IUID is an innovative system the US Department of Defense developed to identify. It tracks items throughout their lifecycle uniquely. Using machine-readable codes, IUID provides unparalleled traceability and accountability. This article will deeply dive into IUID, the basic program definitions, key features, and real-world applications across various industries.
What is IUID?
IUID stands for Item Unique Identification. It is a system developed by the US Department of Defense to provide a unique identifier for each item in a company’s inventory. The identifier consists of:
- a data matrix code,
- a unique identifier,
- and machine-readable information.
The US Department of Defense developed the system to improve inventory management and accountability. Using a standardized, machine-readable code, IUID enables accurate tracking of items throughout their lifecycle, from acquisition to disposal. This allows for better supply chain management, improved asset visibility, and reduced waste. IUID is used in a wide range of industries, including the military, healthcare, aerospace, and manufacturing.
What is IUID Standards?
IUID identifiers follow internationally recognized standards set by organizations such as ISO and ANSI. This ensure uniqueness, non-sequential generation, and machine readability.
Specifically, IUID identifiers comply with ISO/IEC 15459. It defines the structure and format for generating globally unique identifiers. This standard mandates that identifiers must be algorithmically generated to guarantee non-duplication. It also specifies that identifiers should contain 40 alphanumeric characters for maximum uniqueness.
Additionally, IUID identifiers adhere to ANSI MH10.8.2 guidelines for encoding data identifiers in barcodes and RFID tags. This standard provides recommendations for representing identifiers in linear barcodes (e.g., UPC, EAN, JAN, ISBN) and RFID tags (e.g., EPC) to enable automatic scanning and reading.
Key requirements of the IUID program include:
- Assigning a unique identification code (UID) to all qualified property assets. UIDs are 36-character identifiers assigned in accordance with specifications in DFARS 252.211-7003.
- Marking each property item with a UID label and barcode, as defined in MIL-STD-130. Barcodes encode the UID for automated data capture. MIL-STD-129 provides guidance on linear or 2D barcodes.
- Recording each property asset’s UID, value, and other details in accountable property records.
DODI 8320.04 establishes IUID standards for applying UIDs. It marks policies based on property categories, aligned with valuations according to DFARS 211.274.
SECNAVINST 4440.34 implements these IUID requirements for the Department of Navy. Guidance ensures UIDs uniquely identify each item. Even if descriptions or properties change over the asset’s lifespan.
The IUID program enhances the accountability of taxpayer-funded property. It enables advanced inventory management through automated tracking of UIDs. When implemented consistently across the DoD, the IUID program increases operational efficiency, reduces errors, and improves audit readiness.
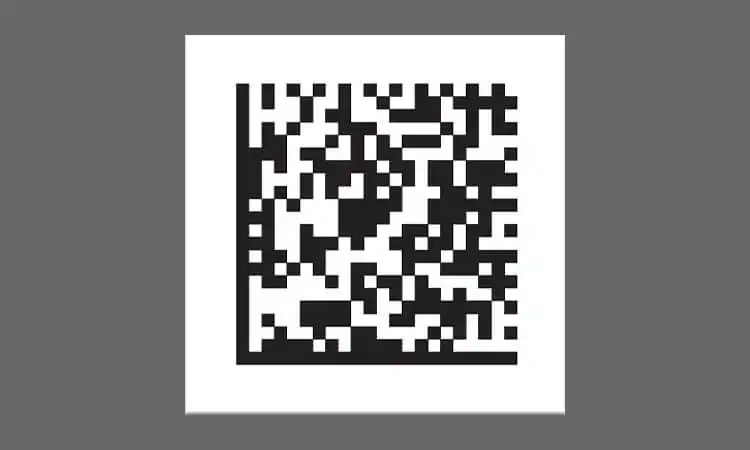
What is Data Matrix: The Backbone of IUID
At the heart of the IUID system is the Data Matrix, a two-dimensional barcode that stores alphanumeric data. This compact, high-capacity code stores large volumes of data within a small space. It enables the encoding of lengthy, unique IUID identifiers.
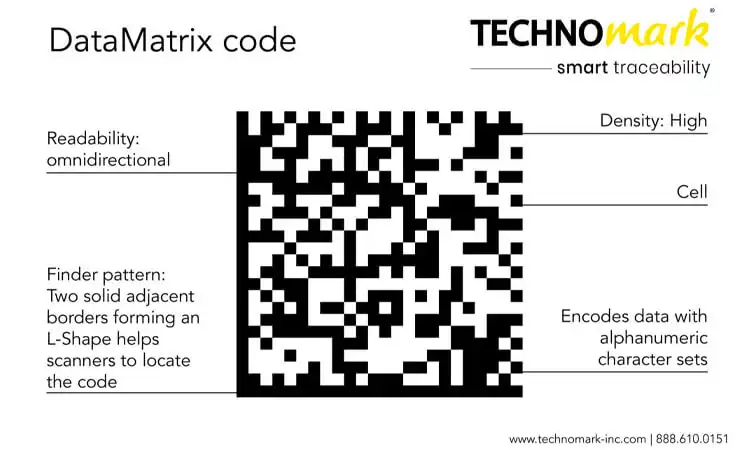
The data matrix provides a machine-readable format that various scanning and reading techniques can decode. It promotes interoperability between systems. We can scan the IUID identifiers encoded in the data matrix using various devices. These devices include handheld and desktop barcode readers as well as fixed RFID readers. It enables seamless data sharing between different devices and platforms.
With advanced error correction capabilities, Data Matrix helps ensure the integrity and reliability of IUID identifiers. No need to worry, even in the case of corrupt, ambiguous, or incomplete scans. Powerful error correction algorithms allow the decoding of defective or partially scanned codes. It also minimizes the possibility of missing or corrupted identifier data.
What is IUID Registry: Centralized Data Management
The IUID registry is used as a centralized data source. It manages information on uniquely identified items throughout their lifecycle. Managed by the DoD, the registry contains key details about each identified asset. The more common ones are the permanent IUID identifier, acquisition cost, associated contracts, and other management data.
Access to this centralized inventory enables data-driven decisions and optimized management of assets. Organizations can leverage information in the registry to make strategic choices regarding the maintenance, replacement, transfer, or disposal of equipment and components. This helps reduce costs, ensure readiness, and maximize the value of deployed technology and systems.
The registry also facilitates transparency and accountability across the asset management lifecycle. The registry creates an auditable chain of custody. It also does so by providing a single, authoritative record of assets and their key attributes. It ensures accurate reporting of resource allocations, expenditures, and disinvestments. This helps meet certain regulatory and oversight requirements for government spending and operations.
What is IUID Marking Requirements
We have outlined some of the IUID logos here for your reference, but the latest regulations should prevail. The main marking requirements are as follows:
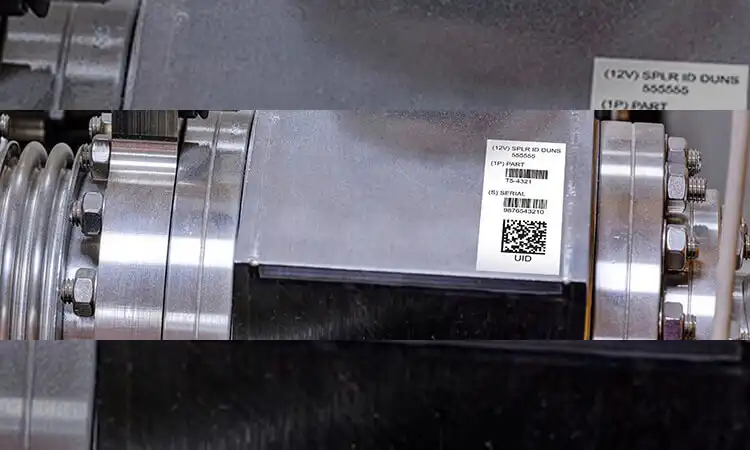

- Placement: Clearly and visibly affixed in an appropriate location. It should be both protective and easy to scan. It must not obscure important information or adversely affect the function or appearance of the item.
- Sizing: The cell size of the 2D Data Matrix barcode. It is suitable for encoding data and scanning capabilities. It allows consistent decoding. Text elements remain legible for the item’s expected lifetime.
- Contrast: High contrast between the mark and surface for optimal scan readability and data decoding. Avoid over-reflective, patterned, or highly absorbent surfaces.
- Quiet zone: Appropriate clear space surrounding the barcode, preventing misregistration or decoding confusion. Follows ANSI specifications.
- Protection: Durable, fade/scratch-resistant material. This material can withstand the environment and usage conditions the item will experience. Re-apply as needed to maintain compliance.
- Quality: Calibration of application equipment, technician training, and quality checks/audits consistently achieve specifications across marked items. Retesting validates secure attachment before item completion.
- Advanced tools: Design/verification software helps optimize mark quality. They also help balance capability requirements with part sizing and verify readability before production. It helps cut rework or non-compliance.
What Does an IUID Number Look Like?
An IUID number encodes a permanent, unique identifier for an item in the form of an alphanumeric code accompanied by a 2D data matrix barcode. IUID numbers are constructed in three primary ways:
- Serialization with Enterprise Identifier (EID). It combines the issuing agency code (IAC), EID, and serial number. They are used for items already assigned an EID. e.g. ABC123-ABCD-12345
- Serialization within Original Part/Lot/Batch Number. It combines IAC, EID, original part number, and serial number. Used if the item has a relevant part number. e.g. ABC123-ABCD-PART123-54321
- IUID Equivalents. Adopts an existing commercial identifier if it meets key requirements. e.g., Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) as IUID. The format is IAC, then EID, followed by commercial code.
For example, an IUID could be:
ABC123-1234-PART123-54321 (Serialization within Part Number)
ABC123-ABCD-12345 (Serialization with Enterprise ID)
ABC123-1234-123ABCDE456FG78IJ9 (VIN as IUID Equivalent)
IUID numbers aim to provide a permanent, globally unique identifier for an item. It can be automatically captured and shared between systems. They adhere to standardized generation principles mandated by organizations like ISO and ANSI. It ensures uniqueness, non-sequential Order, and machine readability.
IUID in Other Industries: Beyond Defense
Although the Department of Defense originally implemented IUID, it is now being adopted by other industries as well. For example, aerospace companies use IUID to track and manage aircraft components. Its use ensures safety and compliance with regulations. In the automotive industry, IUID has improved parts tracking through better. It helps companies improve the efficiency of their supply chains. Some healthcare organizations are also beginning to use IUID to manage medical devices, track usage, and track maintenance. It ensures patient safety and reduces costs.
Challenges and Future Prospects: Expanding IUID
Despite its advantages, IUID implementation can be challenging. Factors such as the cost of equipment and training, data security concerns, and resistance to change can hinder adoption. However, the ongoing development of new technologies, such as advanced barcode scanners and RFID systems, may decrease these barriers in the future. As IUID continues to evolve, it will likely become more accessible and beneficial to a broader range of industries.
Despite challenges, the future of IUID is promising, with ongoing advancements in technology and growing adoption across various sectors.
Related Articles:
What is a UID(Unique Identifier)?
What is a UII(Unique Item Identifier)?
About DoD’s Item Unique Identification (IUID) FAQs
-
What is the purpose of the DoD’s Item Unique Identification (IUID) program?
The purpose of the DoD IUID program is to provide a unique identity for items critical to the DoD mission. It assigns a unique identifier to each item that can be used to track and manage the item throughout its life cycle.
-
What types of items are required to have an IUID mark?
The DoD requires that certain types of items be marked with an IUID. This includes serially managed, mission-critical, high-value, or sensitive items requiring special handling or storage.
-
What is the process for obtaining an IUID mark for an item?
The process for obtaining an IUID mark for an item involves registering the item in the DoD’s Item Unique Identification Registry (IUIR) and assigning a unique identifier to the item. It marks the item with the identifier using a compliant marking method.
-
What are the consequences of not complying with the IUID program requirements?
Failure to comply with the IUID program requirements can result in penalties. This includes rejecting non-compliant items, losing contract awards or renewals, and potential legal or financial liabilities.
-
How does the IUID program integrate with other DoD identification and tracking systems?
The IUID program integrates with other DoD identification and tracking systems. Such as the Defense Logistics Agency’s (DLA) Logistics Information Services (LIS) and the Joint Asset Management and Engineering Solution (JAMES). It enables the tracking and managing of items across the DoD’s logistics and supply chain network.
-
How does the IUID program enhance asset visibility and accountability?
The IUID program enhances asset visibility and accountability by providing a unique identifier for each item that can be tracked and monitored throughout its lifecycle. It enables the DoD to understand better its assets’ location, condition, and status.








