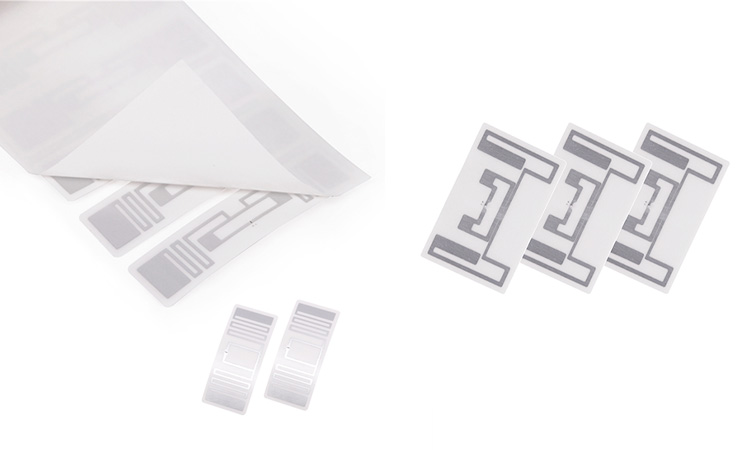
In recent years, with the popularization and application of RFID labels. It drives the flourishing of different industries around the world. Wal-Mart, SAP, BEA, Intel, and other prominent international organizations bear the brunt. They are a solid strength to prove the considerable development space of RFID and a wide range of application prospects. So are you using RFID labels now? How much do you know about it? For RFID labels, this article will describe the composition of RFID labels in detail.
What are RFID Labels?
RFID Labels meaning refer to the small tags or labels that contain electronic data and can be wirelessly read by a reader device. RFID labels consists of several components, including an antenna, a transponder, and a microchip. The antenna is responsible for transmitting and receiving radio frequency signals, while the transponder is responsible for receiving and processing the signals. The microchip contains the information that is to be transmitted to the reader.
The following video describes the production process of RFID tags:
RFID labels can be attached to any part of an object and used to track equipment, inventory, or other objects. It uses contactless automatic identification technology (RFID) to get data on the target object. It is small, versatile, and straightforward to use. It can track animals, mass-produced items in factories, and goods in transit.
Compared to regular barcodes, it is much better. It is waterproof, anti-magnetic, heat resistant, and has a longer life span and more memory capacity. It can read data for single or many items, unlike bar codes that can only identify one type of item and need to be read one by one. The company can place it inside the item, and the reader reads the item through the outer material. In contrast, a bar code must rely on a laser or infrared ray to read the data on the external material surface of the item.
It will vary depending on the power supply method. It can be divided into active, passive, and semi passive labels.
The use of transmitting frequency can be low frequency (LF RFID), high frequency (HF RFID), ultra-high frequency (UHF RFID), and microwave (MW RFID). These are four kinds.
This is a table comparing the characteristics and applications of LF RFID, HF RFID, UHF RFID, and MW RFID:
| Characteristic | LF RFID | HF RFID | UHF RFID | MW RFID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency range | 30 kHz to 300 kHz | 3 MHz to 30 MHz | 300 MHz to 960 MHz | 2.4 GHz to 5.8 GHz |
| Operating range | Up to 10 cm | Up to 1 m | Up to 12 m | Up to 100 m |
| Data transfer rate | Up to 1 kb/s | Up to 424 kb/s | Up to 640 kb/s | Up to 10 Mb/s |
| Power requirements | Low power | Moderate power | Moderate power | High power |
| Application examples | Animal tracking, access control | Contactless payment, library book tracking | Inventory management, supply chain tracking | Toll collection, vehicle tracking |
Some additional notes:
- LF RFID is often used for applications where the tags must be read at a very close range, such as animal tracking or access control systems.
- HF RFID is commonly used for contactless payment systems and tracking items like library books.
- UHF RFID is often used for inventory management and supply chain tracking, as it allows for reading multiple tags simultaneously over a longer range than LF and HF RFID.
- MW RFID is used for applications requiring long-range reading, such as in toll collection or vehicle tracking systems. However, it also requires higher power than the other types of RFID, which can limit its use in certain applications.
According to different packaging forms, its style will also be different. It can be credit card labels, linear labels, paper labels, and other special-purpose-shaped labels.
On June 13, 2022, Market Research Future (MRFR) published a new comprehensive research report. The report states that the growing adoption of RFID in the healthcare industry has contributed to the growth of the RFID tags market. The report forecasts that the RFID market will reach USD 7,982.2 million by 2027. The market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 13.67% throughout 2020-2027.
What are the Famous RFID Label Manufacturers?
Many companies manufacture RFID tags, and some of the most well-known manufacturers include:
- Alien Technology
- Avery Dennison
- Impinj
- NXP Semiconductors
- Zebra Technologies
- Smartrac
- HID Global
- Omni-ID
- Confidex
- Tageos
These companies produce RFID tags for various industries and applications, including retail, healthcare, logistics, and more.
There are more companies that produce RFID labels: 21 Top RFID Companies in World
Overview of RFID Label Components
RFID labels consist of several essential components. The antenna, typically made of conductive materials, receives and transmits radio waves. The integrated circuit (IC) chip processes data and communicates with RFID readers. The substrate provides support and protection for the antenna and IC chip. Encapsulation materials shield the RFID components from environmental factors such as moisture and physical damage. The adhesive backing securely attaches the label to various surfaces.
Integrated Circuit (IC) Chip: Powering RFID Functionality
The integrated circuit (IC) chip is the brain of the RFID label, storing and processing data. An RFID tag chip can also be called a microchip (IC) or electronic circuit. It contains a unique identifier that distinguishes each label from others. The IC chip communicates with the RFID reader, exchanging information and enabling data capture. Different types of IC chips offer varying storage capacities and capabilities, such as read-only or read-write functionality.

IC usually requires power to operate. In the case of an active tag, its power comes from a battery in the body. Passive tags come from the energy harvested from the reader’s radio waves.
IC is created on large semiconductor wafers. There are up to 40,000 IC on a single wafer. The IC on these wafers will be cut, separated by specialized personnel, and then connected to the tag antenna. The size of the IC determines the cost and the amount of power required to run it. The smaller the IC used, the lower the business’s running cost. With the advancement of technology, it is believed that IC designs will become smaller and smaller in the future.
RFID Label Chip Manufacturers
Several companies manufacture RFID tag chips and integrated circuits containing radio frequency identification technology. Some of the well-known RFID tag chip manufacturers include:
- NXP Semiconductors
- Alien Technology
- Impinj
- STMicroelectronics
- Texas Instruments
- Infineon Technologies
- EM Microelectronic
- Murata Manufacturing Co.
- Fujitsu Limited
- Atmel Corporation
These companies produce RFID tag chips with various features, such as different frequency ranges, memory sizes, and read ranges, to meet the needs of different applications and industries.
Antenna: The Backbone of RFID Labels
The antenna in RFID labels serves as the communication medium between the tag and the RFID reader. It receives and transmits radio waves, allowing data exchange. Antennas can vary in size, shape, and frequency range depending on the specific application requirements. The antenna’s design and placement affect the RFID label’s read range and performance.
It is usually made of three main elements: copper, aluminum, and silver. The RFID tag antenna’s role differs depending on the type of tag. For active tags, the RFID tag antenna mainly focuses on transmitting signals. For semi passive or passive tags, it will reflect the signal. In the case of passive tags, the RFID tag antenna also collects energy from radio waves and provides it to the IC.
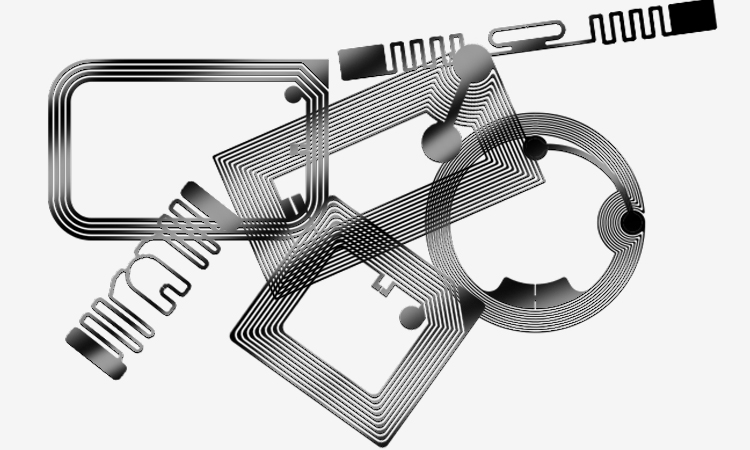
Matching the tag’s operating frequency can have a variety of shapes. There are general single dipoles, double dipoles, folded dipoles, etc.
It is generally deposited on the substrate by three methods. There are copper etching, screen printing, and foil stamping. Screen printing is by far the fastest and cheapest method. But the antenna manufactured by this method is also the least efficient. The other two are usually chosen to improve the efficiency of employees.
RFID Labels Antenna Manufacturers
Several companies manufacture RFID label antennas, which are the components that enable communication between the RFID tag chip and the reader device. Some of the well-known RFID tag antenna manufacturers include:
- Laird Connectivity
- Taoglas
- Kathrein RFID
- Alien Technology
- Times-7
- Turck Vilant Systems
- CAEN RFID
- Zebra Technologies
- RFMAX
- Inpaq Technology Co.
These companies produce RFID tag antennas with various designs, sizes, and frequency ranges to meet the needs of different applications and industries.
Substrate: Providing Support and Protection
The substrate in RFID labels acts as a support structure for the antenna and IC chip. It provides mechanical stability and protects the internal components from physical damage. Substrates are commonly made of materials like polyester or paper and are chosen based on the label’s intended use and environmental conditions. Most passive tags choose RFID tag substrates made of flexible materials.
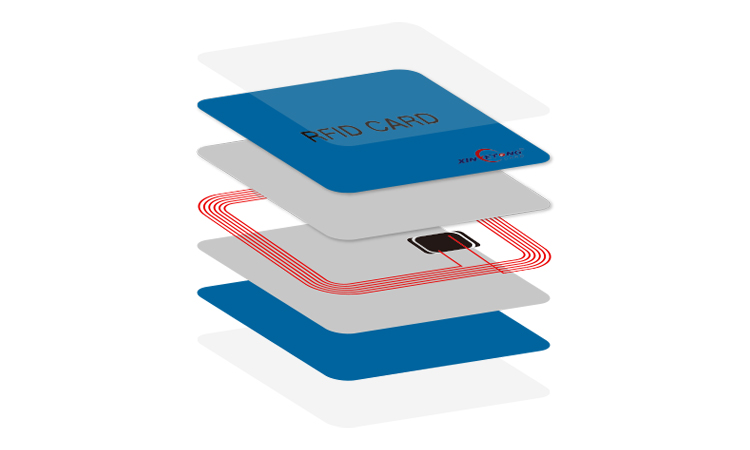
When designing RFID tag substrates, one needs to consider more. They can withstand high temperatures, moisture, chemicals, or other corrosion. And whether they can withstand environmental conditions such as shock and abrasion. It is also essential in the selection of materials because the material may have an impact on the frequency of the antenna.
Encapsulation: Shielding RFID Components
Encapsulation materials surround the antenna and IC chip, protecting them from moisture, dust, and other external factors. These materials ensure the longevity and reliability of RFID labels in harsh environments. Encapsulation methods may include lamination, over-molding, or coating, depending on the specific requirements of the label.
Adhesive: Securing RFID Labels to Surfaces
The adhesive backing on RFID labels enables easy attachment to various surfaces, such as product packaging, assets, or identification cards. The adhesive ensures a strong bond and withstands different environmental conditions.
What are RFID Label Substrate Materials Available?
RFID tags can be manufactured using various substrate materials, the base materials used to build the tag. Some of the commonly used RFID tag substrate materials include:
- Paper: This is a low-cost substrate material commonly used in asset tracking, supply chain management, and inventory control applications.
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET): PET is a durable, flexible, lightweight substrate material commonly used in applications such as RFID labels, smart cards, and contactless payment cards.
- Polyimide (PI): PI is a high-temperature-resistant substrate material commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and industrial environments.
- Ceramic: Ceramic is a hard and durable substrate material commonly used in high-temperature and harsh environments such as industrial and aerospace applications.
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC): PVC is a versatile substrate material commonly used in access control, asset tracking, and supply chain management applications.
The choice of substrate material depends on the specific application requirements, such as the environment in which the tag will be used, the required read range, and the desired durability and cost.
RFID Labels Application Scope
RFID labels have a wide range of applications. For the logistics industry, it can be used as cargo tracking in the logistics process. It can automatically collect cargo information. In the retail industry, it can provide real-time statistics on the sales data of goods so that the goods are always in stock. For the manufacturing industry, it will track production data in real time. It can better control the quality of products. It can better assist companies in achieving the goal of automated production. People also can use it in several industries, such as the apparel industry, Healthcare industry, automotive manufacturing, etc.
The popularity of RFID labels has brought many benefits to businesses. They are more expensive than barcodes but offer greater durability and can store more data. It increases employee productivity and reduces error rates. It allows companies to manage corporate assets better. It makes it easier for people to travel. Understanding the components of an RFID label, and potential applications is important for organizations looking to reap the benefits of this technology.
About RFID Labels FAQs
-
Can I Print My own RFID Labels?
You can print your RFID labels with the right equipment and knowledge. It would be best if you had an RFID printer and compatible label stock to print RFID labels. The printer software must encode the RFID chip data. It’s essential to verify that the label and chip are encoded correctly. You were testing the labels after printing is recommended. Consult with an expert or vendor for guidance.
-
Is RFID Better than a Barcode?
RFID offers advantages over barcodes. It enables automation, faster data capture, and real-time tracking. RFID is more secure and reliable than barcodes and can be used in harsh environments. However, RFID can be expensive to implement and has some privacy concerns. In summary, in some use cases, RFID can be better than barcodes, but not all.