The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is gradually changing healthcare today. IoMT devices are changing how we track, diagnose, and treat patients. IoMT allows doctors and patients to track and trace health data in real-time. This allows them to improve outcomes and increase efficiency. However, with these benefits come risks, such as privacy and security concerns. This blog will explore the world of IoMT devices, their benefits, and their challenges. And their potential impact on the healthcare industry.
What is the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)?
The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) refers to internet-connected medical devices and healthcare applications. It is also called the healthcare Internet of Things. It is a specialized subset of the Internet of Things (IoT) tailored for the healthcare industry.
IoMT devices enable machine-to-machine communication that can remotely track patients in their homes. This practice, also known as telemedicine, can spare patients from traveling to a hospital or physician’s office.
While IoT devices are primarily designed for consumer use, enhancing convenience and usability. However, IoMT solutions are targeted at healthcare providers and patients. Examples of IoMT include:
- Smart thermometers and insulin pumps for diabetes management.
- Remote patient monitoring devices to track health metrics from home.
- Personal emergency response systems for seniors or high-risk patients.
- Wearable sensors and monitors for measuring heart rate, oxygen levels, or glucose.
- Ingestible sensors and cameras for diagnosing issues in the gastrointestinal tract.
- Medical equipment like MRI machines with internet connectivity.
IoMT can improve patient engagement and enhance monitoring. It can also streamline data sharing between physicians and customers. It transforms healthcare by making medical services more personalized, precise, and preventative. By harnessing the power of IoT and technology, IoMT delivers smarter, optimized care at lower costs.
Types of IoMT Devices
IoMT encompasses connected medical technologies categorized as in-home, wearable, mobile, public, or in-hospital solutions. Each provides insights and capabilities supporting optimized care, monitoring, management, and access.
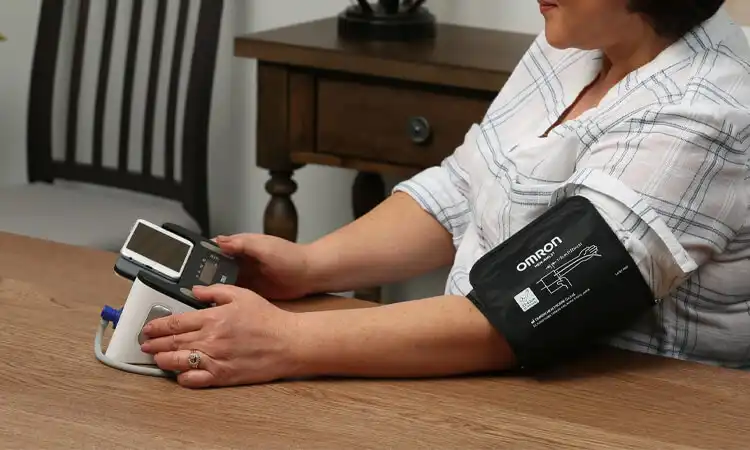
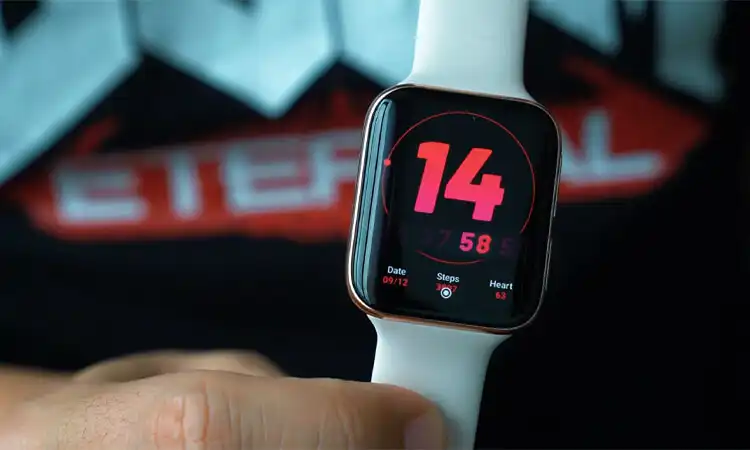


In-home IoMT
In-home IoMT devices refer to those placed in patients’ homes to track health. These devices are used to track health and well-being or alert caregivers in case of an emergency. This includes:
- Personal emergency response systems. They detect medical issues and alert local hospitals for help.
- Remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices for managing chronic conditions at home.
Wearable IoMT
Wearable IoT technologies, as we also call them, are on-body IoMT. They are attached to the patient’s body and record medical information about the patient in their daily work. These devices include:
- Consumer smartwatches and fitness trackers. These devices measure health metrics like heart rate and glucose for wellness tracking.
- Medical-grade wearable devices used under the supervision of a physician. Common examples include neuromodulation devices that manipulate the nervous system to reduce pain.
- Ingestible sensors or “smart pills” reading information inside the body.
Mobile IoMT
Mobile IoMT uses mobile technology to connect and control other IoT devices. Patients can control web-connected glucose monitors through a mobile app and interface. They can also share data with their doctors.
Public IoMT
Public IoMT, or community IoMT, includes dispersed devices. They can improve healthcare in remote areas where traditional facilities are not available. For example, point-of-care kiosks provide medical supplies and basic services.
In-hospital IoMT
In-hospital IoMT facilitates patient care through internet-connected devices and systems. This includes:
- Infusion pumps integrated with analytics dashboards for optimized management.
- Hospital beds with sensors measuring vital signs like heart rate, oxygen levels, and respiration.
- RFID tags are used to track the location/distribution of medical equipment, patients, and staff. People can use this location information for inventory, management, and wayfinding.
How Does IoMT Impact Healthcare?
IoMT provides huge volumes of health data to inform better patient and provider decisions. It generates data from various interconnected sources. It collects and shares information faster than traditional modes. More comprehensive data support optimized care.
MIoT technology enables devices, networks, and infrastructure to deliver telehealth services. This technology provides more options for telemedicine and virtual care. These capabilities became crucial during the COVID-19 pandemic to limit facility visits. It reduces stress on overburdened hospitals and continues treating patients safely.
Telemedicine expands access to care for underserved populations. It provides patients with greater access to specialists and quality care. This approach allows them to be unrestricted by location or distance from a brick-and-mortar medical facility. This includes:
- Rural and remote communities. Telemedicine makes it easier for people far from urban or medical centers to get medical help.
- Specialty care. Telemedicine offers the opportunity to consult with specialists. This allows patients to receive impossible care with limited time or mobility.
- Chronic disease management. For chronic illnesses like diabetes, heart disease, or mental health conditions, telemedicine enables more frequent monitoring, education, and change of treatment plans as needed between in-person visits.
- Emergency or urgent care. Telemedicine can be utilized for an initial assessment when an urgent issue arises. They can determine if the patient really needs to be seen in the emergency room. Physicians can also determine if they can adequately address the problem remotely. In this way, overuse of emergency services can be avoided.
Related Articles: Telemetry Unit in a Hospital
Benefits of IoMT in Healthcare
As a key component of the telemedicine infrastructure, IoMT technology offers us the following advantages:

- Patient monitoring. IoMT enables continuous tracking of health metrics and chronic conditions. They keep physicians informed about the well-being and living conditions of their patients. This allows care to be more closely managed.
- Accessibility. IoMT expands access to healthcare services through telehealth and remote options. Patients have greater flexibility and choice in how and where they receive care.
- Cost efficiency. IoMT reduces costs by minimizing in-person facility visits when possible. RPM and telehealth lower overhead while improving workflow efficiency. This frees up their resources to focus on complex care.
- Enhanced experience. IoMT offers new self-service technology options and a streamlined process. This enables patients to have a superior experience. Connected health devices give patients better access and control over their health data and health status.
- Data accuracy. IoMT provides data-rich insights through connected monitoring solutions. Many days of indicators exceed the snapshot of a single visit. This approach allows physicians to identify changes early and develop the best treatment plan.
- Logistics optimization. IoMT supports smart tracking of healthcare facilities’ equipment, supplies, patients, and staff. This reduces errors and decreases waste. This allows them to improve overall operations through alerts and data-driven process optimization.
Challenges of IoT in Healthcare
IoMT technologies provide opportunities for enhanced patient monitoring and logistics optimization in healthcare. However, their application also introduces several important questions that must be addressed.
- Complex implementation. Integrating IoMT solutions requires interoperability and standards compliance between connected devices. This is to enable seamless data sharing and conversion between care environments. Such complex implementations tend to be more costly and difficult.
- High upfront investment. The initial technology and integration investments required for IoMT can be quite high. Realizing a return on investment may take time through reduced spending and financial benefits. Ongoing costs also include maintenance, security, and management of IoMT infrastructure.
- Security and privacy risks. IoMT introduces security and privacy risks due to the sensitive health information transmitted and stored digitally. There is a high threat of hacking, data breaches, fraud, and medical services or controlled substance theft. Compliance with regulations like HIPAA also increases liability and penalties. Robust security is essential but adds to implementation and maintenance costs.
- Unclear data ownership. It is unclear if IoMT data belongs to patients, technology companies, healthcare providers, or others. Differing perspectives introduce complexity, limiting data sharing and use. Policies and consent are needed but challenging to establish.
- Blurred data classification. IoMT generates varied health data, blurring lines around what qualifies as medical information. AI and analytics also produce “emergent medical data” from non-health sources. Regulations have not fully adapted, creating governance issues.
- Suboptimal user experience. Medical devices and applications must be intuitive and easy to use for patients to willing and able to collect data properly. Poor usability leads to limited, flawed, or missing information, reducing the potential benefits of IoMT. Simplicity is important but difficult to achieve, given technical capabilities.
IoMT vs. IoT: What is the Difference between IoMT and IoT?
IoT refers to connected digital devices that communicate autonomously over a network. They gather and share data using sensors without human intervention. IoT examples include:
- Smartphone sensors detect motion and location, communicating with surrounding devices.
- Smart thermostats measure and regulate the temperature in buildings.
- Smart home devices like sensors, motion detectors, and smart locks.
- Moisture sensors help farmers direct irrigation to crops needing water.
IoMT comprises IoT technologies applied to healthcare. IoMT enables medical devices to connect over networks autonomously. Then, they can collect and transmit patient data to providers with limited direction.

Key differences between IoT and IoMT include:
- Purpose. IoT supports general data collection and automation. IoMT focuses on healthcare, monitoring patients, and facilitating virtual care.
- Sensitivity. IoMT handles sensitive health information, requiring extra security, privacy, and compliance considerations.
- Medical expertise. IoMT solutions are designed for medical use under professional guidance. IoT applications range widely and often target consumer or commercial use cases.
- Regulations. IoMT must adhere to healthcare regulations like HIPAA. It exceeds regulatory requirements for general IoT technologies.
- Examples. Representative IoMT devices include patient monitors, medical wearables, remote diagnostic tools, and kiosks. IoT examples outside of healthcare include smart home devices and utility meters.
Here is a table outlining some of the key differences between IoT and IoMT:
| Criteria | IoT | IoMT |
|---|---|---|
| Domain | General-purpose | Healthcare-specific |
| Purpose | Improving efficiency and automation | Improving healthcare outcomes |
| Devices | Smart home devices, wearables, etc. | Medical devices, sensors, and wearables |
| Data types | Non-sensitive data (e.g. temperature) | Sensitive health data (e.g. vital signs) |
| Data privacy | Important but not as critical as IoMT | Critical due to sensitive health data |
| Security | Important but not as critical as IoMT | Critical due to potential harm to patients |
| Interoperability | Important but not as critical as IoMT | Critical for seamless patient monitoring |
| Regulatory compliance | Generally less regulated than IoMT | Strictly regulated |
| Use cases | Smart homes, transportation, etc. | Remote patient monitoring, medical imaging |
| AI integration | Important but not as critical as IoMT | Critical for data analysis and insights |
| Healthcare expertise | Not required | Required for effective implementation |
The Future of IoMT Devices
The COVID-19 pandemic hastened telehealth adoption and the growth of connected medical technologies like IoMT. The number of IoMT devices is projected to continue increasing rapidly.
Advancing IoT will drive IoMT innovations, integrating new capabilities into connected health solutions. For example, improved sensors will provide more/higher-quality real-time patient data. AI and machine learning will enhance predictive, preventative care using IoMT insights.
IoMT data will enable improved research, discovering new treatment options. IoMT and AI can simplify management and reduce costs. They can boost collaboration across healthcare organizations through data sharing and insights.
Some key areas shaping the future of IoMT include:
- Precision medicine. IoT and AI will enable precision care tailored to individuals, made possible by huge amounts of patient data. Treatments can be customized to a person’s genetics, environment, lifestyle, etc.
- 5G networks. Faster 5G wireless networks will improve IoMT reliability, responsiveness, and capability. This facilitates new virtual reality applications for surgery, counseling, or rehabilitation.
- At-home monitoring. IoMT implants, wearables, and AI will allow continuous at-home monitoring for chronic disease management or recovery. Home can become an extension of the hospital.
- Automation. IoMT and AI will automate many medical tasks, optimizing workflows. It frees professionals to focus on higher-level care. Robots assist with surgeries, deliver medications or track patients.
- Public health. IoMT will enhance large-scale public health monitoring and rapid detection of outbreaks. It can make smarter allocation of resources. Sensors track air/water quality, the spread of diseases, the availability of supplies, etc.
The Internet of Medical Things enables precision, automation, and insight. Though complex, IoMT’s promise is transforming health systems. By anticipating challenges while advancing innovation, IoMT can realize sustainable benefits: optimized care. It can access all, cost control, and wellness at scale. The future of medicine is connected, personalized, and data-driven.
General Q&A About Internet of Medical Things
-
How does IoMT work?
IoMT connects medical devices, sensors, and applications to the internet. It allows for real-time data collection and analysis. This data can then be used to improve patient care and outcomes.
-
How is patient data protected in IoMT?
Patient data is protected in IoMT through various measures. These include encryption, access controls, and network security protocols.
-
How is IoMT being used in remote patient monitoring?
IoMT is used in remote patient monitoring to enable healthcare professionals to track patients from a distance. It reduces the need for in-person visits and improves patient outcomes.
-
How does IoMT affect healthcare professionals?
IoMT can affect healthcare professionals by giving them more data to make informed decisions. It can improve communication and collaboration and increase efficiency.
-
How does IoMT affect patient privacy?
IoMT can affect patient privacy by collecting and sharing sensitive health information. However, measures such as data encryption and access controls can mitigate these risks.
-
How does IoMT fit into the larger healthcare ecosystem?
IoMT is a key component of the larger healthcare ecosystem, enabling the collection and sharing of healthcare data. It can help doctors improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.