In today’s fast-paced warehouse environments, efficiency is key. Barcode technology is a proven solution for improving accuracy and boosting customer satisfaction. Research shows that barcode systems can reduce errors by up to 99.9% and increase productivity by up to 50%. With benefits like these, it’s no wonder that more and more warehouses are adopting barcode systems.
Why Use Barcode System for Warehouse?
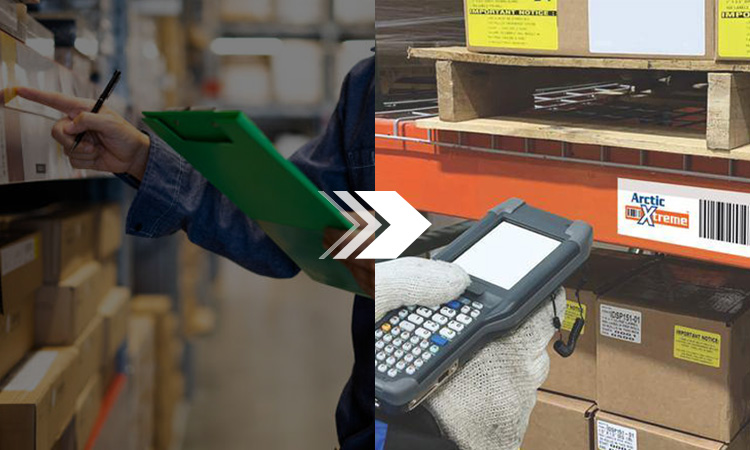

Suppose companies want to improve the efficiency of warehouses. They must update the original traditional technology. Initially, people were performing inventory records through spreadsheets and manually. Management in the warehouse may be based on more straightforward methods. However, an extremely high error rate occurs using this conventional technique.
As technology continues to evolve, barcodes have emerged. Companies can easily manage their warehouses using barcode labels. It effectively reduces the human error rate.
Companies can use warehouse location barcodes to tag each item to get its location. These items can be shelves, pallets, containers, etc. It increases the efficiency of warehouse movement for bulk containers and individual products.
How Much do You Know About Warehouse Barcodes?
The most crucial component of a barcode system is the label. Companies need to know something about barcodes.
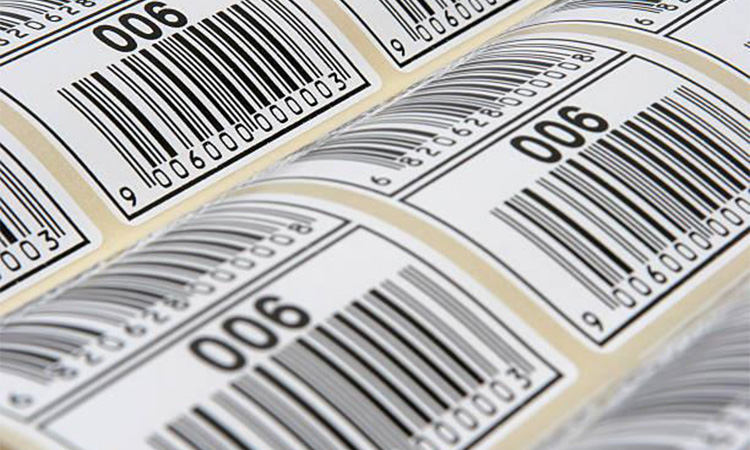
What are Barcode Labels?

Barcode labels are an effective tool for tracking assets and inventory throughout the supply chain. It is also helpful for cross-organizational tracking. It can be presented in various ways, but there are three common types of presentation. These three types are:
- Barcodes with numbers only
- Barcodes with letters and numbers
- Two-dimensional barcodes
Each of these three types of barcodes has its characteristics. The first type is purely numeric. The second type also contains letters. These two are collectively referred to as one-dimensional barcodes. The two-dimensional barcode is slightly different, usually presented as a square or rectangle. These shapes reveal a distinctive pattern with several dots arranged on top.
Companies often choose simple barcode labels for warehouse tracking and management. The following are some common barcode symbols.
UPC Code (1D barcode containing only numbers)

It is one of the oldest and most widely used barcodes in GS1 barcode. It is also one of the most recognized barcodes in the United States.
It consists of 12 digits and can identify individual products in a store. Businesses can identify specific products and manufacturers by identifying this code. It is particularly popular with retailers.
EAN Code (1D barcode containing only digits)

The EAN code is almost identical to the UPC. However, it applies to POS systems widely used in convenience stores.
It is compatible with countries’ Universal Product Code (UPC), such as the United States and Canada. It is also compatible with the Japanese Article Number (JAN).
Most commercial products can use on it in the store.
Plessey Code (1D barcode with numbers and letters)

It was developed in 1971 by the British Company Plessey. It has several variants, including Anker Plessey and MSI Plessey.
At first, people used it only in local European grocery stores and libraries. Because of its higher density than other standard symbols, it is used in dot matrix printers.
Code 39 (1D barcode with numbers and letters)

This code is a barcode developed by Intermec Corporation in 1975. It can contain up to 43 characters.
It is primarily used in non-retail industries. It is prevalent in the automotive, electronics, and defense industries.
Two-Dimensional Code (2D barcode)
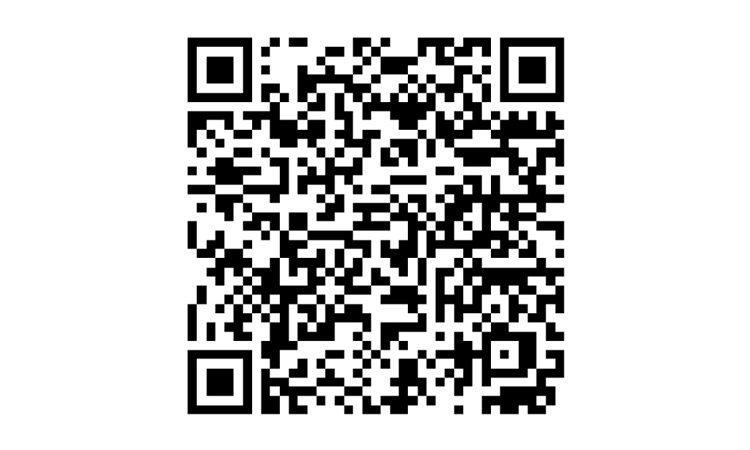

A 2D code is a two-dimensional version of a barcode. It is one of the most widely known two-dimensional barcodes.
It consists of a unique pattern of black and white pixels. It is capable of storing more data than a standard 1D barcode. It contains up to 2,509 numeric-only characters or 1,520 characters made up of letters and numbers.
People initially used it only to track parts manufactured in automobiles. Today people can use it in various applications. It includes business tracking, entertainment, and transportation ticketing.
Companies often choose to adopt a barcode style like the UPC for use in warehouse management. Companies that need to handle retail products can also apply for registration with GS1. The organization that standardizes barcodes worldwide. Registering GS1 barcodes helps companies globalize their merchandise.
When was the Barcode Invented?
The barcode was invented in 1948 by Norman Joseph Woodland and Bernard Silver in the United States. The two inventors were inspired to create a system for automatically identifying products after a local grocery store owner asked them to devise a solution to speed up checkout lines. After several years of experimentation, Woodland and Silver developed the first barcode system, which used a series of lines of varying width to represent a code that a scanner could read. The first barcode was used commercially in 1966, and today barcodes are used in various industries for tracking and inventory management.
Advantages of Using Warehouse Barcodes
Warehouse Barcodes Make Inventory Tracking Easier
Traditional manual records are time-consuming and error-prone. Using warehouse location barcodes helps companies get an accurate audit trail. Workers can easily track inventory by scanning barcodes.
Easy Setup
Using warehouse barcodes labels for all items in the warehouse can take a lot of time at first. But compared to other inventory tracking technologies, it is simply about material requirements. It’s also simple to use. You need to paste the warehouse barcode on the item, and you can call it up by scanning it. It’s handy to apply, primarily if you already use SKU numbers.
Reducing the Incidence of Errors
The accuracy of data is critical for businesses. Traditional manual data entry is more than ten times more error-prone than scanning. Data that is incorrect has the potential to cause severe losses. Employees filling in the wrong data can affect the operator’s judgment of inventory levels. Thus, it will likely affect the enterprise’s operation plan later. Using warehouse inventory barcodes can reduce the incidence of manual errors significantly.
Safer Goods
Every Company has potential problems such as theft, misplaced goods, etc. Traditional manual counting can take a long time to produce the data. Usually, companies are not aware of such problems when they occur. The use of warehouse barcodes can prevent this from happening. It can track products and reduce product mix-ups. Relatively, it can reduce the loss of misplaced items.
So Did You Know that Your Warehouse Needs Barcodes?
Before you are ready to update your existing warehouse management technology, there is one question you need to consider. That question is whether you will benefit from using warehouse barcode labels. Of course, the result is usually a resounding yes. However, because of the time and money involved in investing in a barcode system, you must think about it.
Several reasons typically influence companies to use warehouse barcodes:
- MRO inventory needs
- The suppliers and retailers that your business is dealing with are already using warehouse barcodes
- The need to keep a close eye on the quantity of inventory you deposit in the warehouse
- The need to continuously maintain accurate records of inventory levels
- Wait a long time to get the inventory records
Once you have considered your need to install a barcode system in your warehouse, you are ready to take the next step. You are ready to lay the groundwork for installing the barcode system.
Setting Up a BarCode System
Setting up a complete barcode system is simple. Companies can prepare barcodes, scanners, and inventory management software.
Designing Warehouse Barcodes
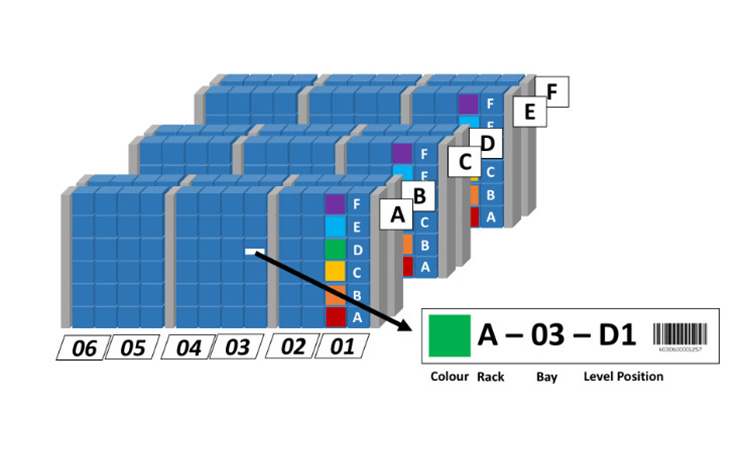
Companies must design barcodes that perfectly match the target application in the warehouse.
The Company can design these warehouse barcodes under different conditions. These conditions include physical environments and connection methods.
Some more common warehouse barcode labels include single-layer and container labels.
Companies can also choose labels for specific items based on several other factors. These factors include the operating environment, the item’s size, the attachment method, etc.
Of course, you can also buy barcodes in a shared database such as UPC. You can then generate barcode codes for your inventory.
Most companies will generate barcode codes in two ways:
- One is a barcode for internal use for product tracking and product security. It is generally done by searching online for a barcode generator to generate a specific warehouse barcode. These barcode companies can use them directly by printing them as stickers.
- The second type sells products on online platforms such as Amazon. It requires a standard barcode as defined by the UPC. The Company can usually purchase them online from any registered retailer.
If you want to know how to implement a barcode system in your warehouse, you can take a look at this article: What is Warehouse Organization?
Warehouse Barcode Scanners
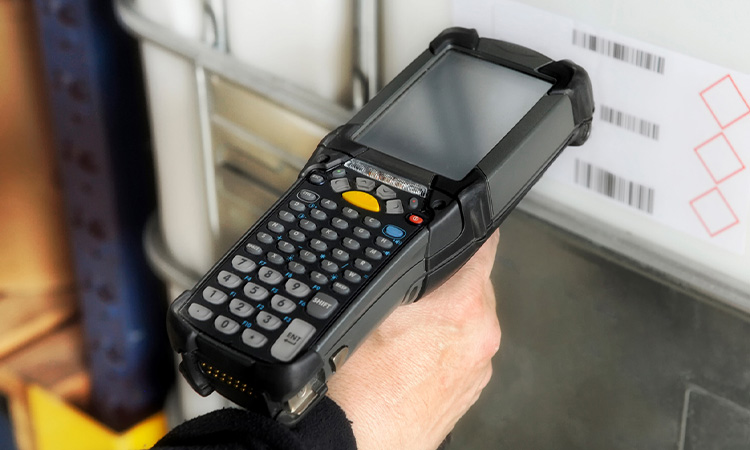

The more common scanners on the market are both wired and wireless. It is mainly used to scan barcodes and get data information from them. There are hundreds of models of barcode scanners. They have different feature sets and can be adapted to various specifications or business needs.
- The most widely known barcode scanner today is the laser barcode scanner
- It scans and reads black and white labels on tags, mainly in linear or omnidirectional mode. It has a more comprehensive reading area than a typical scanner. It is easier to operate and use than linear scanners.
- The linear barcode scanner is only suitable for reading 1D barcode use
- It primarily uses image capture technology to scan barcodes. A digital image processing function will decode the scanned barcode to get data information.
- Our most common is the 2D barcode scanner
- It works similarly to a linear imager. However, they are pretty different. It can read stacked barcodes or 2D barcodes. It also allows the user to scan barcodes in any direction.
In addition to understanding the types of warehouse barcode scanners, there are many things you need to consider:
The Environment of the Warehouse Barcode Scanner
Businesses purchase scanners based on the environment in which they are used. It will help reduce unnecessary replacement costs later.
Rugged warehouse barcode scanners are suitable for outdoor environments. Companies can choose from IP54 or IP65-rated scanners. The higher the rating, the better the scanner can withstand environmental hazards.
An excellent indoor environment allows you to choose a regular warehouse scanner. But suppose your warehouse may have potentially hazardous conditions such as chemicals and heavy dust. You should purchase a scanner with a high IP rating for more excellent durability.
Processing Speed
The power of warehouse barcode scanners on the market varies, and so does the scanning processing speed. Some can scan quickly and continuously, obtaining up to 60-120 images per second. Some are relatively slow, taking a few seconds to process each scan. Assuming you have many physical assets to handle, choosing a scanner with a faster processing speed is recommended.
Scanning Distance
Companies need to consider the distance employees scan products in real-world applications. Some barcodes can decode 1D at longer distances, but decoding 2D barcodes requires closer distances. Some remote scanners allow employees to scan barcodes from floor-to-ceiling distances.
Inventory Management Software
The most crucial thing in creating a barcode system is the choice of inventory management software. Inventory management software mainly serves the purpose of storing and managing inventory data.
Employees can upload the data from the barcode scanned by the scanner to the inventory management software. When it is scanned again, it is linked directly to the product records with the help of this software. Also, employees can see specific product details on it.
It also provides more specific information about inventory levels. Companies can readily adjust their business strategies based on inventory level information.
How to Implement Warehouse Barcodes
In today’s fast-paced warehouse environments, efficiency is key. Barcode technology is a proven solution for improving accuracy and boosting customer satisfaction. Research shows that barcode systems can reduce errors by up to 99.9% and increase productivity by up to 50%. With benefits like these, it’s no wonder that more and more warehouses are adopting barcode systems.
If you’re considering implementing barcode technology in your warehouse, you must plan carefully. Start by selecting the right type of barcode for your needs. Common options include 1D and 2D barcodes, as well as RFID. Consider factors like scanning distance, durability, and data storage capacity when choosing.
After selecting the appropriate barcode technology, you must create labels and place them in the best location. Make sure the labels are scannable and resistant to wear and tear. Common placement options include product packaging and storage containers.
You also need to train your employees to use the barcode system. These include how to scan barcodes accurately and troubleshoot issues. Additionally, it’s a good idea to have a backup plan if the system goes down. Consider keeping a paper-based inventory and order record as a backup.
Implementing a barcode system can significantly increase warehouse efficiency. According to a study by the Aberdeen Group, companies using barcode systems achieved an average inventory accuracy rate of 94% and a 15% reduction in labor costs. By following these steps and investing in the right technology, your warehouse can experience similar benefits. With real-time inventory tracking, and faster order processing, a barcode system can help streamline your warehouse operations.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Warehouse Barcodes
While warehouse barcodes can greatly improve efficiency, there are some common mistakes to avoid:
- Low-quality barcode labels: Using poor-quality labels can cause scanning errors and delays. Opt for high-quality, durable labels that can withstand wear and tear.
- Improper label placement: Barcodes should be placed in a location that’s easy to scan and won’t be covered or obscured. Incorrect placement can lead to scanning errors and delays.
- Failure to update labels: Barcode labels must be updated when product information changes to ensure accurate inventory records. If you don’t do this, it can lead to costly mistakes.
- Not testing the system: Thoroughly testing the barcode system before full implementation is crucial to ensure it works correctly. Skipping this step can lead to costly errors down the line.
Studies show that barcode-related mistakes can have serious consequences, with scanning errors accounting for nearly 70% of all barcode-related issues in warehouses. According to a study by VDC Research, these mistakes can cost companies an average of $58,000 per year.
Implementing a barcode system in your warehouse can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy. Choosing the appropriate barcode technology, producing durable labels, and sidestepping common errors are all keys to maximizing the benefits of this system. You’ll enjoy faster order processing, real-time inventory tracking, and reduced labor costs by doing so. Don’t hesitate to invest in a barcode system for your
Implementing a barcode system in your warehouse can significantly improve efficiency and accuracy. Choosing the appropriate barcode technology, producing durable labels, and sidestepping common errors are all keys to maximizing the benefits of this system. You’ll enjoy faster order processing, real-time inventory tracking, and reduced labor costs by doing so.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
How do You Select the Right Barcode Technology for Your Warehouse?
You must consider many factors when selecting barcode technology, such as scanning distance, durability, data storage capacity, and cost. Common options include 1D and 2D barcodes and RFID.
-
Can Barcodes Help Reduce Errors in Order Processing and Inventory Tracking?
Yes, barcodes can help reduce errors by automating processes, reducing manual data entry, and improving accuracy in inventory tracking.
-
What is the Difference Between 1D and 2D Barcodes, and Which is Better for a Warehouse?
1D barcodes contain only vertical lines, while 2D barcodes contain vertical and horizontal lines. 2D barcodes can store more information than 1D barcodes. It makes them a better choice for warehouses that need to track more detailed information.
-
How do You Create and Print Barcode Labels for Warehouse Inventory?
Barcode labels can be created and printed using specialized software or online tools. The labels can then be printed onto adhesive labels and placed on products or storage containers.
-
Can RFID be an Alternative to Traditional Barcode Systems in a Warehouse?
Yes, RFID can be used as an alternative to traditional barcode systems. RFID tags can be read from a greater distance and store more information than traditional barcodes, but they are also more expensive.











