Are you looking for a way to improve your supply chain management? If so, you may be interested in learning about Electronic Product Code. This standardized identification system uses RFID technology to track and trace products throughout their lifecycle in the supply chain. With EPC, businesses can gain real-time visibility into the movement of goods, which has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management. In this article, we’ll cover the basics of EPC, including what it is, how it works, and the benefits it offers to businesses.
What is an Electronic Product Code?
The Electronic Product Code (EPC) is a unique identifier that tracks physical objects in the supply chain. It is a code assigned to a specific product and used to identify and track that product throughout its lifecycle. EPC is a standard used in RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology, which tracks and manages inventory in the supply chain.
The EPC system comprises three main components:
- EPC Tag: A small electronic device attached to a physical object. It contains a unique identifier that can be read wirelessly using an RFID reader.
- RFID Reader: A device that reads the EPC tag wirelessly and communicates the information to a computer system.
- EPC Middleware: A software system that manages the EPC data and communicates with other enterprise systems.
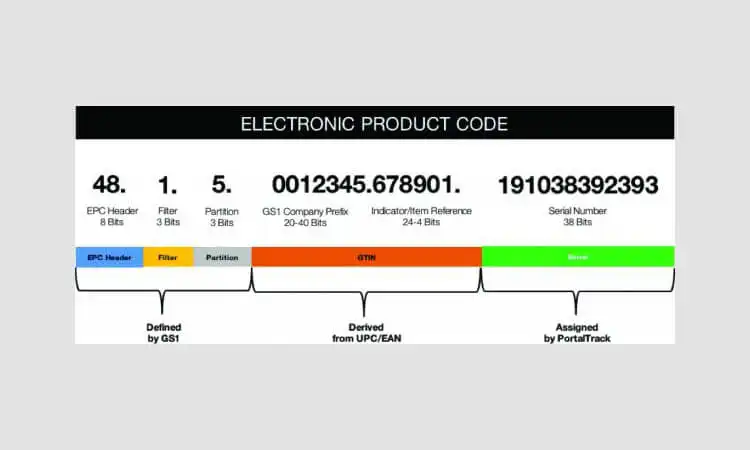
Here is an example of an Electronic Product Code:
urn:epc:id:sgtin:0614141.107346.2018
This EPC is composed of several parts:
urnis the Uniform Resource Name prefix, indicating that this is a standardized identifier.epcis the identifier scheme, indicating that this is an Electronic Product Code.idis the scheme-specific identifier, indicating that this is a unique identifier for a specific product.sgtinis the scheme used for identifying trade items and logistics units, indicating that this identifier is for a specific trade item.0614141is the GS1 Company Prefix assigned to the company that owns this trade item identifier.107346is the unique item reference assigned by the company to this specific trade item.2018is the manufacturing date of the trade item in the format of YYYY.
Overall, this EPC uniquely identifies a specific trade item, including information about the company that owns it and its manufacture date.
EPC GS1 Keys
EPC GS1 Keys are an important aspect of RFID technology. Each object with an RFID tag is assigned a GS1 key that corresponds to its class of object. The GS1 key serves several functions, such as assigning and managing keys, defining data structures, and providing context for the EPC data.
If you’re interested in learning more about the different types of EPC GS1 keys and their specific uses, here are some examples:
- GDTI (Global Document Type Identifier) is used for identifying documents.
- GSRN (Global Service Relation Number) is used to identify services.
- GTIN (Global Trade Item Number) is used for identifying trade items.
- GRAI (Global Returnable Asset Identifier) identifies returnable/reusable assets.
- GLN (Global Location Number) is used for identifying locations.
- SSCC (Serial Shipping Container Code) is used for identifying logistical units.
- GIAI (Global Individual Asset Identifier) is used for identifying fixed assets.
What is the Format of the Electronic Product Code?
The Electronic Product Code has a specific format that consists of four parts: header, EPC manager number, object class, and serial number. The header is an 8-bit number that indicates the EPC’s length, type, structure, version, and partitioning scheme. The EPC manager number is a 28-bit number that identifies the manufacturer or company that produces the product. The object class is a 24-bit number identifying the product type, while the serial number is a variable length number uniquely identifying each product instance.
How does EPC Work?
The EPC is made up of a unique identification number that is assigned to a product. The number is stored in an RFID tag attached to the product. The RFID tag contains an antenna and a microchip that stores the EPC number. When an RFID reader scans the RFID tag, the EPC number is transmitted to the reader, sending the information to a computer system. The computer system can then use the EPC number to identify the product and track its movement through the supply chain.
EPC uses a hierarchical structure to assign identifiers. The structure consists of three parts:
- Header: This identifies the type of EPC being used.
- Object Class: This identifies the type of object being tagged, such as a product or asset.
- Serial Number: This is a unique identifier assigned to each object.
Benefits of EPC
EPC offers several benefits to businesses and consumers alike. For businesses, EPC provides a more efficient and accurate way to manage inventory and track goods throughout the supply chain. This can lead to cost savings, improved productivity, and better customer service.
For consumers, EPC can help ensure the authenticity and safety of products. By tracking items from production to sale, EPC can help prevent counterfeit goods from entering the supply chain, as well as identify and remove products that may be unsafe or defective.
EPC and Sustainability
In addition to its operational benefits, EPC can also play a role in promoting sustainability. EPC can help reduce waste and prevent overproduction by providing more accurate tracking of goods. It can also help identify areas for improvement in the supply chain, such as reducing transportation emissions or improving packaging efficiency.
EPC and Privacy
One concern with EPC is privacy. Because EPCs are unique identifiers, they can be used to track individuals and their movements. To address this concern, the EPCglobal organization has developed a set of privacy guidelines for EPC use. These guidelines include:
- Providing notice to individuals about EPC use
- Obtaining consent from individuals for EPC use
- Limiting the use of EPC data to specific purposes
- Providing individuals with access to their EPC data
- Ensuring the security of EPC data
Examples of EPC Applications
The EPC is used in various industries, including retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and logistics. Here are some examples of EPC applications in these industries:

Retail
EPC can be used to track inventory levels, reduce out-of-stock, and improve the shopping experience for customers. Retailers can use EPC to monitor product availability in real-time, ensuring that popular items are always in stock. This can help improve customer satisfaction and increase sales.
Healthcare
In healthcare, EPC is used to track medical devices, drugs, and other assets, ensuring they are available when needed and reducing waste. By using EPC to monitor the location and status of medical equipment, hospitals can improve patient care and reduce the risk of equipment shortages.
Manufacturing
EPC can be used to track raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods, improving production efficiency and reducing waste. Manufacturers can use EPC to monitor the flow of materials and products through the supply chain, identifying bottlenecks and optimizing production processes.
Logistics
EPC is used in logistics to track and manage shipments, reduce theft and loss, and improve supply chain visibility. Logistics companies can use EPC to monitor the location and status of shipments in real time, ensuring that products are delivered on time and in good condition. This can help improve customer satisfaction and reduce costs.
How do I Get an Electronic Product Code?
You must follow their established standards if you want an Electronic Product Code from GS1. This includes having a Universal Product Code (U.P.C.) and a unique serialized item identifier. The U.P.C. comprises a U.P.C. Company Prefix, an Item Reference Number, and a Calculated Check Digit. A globally unique EPC is created when combined with a unique serial number. If you’re unsure how to choose a unique serial number, GS1 provides a helpful resource called the Developing an RFID Serialization Plan document. This document outlines common serialization solution approaches and can guide you in selecting the best option for your needs.
Electronic Product Code is a powerful tool for improving supply chain efficiency, ensuring product safety and authenticity, and promoting sustainability. As businesses look for ways to optimize their operations and meet consumer demands, EPC will likely play an increasingly important role in the coming years.
Science
What is an EPC GS1?
If you’re looking to assign unique identification numbers to physical objects like products, cases, and pallets in your supply chain management system, EPC GS1 (Electronic Product Code Global Standard 1) is a set of standards you should consider. Developed by GS1, a global organization that maintains supply chain management standards, EPC GS1 uses RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) technology to assign these unique identification numbers. If you’re writing code, you can implement EPC GS1 using the language of your choice; just make sure to include the appropriate libraries and functions.
What is OEM?
OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. This means an OEM company designs and manufactures parts or equipment used in another product. Regarding RFID technology, OEM companies may produce RFID tags or readers used by other companies to implement EPC-based tracking systems. For example, a company that produces RFID tags may sell them to a retail company that wants to track inventory using EPC technology.