La scienza e la tecnologia si stanno sviluppando e gli esseri umani stanno progredendo. Con la ricerca approfondita sull'RFID, l'uso dell'RFID ha effettivamente migliorato la vita delle persone. Oggi, i prodotti sviluppati dalla tecnologia RFID possono essere trovati ovunque nella vita quotidiana delle persone. Quindi sai cos'è l'RFID e quali sono i suoi migliori usi nel mondo degli affari?
Che cos'è l'RFID?
RFID è l'acronimo di Radio Frequency IDentification. È un tipo di tecnologia di identificazione automatica e raccolta dati. Raggiunge la comunicazione dati bidirezionale senza contatto attraverso segnali elettromagnetici. Utilizza la radiofrequenza per identificare un target specifico (tag elettronico o scheda a radiofrequenza) per lo scambio di dati. È diverso dal normale codice a barre. Non è necessario che sia sempre attaccato alla superficie dell'oggetto da tracciare. Le persone possono incorporarlo nel suo corpo. È più efficiente di utilizzando un codice a barre. Utilizzando un lettore è possibile leggere centinaia di etichette RFID alla volta.
La tecnologia RFID è diventata uno strumento essenziale per le aziende che richiedono un tracciamento efficiente dei prodotti. Sono disponibili principalmente due tipi di lettori RFID: fissi e mobili.
I lettori RFID fissi sono generalmente installati in un luogo specifico, ad esempio un magazzino. Catturerà i dati dei tag RFID mentre passano attraverso la zona RF del lettore. Ad esempio, i negozi Amazon Go utilizzano lettori fissi per automatizzare il checkout. Consente ai clienti di attraversare il negozio e di addebitare automaticamente i loro acquisti sui loro conti.
D'altra parte, i lettori RFID mobili sono dispositivi portatili che offrono flessibilità e praticità, in quanto possono essere portati ovunque. Questi dispositivi sono ideali per le aziende che richiedono il monitoraggio in movimento o devono eseguire controlli di inventario in varie località.
Indipendentemente dal tipo di lettore utilizzato, il processo di tracciabilità RFID prevede tipicamente quattro fasi:
- Le informazioni vengono memorizzate su un'etichetta RFID e allegate a un articolo, come un prodotto o una risorsa.
- L'antenna riconosce il segnale di un'etichetta RFID vicina.
- Un lettore si collega in modalità wireless all'antenna e recupera le informazioni memorizzate sul tag.
- Il lettore invia i dati RFID al database, dove vengono archiviati e analizzati.
I tag RFID sono disponibili in diversi tipi, ognuno con i propri vantaggi e limiti. TI due tipi più comuni sono i tag RFID attivi e passivi.
I tag RFID attivi hanno una propria fonte di alimentazione e possono essere letti da una distanza di 100 metri o più. Sono generalmente utilizzati in applicazioni in cui l'ubicazione delle risorse o i miglioramenti logistici sono fondamentali. Ad esempio, le aziende che devono tenere traccia di risorse di alto valore in una vasta area possono utilizzare tag attivi per ottenere visibilità in tempo reale sulla posizione e sullo stato di queste risorse.
D'altra parte, i tag RFID passivi non hanno una fonte di alimentazione e si basano sull'energia elettromagnetica del lettore per l'accensione e la trasmissione dei dati. Di conseguenza, il loro raggio di lettura è limitato a pochi metri, in genere fino a 25 metri. Tuttavia, hanno un costo inferiore e possono essere incorporati in etichette adesive o direttamente nell'oggetto stesso. Ad esempio, quando ricevi una cassa di prodotti da un fornitore, questi può applicare etichette passive alla cassa per facilitare il monitoraggio e la gestione dell'inventario. Una volta rimossi i prodotti e scartata la custodia, i tag vengono eliminati.
I tag semipassivi sono un altro tipo di tag RFID che combina i principi dei tag passivi e attivi. Hanno una batteria che aiuta a estendere il loro raggio di comunicazione, ma si affidano comunque al lettore per fornire energia per la trasmissione dei dati.
La tecnologia RFID è ampiamente utilizzata in vari settori, tra cui quello sanitario, automobilistico e dei trasporti. Nelle impostazioni di vendita al dettaglio, la tecnologia RFID ha molti usi che possono migliorare le operazioni del negozio. Ciò migliora l'esperienza del cliente e aumenta le vendite.
Un modo in cui l'RFID può migliorare le operazioni del negozio è migliorare la gestione dell'inventario. Con l'RFID, i rivenditori possono facilmente monitorare il movimento dei prodotti e automatizzare il rifornimento. Ad esempio, i tag RFID possono avvisare i dipendenti quando un prodotto specifico è esaurito o ha un inventario basso. Mostra loro dove trovare il prodotto nel retrobottega e quanti tirarne. Questo aiuta a evitare l'esaurimento delle scorte e a ridurre l'eccesso di scorte, migliorando le vendite e la redditività.
L'RFID può anche analizzare i modelli di traffico in negozio e migliorare il layout del negozio. Tracciando il movimento degli articoli in un negozio, i rivenditori possono conoscere le aree ad alto traffico del loro negozio, i prodotti popolari e il comportamento dei clienti. Queste informazioni possono essere utilizzate per ottimizzare il layout del negozio, le promozioni e l'inserimento di prodotti. Alla fine porta a maggiori vendite e una migliore esperienza del cliente.
Un altro uso dell'RFID nella vendita al dettaglio è la creazione di camerini virtuali. I rivenditori possono tracciare l'articolo e mostrare i colori e gli stili disponibili utilizzando un tag RFID di geolocalizzazione. Raccomanda vestiti complementari e fornisce informazioni rilevanti sul prodotto. Questo aiuta a personalizzare l'esperienza di acquisto, migliorare il coinvolgimento dei clienti e aumentare le vendite.
La tecnologia RFID può anche consentire pagamenti senza contatto, che stanno diventando sempre più popolari nella vendita al dettaglio. I clienti possono passare attraverso una cassa RFID e verificare la propria identità utilizzando scanner biometrici. Possono pagare gli articoli senza toccare una tastiera o interagire con un cassiere. Ciò migliora l'esperienza del cliente, riduce i tempi di pagamento e aumenta la produttività.
Oltre a questi usi, la tecnologia RFID può aiutare con il prelievo delle scorte nei magazzini. I droni abilitati RFID, come RFly, possono scansionare i tag RFID e individuare i prodotti all'interno di un magazzino, anche se impilati su scaffali alti. Questo aiuta a migliorare l'efficienza e ridurre i costi di manodopera.
L'RFID può essere utilizzato anche per monitorare la temperatura delle merci, in particolare i prodotti deperibili che devono essere conservati a temperature specifiche. I sensori all'interno dei tag RFID possono monitorare la temperatura e tenerne traccia. Assicura che i prodotti siano conservati nelle giuste condizioni e riduce gli sprechi.
Infine, l'RFID può migliorare l'accuratezza delle scorte in negozio, riducendo il tempo e gli sforzi necessari per la gestione dell'inventario. Con l'RFID, i rivenditori possono controllare istantaneamente intere spedizioni piuttosto che fare affidamento sulla scansione dei singoli pacchi e sulle ricevute cieche. L'RFID può anche trovare articoli, ridurre il tempo di conteggio del ciclo e riordinare automaticamente i prodotti a livelli di scorte di sicurezza. Li aiuta a ridurre le scorte e migliorare la soddisfazione del cliente.
Come usare l'RFID?
Il sistema RFID comprende un lettore, un'etichetta elettronica e un sistema di gestione dei dati. Il lettore è generalmente abituato a leggere i dati di uno specifico tag elettronico. Diversi lettori possono leggere e scrivere diversi tipi di etichette elettroniche. L'etichetta elettronica è lo strumento per la memorizzazione dei dati. Il corpo dell'etichetta elettronica utilizza il chip per essere diverso, può memorizzare la capacità dei dati e può avere una differenza.
Il sistema di gestione dei dati si riferisce al lettore dopo aver letto i dati di una specifica etichetta elettronica. Viene trasferito sulla LAN al database sul server. Può essere piccolo come un chip che può essere incorporato nel corpo di un animale, oppure può essere trasformato in un elemento essenziale per il viaggio come una carta dell'autobus o una carta d'identità. Ha molti usi. Le persone possono usarlo nella gestione dei materiali, nell'automazione della linea di produzione, nel controllo dei parcheggi, ecc.
Vantaggi Utilizzo di RFID
L'RFID è una tecnologia versatile che offre molti vantaggi rispetto ai metodi di identificazione tradizionali. Utilizzando l'RFID, le aziende possono risparmiare tempo e denaro. Aiuta anche le aziende a migliorare la precisione e l'efficienza. Alcuni dei principali vantaggi dell'RFID includono il monitoraggio migliorato, la gestione dell'inventario e l'esperienza del cliente. Puoi anche migliorare la sicurezza, l'identità e la gestione delle risorse utilizzandolo.
Utilizzo di RFID per il monitoraggio delle risorse
L'RFID è un metodo sempre più popolare per tracciare le risorse. Le aziende possono utilizzare i tag RFID per tracciare e monitorare la posizione delle proprie risorse in tempo reale. Questo aiuta a ridurre gli errori di inventario e garantisce che le risorse siano dove dovrebbero essere. L'RFID può anche mostrare quando le risorse sono state spostate da un luogo all'altro. Aiuterà le aziende a identificare rapidamente eventuali discrepanze che potrebbero verificarsi.
Gestione della logistica
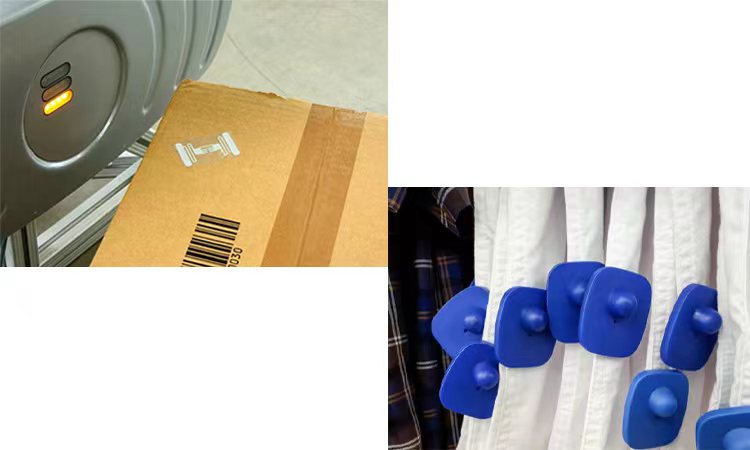
La maggior parte delle aziende utilizzerà la tecnologia RFID per migliorare la gestione della logistica. Applicando tag RFID alle merci, le aziende possono localizzare e monitorare rapidamente i propri prodotti in qualsiasi punto della catena di approvvigionamento. Questo aiuta a ridurre i ritardi e migliorare la precisione. Fornisce inoltre un modo semplice per monitorare e gestire l'inventario. I tag RFID possono anche monitorare i livelli di temperatura e umidità. Garantisce che le merci siano mantenute nelle migliori condizioni possibili durante il trasporto.
L'RFID è una tecnologia altamente versatile che l'azienda può utilizzare in tutti gli aspetti dell'impresa. Dal processo di fabbricazione dei prodotti alla regolare manutenzione e riparazione delle apparecchiature. L'azienda può utilizzare il monitoraggio e la distribuzione tardiva delle merci e persino la gestione patrimoniale dell'intero settore.
Uso commerciale dell'RFID
L'ubiquità dell'RFID è particolarmente evidente nell'uso commerciale. Il 4 marzo 2020, Università di AuburnIl laboratorio RFID di ha completato uno studio con GS1 negli Stati Uniti. Sono uno studio di prova per "tecnologia blockchain e RFID per migliorare la condivisione dei dati nel settore della vendita al dettaglio". Il progetto si chiama “Prova di concetto del progetto di integrazione della catena (PATATA FRITTA)." I risultati dello studio mostrano che i rivenditori possono condividere i dati dei prodotti codificati nei tag RFID su una rete blockchain. Dimostra che l'uso dello scambio automatizzato di dati sui prodotti serializzati è affidabile. Può aumentare la produttività della supply chain in modo più efficace. Può ridurre il costo della revisione manuale. In genere, i tag RFID agiscono sulla merce di un negozio al dettaglio. Previene il furto e il taccheggio da parte dei dipendenti e consente ai clienti di effettuare il checkout automatico. Ridurrà le code alla cassa.
Nel 2010, Vail Resorts ha aperto le porte a un nuovo mondo nel settore dello sci utilizzando i tag RFID negli skipass. Nello stesso anno, l'RFID ha fatto il suo debutto alla conferenza annuale di Facebook e da allora è stato utilizzato sotto forma di schede RFID nella maggior parte dei loro eventi dal vivo. 2011-2013, i marchi automobilistici più famosi hanno utilizzato l'RFID per il social media marketing.
L'RFID può essere utilizzato anche in altri settori, come le carte d'identità. Una persona con una carta di identificazione RFID può essere identificata avvicinandosi al lettore RFID entro una certa distanza. Naturalmente, l'azienda può utilizzarlo anche per i viaggi in auto nel garage. Il conducente deve solo posizionare il tag RFID sulla targa o sulla parte più visibile dell'auto. E quando il veicolo raggiunge il raggio di lettura della macchina, può essere verificato facilmente.

Alcuni usi comuni delle applicazioni RFID:
- Uso di RFID nell'industria sanitaria
- Uso di RFID nella produzione
- Uso di RFID nella gestione dell'inventario
- Uso di RFID nella catena di approvvigionamento
- Uso dell'RFID in Biblioteca
RFID contro codici a barre
Questa tabella descrive le differenze tra RFID e codici a barre:
| Caratteristica | RFID | Codici a barre |
|---|---|---|
| Capacità di memorizzazione dei dati | Alto | Basso |
| Gamma di lettura | Lungo raggio (fino a 100 metri) | Corto raggio (fino a 10 cm) |
| Velocità di lettura | Alto | Basso |
| Durata | Alto | Basso |
| Costo | Alto | Basso |
| Applicabilità | Può leggere più elementi contemporaneamente | Può leggere solo un elemento alla volta |
| La sicurezza dei dati | Alto | Basso |
Questa tabella descrive i vantaggi e gli svantaggi di RFID e codici a barre:
| Caratteristica | RFID | Codici a barre |
|---|---|---|
| Vantaggi | Può leggere più elementi contemporaneamente | Basso costo |
| Lungo raggio di lettura | Ampiamente adottato | |
| Elevata velocità di lettura | Facilità d'uso | |
| Elevata capacità di memorizzazione dei dati | Rapida implementazione | |
| Elevata sicurezza dei dati | Facilità di integrazione con i sistemi esistenti | |
| Durata | Affidabile | |
| Svantaggi | Costo alto | Bassa capacità di memorizzazione dei dati |
| Non ampiamente adottato | Breve raggio di lettura | |
| Richiede attrezzature e formazione specializzate | Bassa velocità di lettura | |
| Vulnerabilità di sicurezza | Suscettibile di danni e usura |
RFID contro NFC
Questa tabella descrive le differenze tra RFID e NFC:
| Caratteristica | RFID | NFC |
|---|---|---|
| Banda di frequenza | 125 kHz, 13,56 MHz, 868 MHz | 13,56MHz |
| Gamma di lettura | Lungo raggio (fino a 100 metri) | Corto raggio (fino a 10 cm) |
| Velocità di trasferimento dati | Dal basso all'alto | Alto (fino a 424 kbps) |
| Compatibilità | Comunicazione unidirezionale | Comunicazione bidirezionale |
| Sicurezza | Può essere suscettibile di hacking | Più sicuro grazie alla crittografia |
| Costo | Alto | Da basso a moderato |
Questa tabella descrive i vantaggi e gli svantaggi di RFID e NFC:
| Caratteristica | RFID | NFC |
|---|---|---|
| Vantaggi | Lungo raggio di lettura | Elevata velocità di trasferimento dati |
| Può leggere più elementi contemporaneamente | Comunicazione bidirezionale | |
| Elevata capacità di memorizzazione dei dati | Maggiore sicurezza grazie alla crittografia | |
| Durata | Facile integrazione con gli smartphone | |
| Compatibilità con varie frequenze | Facile da usare | |
| Svantaggi | Può essere suscettibile di hacking | Breve raggio di lettura |
| Richiede attrezzature e formazione specializzate | Intervallo limitato per il trasferimento dei dati | |
| Velocità di trasferimento dati limitata | Compatibilità limitata con le frequenze | |
| Costo alto |
Quali aziende utilizzano l'RFID?
La famosa Amazon ha già adottato la tecnologia RFID per realizzare “Just Walk Out”. Tutto quello che devi fare è scaricare l'app Amazon Go sul tuo telefono e accedere al tuo account Amazon. Mostrando il tuo account al dispositivo scanner quando entri nel negozio. Quando ritiri l'articolo che desideri acquistare e lasci il negozio, il costo del prodotto verrà addebitato direttamente sul tuo account Amazon. Non è necessario trovare un essere umano o una macchina per eseguire l'operazione di pagamento. Rende lo shopping più facile e veloce.
Zara, un gigante della vendita al dettaglio nel settore dell'abbigliamento, utilizza la tecnologia RFID per la gestione dell'inventario. Quando l'articolo viene venduto, il magazzino verrà immediatamente avvisato e l'inventario verrà rifornito in tempo. La merce è sempre conservata in condizioni sufficienti.
Anche BJC HealthCare utilizza la tecnologia RFID da molti anni. Usano l'RFID per tenere traccia delle forniture mediche chirurgiche dell'ospedale, dell'inventario dei farmaci, delle date di scadenza e altro ancora. Può anche tenere traccia delle risorse e prevenire efficacemente incidenti come la carenza e la perdita di forniture mediche.

L'uso dell'RFID nella posizione corretta in base alle esigenze dell'impresa è quello di realizzare il massimo vantaggio dell'impresa. Si ritiene che in futuro, poiché l'RFID è al passo con i tempi, le aziende lo utilizzeranno pienamente in un numero sempre maggiore di luoghi.
Altre domande sull'uso dell'RFID
-
Quali sono i vantaggi dell'utilizzo dell'RFID rispetto ai tradizionali sistemi di codici a barre?
La tecnologia RFID offre numerosi vantaggi rispetto ai tradizionali sistemi di codici a barre. Come tempi di lettura più rapidi, la capacità di leggere più tag contemporaneamente e la capacità di leggere i tag a distanza senza una linea di vista. Inoltre, i tag RFID possono memorizzare più dati rispetto ai codici a barre e possono essere letti in ambienti difficili, come temperature elevate o umidità.
-
Sono disponibili diversi tipi di tag RFID, inclusi tag passivi, attivi e semi-passivi. I tag passivi non hanno una batteria e dipendono dall'energia del lettore. I tag attivi hanno la propria fonte di alimentazione e possono inviare dati su distanze maggiori. La scelta del tag dipende dall'intervallo di lettura, dalla durata e dal costo.
-
Come installo e configuro un sistema RFID nella mia struttura?
La configurazione di un sistema RFID richiede diversi passaggi, tra cui la scelta dell'attrezzatura giusta, l'installazione di antenne, la creazione di un database e il test del sistema. Si consiglia di consultare un integratore RFID esperto per garantire una corretta installazione e configurazione.
-
In che modo la tecnologia RFID può migliorare il monitoraggio delle risorse e la sicurezza nella mia organizzazione?
La tecnologia RFID può migliorare il monitoraggio e la sicurezza delle risorse fornendo informazioni sulla posizione e sullo stato in tempo reale. Consente ipotesi migliori e riduce il rischio di smarrimento o furto.
-
Quali sono i potenziali rischi per la privacy e la sicurezza associati all'RFID e come posso mitigarli?
Alcuni potenziali rischi per la privacy e la sicurezza associati all'RFID includono la lettura non autorizzata di tag, la violazione dei dati e il tracciamento di individui senza il loro consenso. Le misure di mitigazione includono l'utilizzo della crittografia, la limitazione dell'accesso ai dati e l'implementazione di politiche e procedure per la protezione da accessi non autorizzati.
-
Come posso integrare la tecnologia RFID con altri sistemi e software come ERP o WMS?
L'integrazione della tecnologia RFID con altri sistemi e software comporta la mappatura dei dati dal sistema RFID al sistema esistente e la garanzia della compatibilità. Questo può essere fatto tramite API, middleware o sviluppo software personalizzato.
-
Quali sono le sfide comuni associate all'uso della tecnologia RFID e come posso superarle?
Le sfide comuni associate all'utilizzo dell'RFID includono il posizionamento dei tag, l'interferenza di altri segnali radio e l'accuratezza dei dati. Queste sfide possono essere superate attraverso un'attenta pianificazione, test e ottimizzazione del sistema RFID.











