harming its passengers? These complex ethical questions must be addressed as autonomous AI continues to advance.
With the above, you have a better understanding of autonomous artificial intelligence. Advances in artificial intelligence have a positive impact on us. You can use autonomous artificial intelligence systems for boring, dangerous, and dirty jobs. This way, you can spend more time on the work that is necessary for you.
If you want to learn more about machine learning, you can read:
Artificial Intelligence Glossary
Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI that involves training algorithms to make predictions or decisions based on data.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI): The hypothetical future development of AI that could exhibit human-like intelligence and reasoning abilities.
Deep Learning: A type of ML that uses neural networks with multiple layers to extract increasingly complex features from data.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): A branch of AI that enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
Neural Network: It is a set of algorithms modeled after the structure of the human brain used to recognize patterns in data.
Predictive Analytics: It refers to the use of statistical models and machine learning algorithms to analyze data and predict future events or trends.
Robotics: It is a branch of AI that deals with robot design, construction, and operation.
Supervised Learning: This is a type of ML that involves training a system on labeled data to predict outcomes for new, unlabeled data.
Computer Vision: A branch of AI that enables machines to interpret and analyze visual information from the world around them.
Singularity: A hypothetical point in the future when AI surpasses human intelligence and becomes capable of self-improvement beyond human control.
Cognitive Computing: A branch of AI that focuses on building systems that can understand and reason like humans.
AI Safety: The field of research focused on ensuring that advanced AI systems remain safe and beneficial for humans as they become more capable and autonomous.
Explainability: The ability of an AI system to provide clear and understandable explanations for its decision-making processes.
Ethics in AI: A growing field that addresses the ethical implications of AI development and deployment, including issues related to bias, privacy, and human autonomy.
Singularity: A hypothetical point in the future when AI surpasses human intelligence and becomes capable of self-improvement beyond human control.
Transparency: The degree to which an AI system’s decision-making processes are visible and understandable to human users.
Data Mining: The process of discovering patterns and insights in large datasets using machine learning algorithms.
Machine Perception: The ability of machines to interpret and understand sensory input from the world around them.







