RFID technology has become pervasive in our daily lives, found in transportation cards, key cards, and credit cards. However, many people lack a comprehensive understanding of RFID cards and their significance in safeguarding information and property. In this article, we will delve into the world of RFID cards, exploring their features, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and security measures.
What is an RFID Card?
RFID cards, typically in the size of a wallet, contain an embedded intelligent chip. These cards offer cardholders a means to authenticate their identity by connecting with a card-authenticated security device. Although commonly associated with debit or credit cards, RFID cards have various applications and are experiencing significant growth in adoption. According to Thales Group’s MarketsandMarkets report, over 30 billion RFID cards are currently in circulation, with the market predicted to reach $21 billion by 2023.
RFID Card Size: Standard Sizing and Custom Options
If you’re looking to use RFID cards for your business or organization, you must know their standard dimensions. TThe “standard credit card” is the most prevalent size, adhering to the ID-1 or CR80 specification outlined by the International Organization for Standards (ISO/IEC 7810). RFID cards typically measure 85.60 by 53.98 millimeters (3 3⁄8″ × 2 1⁄8″) with rounded corners. RFID cards come in a range of thicknesses, typically from 0.5mm to 1mm. These depends on the production process and the specific requirements of the customer. While the standard size works for most applications, customized dimensions are also available for those needing a different size or shape.

RFID Card-Based Materials
RFID cards are used in various applications, but have you ever wondered what materials are used to make these cards? The most common base materials for RFID cards are plastic polymers, particularly PVC and PET, because of their durability, flexibility, and heat resistance.
However, growing concerns about plastic waste and environmental impact have led to exploring alternative base materials for RFID cards. Biopolymers and non-plastic materials, such as wood, are potential options for eco-friendly card production.
For example, some companies have introduced wooden RFID cards to the market, but higher production costs have limited their use in niche applications. Nevertheless, as demand for sustainable materials increases and technology advances, we may see more affordable options for innovative RFID card-based materials in the future.
RFID Card Working Principle
The working principle of an RFID card relies on an integrated chip that encrypts data when connecting to a source. It’s not the same as swiping a card. RFID cards are contactless in the process of payment. Cardholders can pay quickly by simply tapping or waving their hands.
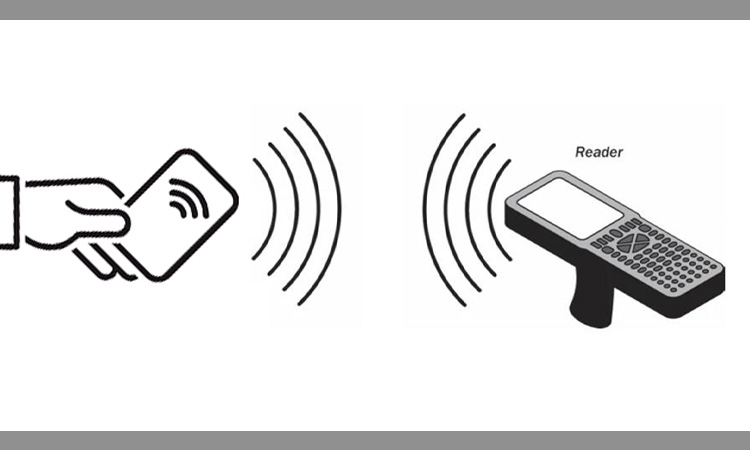
RFID cards can transact by entering the electromagnetic field range of the card reader. Payment details are transmitted to the merchant via radio waves. It promotes consumption and dramatically reduces the time consumers spend waiting to pay.
The popularity of COVID-19 also gives consumers and employees excellent security.
Types of RFID Cards
RFID cards can be categorized based on their communication frequency bands:

- Low Frequency (LF) RFID Card: Operating at 125 KHz, LF cards offer higher security with a shorter reading range, making them suitable for access control and identification purposes.
- High Frequency (HF) RFID Card: Utilizing a frequency of 13.56 MHz, also used in Near Field Communication (NFC), HF cards are commonly seen in bus passes, access control systems, and contactless payment cards.
- Ultra High Frequency (UHF) RFID Card: With a greater read range, UHF cards enable access from a distance, making them useful in applications such as toll booths, parking lots, and gated communities.
Furthermore, RFID cards can be divided into ID cards and IC cards based on the chip inside. ID cards serve access control purposes, containing only an ID number. In contrast, IC cards store value and offer security functions, commonly used for transit swipes, credit and debit cards, and more.
RFID Card Applications – Credit Cards
RFID credit cards, employing RFID technology for secure payment, allow cardholders to complete transactions without physically swiping or inserting the card into a reader. The RFID chip wirelessly transmits payment information to the reader, aligning with the EMV Contactless Communication Protocol Specification (EMV CCPS) used in Near Field Communication (NFC). This contactless payment method offers convenience, requiring only a card wave. It is important to note that banks impose transaction limits on RFID credit cards, typically up to $50 per transaction.
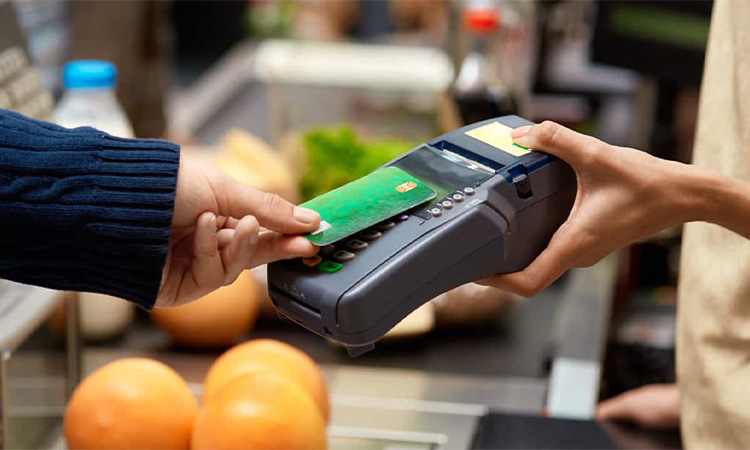

Many contactless payment technologies in real life use RFID. They include contactless payments like MasterCard’s PayPass and Visa’s payWave.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RFID Credit Cards
RFID cards are faster, more convenient, and more secure than regular chip and signature cards. It offers the same high level of payment protection as the other two types of cards.
We can also tie it to a smartphone. The cardholder can view payment history, deactivate it, and perform other operations from a specific cell phone. Especially its convenient transaction method of click-and-pay is convenient for people to travel. It can transact without touching, reducing the transfer of bacteria.
It also has a pronounced disadvantage. Criminals can steal cardholder information with the help of specific tools. These tools may be non-contact card data applications or RFID readers. However, this feasibility is very low, but not impossible to happen.
Are You Afraid of Losing RFID Card Information?
One of the significant RFID crimes in 2022 is RFID skimming. It mainly uses the RFID scanner to get close to you to complete the skimming behavior. It is easy and fast for criminals to use scanning technology to collect information on RFID microchips.
Usually, the theft of information is not smooth. Because It can’t get that close to you, the card reader must be within a few feet of the credit card to read the information. But in a crowded situation, anything is possible. In a crowded train or bus station, it’s easy for criminals to get close to you.
Fortunately, there is a limit to the amount of information they can access. The information criminals may obtain from an RFID credit card chip includes the card number and expiration date. The three security numbers on the back of the card are not accessible. It means that criminals are limited in what they can do.
Securing RFID Cards
RFID cards are usually used in conjunction with a reader, and while RFID cards are easy to obtain, so is a reader. If someone is close enough to your card with a reader, it is easy to steal your payment information.

It is not so easy to steal success. The RFID card has a built-in protection function, significantly reducing the chance of being stolen. It may also mean that these RFID cards are as secure as the new EMV chips.
It is secure in two main ways. The first is proximity. It must be very close to the reader to transmit the information. You must tap or wave your card near the scanner to communicate. The second is the built-in protection feature. Your transaction code is one-time and can only use for unique transactions. It means that if bad actors try to take large sums of money from your account or access your personal information, it will be challenging to do so.
Of course, in addition to these built-in protection features. You also have several external protection options available.
Here are a few measures that can help strengthen the security of RFID cards:
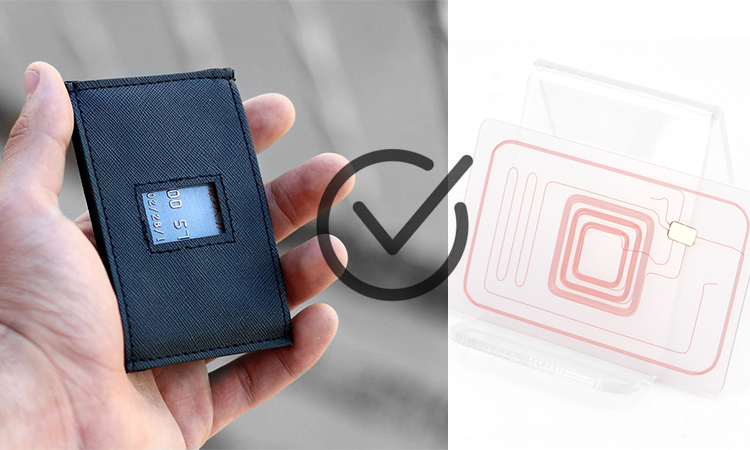
- RFID-shielded wallets: These wallets have unique linings that block radio wave transmissions, often using materials like carbon fiber. They provide an effective shield for RFID cards, preventing unauthorized reading until the card is removed from the wallet.
- RFID jamming cards or devices: These credit card-sized devices actively emit RFID signals, interfering with any attempts to steal information from your RFID card.
- Foil shield: A low-tech and cost-effective method involves wrapping the RFID card with aluminum foil, which interferes with most electronic signals, providing an added layer of protection.
Choosing the Best RFID Shielding Technology
Information security is always the focus of attention. There are many shielding products on the market, but their technology is not all the same.

There are two main types of RFID shielding technology: passive and active.
A passive RFID shield is like a shield rooted in front of your RFID technology. It mainly absorbs or reflects the sudden incoming RFID signals from the outside world. Active RFID shield has a microchip embedded in its body. It will actively disrupt incoming radio waves from the outside world. It will interfere with the scanner’s proceeding.
When selecting RFID shielding products, consider the following factors:
- Active interference capability with external signals.
- Appropriate size to accommodate the RFID card.
- Trustworthy manufacturer.
- Battery-free operation.
- Compatibility with NFC and RFID signals.
RFID cards are increasingly prominent in various aspects of our lives, offering convenience and security in applications like access control and contactless payments. Understanding their features, working principles, and security measures allows us to make informed decisions and protect our information effectively. As the technology evolves, we can expect further innovations and advancements in RFID card-based materials and security technologies.
General Q&A About RFID Card and RFID Credit Card
-
What is an RFID card?
An RFID card is a type of plastic card that contains an embedded radio frequency identification (RFID) chip.
-
How does an RFID card work?
An RFID card uses electromagnetic fields to communicate and transfer data between the card and a reader.
-
What is an RFID credit card?
An RFID credit card is a credit card that contains an RFID chip, allowing for contactless payments.
-
How does an RFID credit card work?
An RFID credit card works by using radio waves to transmit data between the card and a reader. The card is held near the reader, and the payment is completed without physical contact.
-
What are the benefits of an RFID credit card?
The benefits of an RFID credit card include convenience, speed, and ease of use for contactless payments.
-
How secure are RFID credit cards?
RFID credit cards are generally secure, but there have been concerns about the potential for unauthorized access through skimming or hacking.
-
How do I know if my credit card has an RFID chip?
You can check if your credit card has an RFID chip by looking for the symbol that indicates contactless payments, such as the Wi-Fi symbol.
-
What is the difference between an RFID card and a magnetic stripe card?
An RFID card uses radio waves to communicate data, while a magnetic stripe card uses a magnetic stripe to store and transfer data.
-
Which is more secure, an RFID card or a magnetic stripe card?
RFID cards are generally considered more secure than magnetic stripe cards because they use encryption to protect the data on the card.
-
What are some common uses for RFID cards?
Common uses for RFID cards include access control, transportation, inventory management, and payment processing.
-
Can RFID cards be reused?
Yes, RFID cards can be reused if they are not damaged or disabled.
-
How long do RFID cards last?
RFID cards can last for several years or more, depending on the quality of the card and how often it is used.
-
What do I do if my RFID card stops working?
If your RFID card stops working, you can contact the card issuer to request a replacement.
-
Can I use my RFID credit card overseas?
Yes, you can use your RFID credit card overseas if the card is accepted by the payment network in the country you are visiting.










